Biography:John C. Sheehan
John Clark Sheehan | |
|---|---|
 | |
| Born | September 23, 1915 Battle Creek, Michigan, U.S. |
| Died | March 21, 1992 (aged 76) Key Biscayne, Florida, U.S. |
| Alma mater | Battle Creek College University of Michigan |
| Known for | Synthesis of penicillin |
| Awards | ACS Award in Pure Chemistry (1951) Election to National Academy of Sciences (1957) American Chemical Society Award for Creative Work in Synthetic Organic Chemistry (1959) John Scott Award for inventors benefiting mankind (1964) Outstanding Achievement Award of the University of Michigan (1971) Oesper Award (1982)[1] |
| Scientific career | |
| Fields | Organic chemistry |
| Institutions | Massachusetts Institute of Technology, Merck & Co. |
| Doctoral advisor | Werner E. Bachmann |
| Notable students | E.J. Corey |
John Clark Sheehan (September 23, 1915 – March 21, 1992) was an American organic chemist whose work on synthetic penicillin led to tailor-made forms of the drug. After nine years of hard work at the Massachusetts Institute of Technology (M.I.T.), he became the first to discover a practical method for synthesizing penicillin V. While achieving total synthesis, Sheehan also produced an intermediate compound, 6-aminopenicillanic acid, which turned out to be the foundation of hundreds of kinds of synthetic penicillin. Dr. Sheehan's research on synthetic penicillin paved the way for the development of customized forms of the lifesaving antibiotic that target specific bacteria. Over the four decades he worked at M.I.T., Sheehan came to hold over 30 patents, including the invention of ampicillin, a commonly used semi-synthetic penicillin that is taken orally rather than by injection. His research covered not only penicillin, but also peptides, other antibiotics, alkaloids, and steroids.
Early life
He was born on September 23, 1915, in Battle Creek, Michigan, to Florence and Leo C. Sheehan. His family had Irish and Yankee background, and he was raised as a Catholic and attended Catholic grade schools.[2]
His father was then a sports editor and police reporter for a local newspaper, The Battle Creek Enquirer. Leo C. Sheehan left home at the age of fifteen and found work as a reporter in San Francisco . As a skilled writer, he progressed quickly with The Battle Creek Enquirer and became the managing editor. At one point, he functioned as the ghostwriter for Frank Murphy, who was once the governor of Michigan and a Supreme Court Justice. Sheehan's mother was a genealogist who later became the Michigan registrar for the Daughters of the American Revolution. His paternal grandfather, John W. Sheehan, was a successful lawyer, while his maternal grandfather, Nathaniel Y. Green, was a bank manager who had a keen interest in science and nature. Green played a role in stimulating John C. Sheehan's interest in science by giving him a microscope with an oil-immersion lens. He also introduced Sheehan to the curator of a local museum and took his grandson to meetings where Green frequently met with others passionate about astronomy.
At a young age, John Sheehan had been fascinated by science, especially explosives and rocketry. He started with a simple chemistry set and then progressed to a basement laboratory where he built models and performed experiments. A model airplane that he built with a delta wing won a competition in his self-design class. Apart from science, Sheehan was also very competitive in other activities. He was an excellent marble shooter in elementary school, representing his school in the state championships. In addition, he was the winner of a city-wide yo-yo competition, the winner of a Boy Scout election, an active member of his high school football team, as well as Battle Creek College's best tennis player. Sheehan's father had a long struggle with cancer and died at age fifty.[3]
Sheehan had two brothers, Joseph Sheehan and David Sheehan. Joseph is a professor of psychology at the University of California and ran training programs for relieving speech defects with his wife, Vivian. David Sheehan, the youngest of the three, worked in the manufacturing industry in Battle Creek. John Sheehan married Marion Jennings shortly after receiving his Ph.D and had three children: John C. Sheehan Jr., David E. Sheehan, and Elizabeth (Betsy) S. Watkins. He had six grandchildren.
Education
John Sheehan attended Catholic grade schools, even though John and his brother Joseph were not particularly religious later in life. He studied chemistry and political science at Battle Creek College. In 1937, Sheehan graduated as the valedictorian of his class and won a scholarship for graduate studies in any subject of his choice. He decided to study organic chemistry at the University of Michigan, receiving his Master's in 1938 and his PhD in 1941. His doctorate advisor, Werner E. Bachmann, was involved in the synthesis of steroid hormones. As a post-doctoral fellow, Sheehan collaborated with Bachmann on the commercially feasible production of RDX also known as cyclonite, which turned out to give the Allies a huge advantage at sea during World War II.
