Astronomy:NGC 5965
| NGC 5965 | |
|---|---|
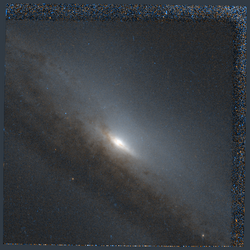 NGC 5965 by Hubble Space Telescope | |
| Observation data (J2000 epoch) | |
| Constellation | Draco |
| Right ascension | 15h 34m 02.5s[1] |
| Declination | +56° 41′ 08″[1] |
| Redshift | 0.011381 ± 0.000017[1] |
| Helio radial velocity | 3,412 ± 5 km/s[1] |
| Distance | 149 ± 22 Mly (45.7 ± 6.7 Mpc)[1] |
| Apparent magnitude (V) | 11.9[2] |
| Characteristics | |
| Type | Sb[1] |
| Apparent size (V) | 6.16′ × 0.84′[1] |
| Other designations | |
| UGC 9914, CGCG 297-016, MCG +10-22-020, PGC 55459[1] | |
NGC 5965 is a spiral galaxy located in the constellation Draco. It is located at a distance of circa 150 million light years from Earth, which, given its apparent dimensions, means that NGC 5965 is about 260,000 light years across. It was discovered by William Herschel on May 5, 1788.[3]
Two supernovae have been observed in NGC 5965: SN 2001cm (type II, mag. 17.5) and SN 2018cyg (type II, mag. 17).[4][5]
NGC 5965 is seen nearly edge-on, with an inclination of 80 degrees. Dust is seen across the galactic disk, while there is also a red dust lane at the nucleus.[6] The bulge is X-shaped, that suggests that the galaxy is actually barred.[7] NGC 5965 along with another edge-on galaxy, NGC 5746, were the galaxies used to confirm that peanut shaped bulges are associated with the presence of a bar, by spectrographically observing the disturbance caused at the velocity distributions of the galaxies.[8][9] The galaxy features some level of disk disturbance, like a warp, as the outer part of the disk along with a ring-like dust lane appear to be on a different plane from the bulge, but it could also be a projection effect.[10][11] When observed in K band, the galaxy features a stellar ring.[11]
NGC 5965 lies in a galaxy filament which also includes NGC 5987 and its loose group,[12] which includes NGC 5981, NGC 5982, NGC 5985, three galaxies known as the Sampler.[13]
Gallery
-
NGC 5963, NGC 5965, and NGC 5971 by GALEX
-
NGC 5965 by the Sloan Digital Sky Survey
References
- ↑ 1.0 1.1 1.2 1.3 1.4 1.5 1.6 1.7 "NASA/IPAC Extragalactic Database". Results for NGC 5965. http://ned.ipac.caltech.edu/cgi-bin/nph-objsearch?objname=NGC+5965.
- ↑ "Revised NGC Data for NGC 5965". http://spider.seds.org/ngc/revngcic.cgi?NGC5965.
- ↑ Seligman, Courtney. "NGC 5965 (= PGC 55459)". http://cseligman.com/text/atlas/ngc59a.htm#5965.
- ↑ List of Supernovae IAU Central Bureau for Astronomical Telegrams. Retrieved 29 December 2015.
- ↑ "Bright Supernova pages - Most prolific galaxies". http://www.rochesterastronomy.org/snimages/sndupe.html.
- ↑ Peletier, R. F.; Balcells, M.; Davies, R. L.; Andredakis, Y.; Vazdekis, A.; Burkert, A.; Prada, F. (11 December 1999). "Galactic bulges from Hubble Space Telescope NICMOS observations: ages and dust". Monthly Notices of the Royal Astronomical Society 310 (3): 703–716. doi:10.1046/j.1365-8711.1999.02980.x. Bibcode: 1999MNRAS.310..703P.
- ↑ Molaeinezhad, A.; Falcón-Barroso, J.; Martínez-Valpuesta, I.; Khosroshahi, H. G.; Balcells, M.; Peletier, R. F. (17 December 2015). "Establishing the level of cylindrical rotation in boxy/peanut bulges". Monthly Notices of the Royal Astronomical Society 456 (1): 692–709. doi:10.1093/mnras/stv2697.
- ↑ Kuijken, Konrad; Merrifield, Michael R. (April 1995). "Establishing the connection between peanut-shaped bulges and galactic bars". The Astrophysical Journal 443: L13. doi:10.1086/187824. Bibcode: 1995ApJ...443L..13K.
- ↑ Athanassoula, E.; Bureau, M. (10 September 1999). "Bar Diagnostics in Edge-on Spiral Galaxies. II. Hydrodynamical Simulations". The Astrophysical Journal 522 (2): 699–717. doi:10.1086/307677. Bibcode: 1999ApJ...522..699A.
- ↑ Miskolczi, A.; Bomans, D. J.; Dettmar, R.-J. (8 December 2011). "Tidal streams around galaxies in the SDSS DR7 archive". Astronomy & Astrophysics 536: A66. doi:10.1051/0004-6361/201116716.
- ↑ 11.0 11.1 Bianchi, S. (26 June 2007). "The dust distribution in edge-on galaxies". Astronomy & Astrophysics 471 (3): 765–773. doi:10.1051/0004-6361:20077649.
- ↑ Narayanan, Anand; Wakker, Bart P.; Savage, Blair D.; Keeney, Brian A.; Shull, J. Michael; Stocke, John T.; Sembach, Kenneth R. (1 October 2010). "Cosmic origins spectrograph and FUSE observations of T ~ 105 K gas in a nearby galaxy filament". The Astrophysical Journal 721 (2): 960–974. doi:10.1088/0004-637X/721/2/960. Bibcode: 2010ApJ...721..960N.
- ↑ Makarov, Dmitry; Karachentsev, Igor (21 April 2011). "Galaxy groups and clouds in the local (z~ 0.01) Universe". Monthly Notices of the Royal Astronomical Society 412 (4): 2498–2520. doi:10.1111/j.1365-2966.2010.18071.x. Bibcode: 2011MNRAS.412.2498M. http://www.sao.ru/hq/dim/groups/galaxies.dat. Retrieved 20 December 2018.
External links
- NGC 5965 on WikiSky: DSS2, SDSS, GALEX, IRAS, Hydrogen α, X-Ray, Astrophoto, Sky Map, Articles and images
 |


