Astronomy:DP Leonis
| Observation data Equinox J2000.0]] (ICRS) | |
|---|---|
| Constellation | Leo |
| Right ascension | 11h 17m 15.92381s[2] |
| Declination | +17° 57′ 41.6804″[2] |
| Apparent magnitude (V) | 17.5-19[3] |
| Characteristics | |
| Variable type | AM Her[3] |
| Astrometry | |
| Radial velocity (Rv) | 0.0[4] km/s |
| Proper motion (μ) | RA: −28.700[2] mas/yr Dec.: −1.444[2] mas/yr |
| Parallax (π) | 3.2781 ± 0.3110[2] mas |
| Distance | 990 ± 90 ly (310 ± 30 pc) |
| Orbit | |
| Period (P) | 0.0623628426[5] yr |
| Eccentricity (e) | 0.0 (fixed) |
| Inclination (i) | 79.5[6]° |
| Details | |
| White dwarf | |
| Mass | 0.6[6] M☉ |
| Temperature | 13,500[5] K |
| Donor star | |
| Mass | 0.09[6] M☉ |
| Other designations | |
| Database references | |
| SIMBAD | data |
| Exoplanet Archive | data |
| Extrasolar Planets Encyclopaedia | data |
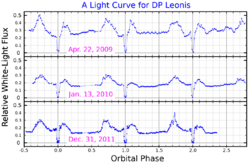
DP Leonis (abbreviated DP Leo) is a binary star system in the equatorial constellation of Leo. It is a variable star that ranges in apparent visual magnitude from 17.5 down to 19.[3] The system is located at a distance of approximately 990 light-years from the Sun based on parallax.[2] It is a cataclysmic variable star of the AM Herculis-type also known as polars. The system comprises an eclipsing white dwarf and red dwarf in tight orbit (nearly 1.5 hours) and an extrasolar planet.[8] This eclipsing variable was discovered by P. Biermann and associates in 1982 as the optical counterpart to the EINSTEIN X-ray source E1114+182.[9]
Planetary system
In 2010, Qian et al. announced the detection of a third body of planetary mass around the eclipsing binary system. The presence of a third body had already been suspected in 2002.[6] The object is roughly 6 times more massive than Jupiter and is located 8.6 AU from the binary.
| Companion (in order from star) |
Mass | Semimajor axis (AU) |
Orbital period (years) |
Eccentricity | Inclination | Radius |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| b | ≥6.1 ± 0.5 MJ | 8.2 ± 0.4 | 28.0 ± 2.0 | 0.39 ± 0.13 | — | — |
See also
References
- ↑ Beuermann, K.; Dreizler, S.; Hessman, F. V.; Schwope, A. D. (February 2014). "Evidence for an oscillation of the magnetic axis of the white dwarf in the polar DP Leonis". Astronomy and Astrophysics 562: A63. doi:10.1051/0004-6361/201323192. Bibcode: 2014A&A...562A..63B.
- ↑ 2.0 2.1 2.2 2.3 2.4 Brown, A. G. A. (August 2018). "Gaia Data Release 2: Summary of the contents and survey properties". Astronomy & Astrophysics 616: A1. doi:10.1051/0004-6361/201833051. Bibcode: 2018A&A...616A...1G. Gaia DR2 record for this source at VizieR.
- ↑ 3.0 3.1 3.2 3.3 Samus, N. N. et al. (2017). "General Catalogue of Variable Stars". Astronomy Reports. 5.1 61 (1): 80–88. doi:10.1134/S1063772917010085. Bibcode: 2017ARep...61...80S. http://www.sai.msu.su/gcvs/cgi-bin/search.cgi?search=DP+Leo. Retrieved 2021-11-30.
- ↑ Duflot, M. et al. (December 1995). "Radial velocities: The Wilson-Evans-Batten catalogue". Astronomy and Astrophysics Supplement 114: 269. Bibcode: 1995A&AS..114..269D.
- ↑ 5.0 5.1 5.2 Beuermann, K. et al. (February 2011). "The giant planet orbiting the cataclysmic binary DP Leonis". Astronomy and Astrophysics 526: 5. doi:10.1051/0004-6361/201015942. A53. Bibcode: 2011A&A...526A..53B.
- ↑ 6.0 6.1 6.2 6.3 Schwope, A. D. et al. (2002). "A multiwavelength timing analysis of the eclipsing polar DP Leo". Astronomy and Astrophysics 392 (2): 541–551. doi:10.1051/0004-6361:20011651. Bibcode: 2002A&A...392..541S.
- ↑ "DP Leo". SIMBAD. Centre de données astronomiques de Strasbourg. http://simbad.u-strasbg.fr/simbad/sim-basic?Ident=DP+Leo.
- ↑ Qian, S.-B. et al. (2010). "Detection of a Giant Extrasolar Planet Orbiting the Eclipsing Polar DP Leo". The Astrophysical Journal Letters 708 (1): L66–L68. doi:10.1088/2041-8205/708/1/L66. Bibcode: 2010ApJ...708L..66Q.
- ↑ Biermann, P. et al. (June 1985). "The new eclipsing magnetic binary system E 1114+182.". Astrophysical Journal 293: 303–320. doi:10.1086/163238. Bibcode: 1985ApJ...293..303B.
Coordinates: ![]() 11h 17m 16.00s, +17° 57′ 41.1″
11h 17m 16.00s, +17° 57′ 41.1″
 |