Early career
After the efficient completion of RDX synthesis, John Sheehan had the experience of applying organic chemistry to real-life problems. Having struggled against pneumonia and mastoiditis in his earlier years, Sheehan was eager to start working on antibiotics. He wrote, "If my doctors had had a course of treatment as effective as that made possible by penicillin, I would probably not have lost that year."[4] In 1941, he accepted a position at Merck & Co. in Rahway, New Jersey. He worked there until 1946 as a senior research chemist under the supervision of Dr. Max Tishler. Sheehan had good results for his work on many projects, including those on calcium pantothenate, streptomycin, and vitamin B6. However, he wanted to pursue the synthesis of penicillin, which was hard in an industrial setting driven by results given that many scientists of his time believed that it was impossible. John Sheehan's work attracted the attention of Arthur C. Cope, who was the head of the Department of Chemistry at the M.I.T. at the time. He decided to join the M.I.T. faculty as an assistant professor at a salary that was half of what he made at Merck. Within his first few years at M.I.T., John Sheehan was already recognized for his ingenuity in synthetic organic chemistry, especially for his new methods of synthesis of peptides, three new syntheses of β-lactams, first synthesis of the penicillin ring system, and his work on several other natural products.
Synthesis of penicillin
For three decades after the discovery of natural penicillin by Sir Alexander Fleming, the source of the antibiotic hardly changed. Scientists made the drug by natural fermentation of Penicillium mold. However, during World War II, the United States government undertook a massive effort to determine the chemical structure of penicillin and to chemically synthesize it in large quantities. The scale of this project was compared to the development of the atomic bomb. This stemmed from the dire need for the antibiotic to treat soldiers on the battlefield. More than a thousand chemists working at thirty-nine laboratories were involved in the project. Despite the huge investment by the government, none proved to be successful in solving this elusive problem.
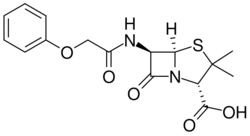
As John Sheehan described in his book The Enchanted Ring: The Untold Story of Penicillin, after the war, most other synthetic chemists abandoned attempting penicillin synthesis, and were convinced that such synthesis was impossible. For the nine years that he worked on penicillin synthesis, there were practically no competitors, leaving Sheehan on a lonely search for a way to synthesize the antibiotic. Most young academic chemists chose not to undertake projects that they perceived to be painfully slow because they wanted to impress faculty tenure committees with many experiments and publications. Even though many of his friends openly questioned his decision of getting involved with the drug, Sheehan was determined to work on the chemical synthesis of penicillin at M.I.T. Once he decided that penicillin was an important problem, and one that had a solution, Sheehan never re-evaluated his position. He explained that one of the reasons he decided to switch from his job at Merck to M.I.T. was because "At M.I.T, I was a research committee of one. I could make the decision to spend the rest of my life on the penicillin problem; it was only my career that was on the line."[4]
At the time, it was known that the molecular weight of penicillin was around 350 g/mol, which was within the range of molecules that had already been chemically synthesized. The problem was the making the chemically unstable beta-lactam ring that was crucial to the antibiotic properties of the molecule. Beta-lactam antibiotics inhibit the formation of the peptidoglycan layer of the cell walls of Gram-positive bacteria. Most of the scientists experienced failure after failure because "the appropriate techniques and reactions for putting together the penicillin molecule simply had not yet been discovered." In the words of Sheehan, using traditional methods at the time was like "placing an anvil on top of a house of cards."[5] After nine years of dogged work in the M.I.T. laboratories, this persistent organic chemist finally solved one of chemistry's most baffling problems at the time.[6] In 1957, John C. Sheehan announced that his group had completed the first synthesis of penicillin V (one of the two most useful forms of the antibiotic). During the process, he had also produced an intermediate, 6-aminopenicillanic acid, which was later used as a foundation for preparing a variety of penicillins.[7] This allowed researchers to combat the resistance that certain bacteria had developed to particular forms of the drug. Sheehan later published his involvement in the synthesis of penicillins in The Enchanted Ring: The Untold Story of Penicillin, which noted a complex legal skirmish over his patents on penicillin synthesis involving M.I.T. and Beecham, a United Kingdom industrial research laboratory that was also working on penicillins.
See also
- National Inventors Hall of Fame
References
- ↑ "Previous recipients of the Oesper Award". University of Cincinnati. https://www.artsci.uc.edu/departments/chemistry/alumni-and-community/the-oesper-award-program-and-symposium/previous-recipients-of-the-oesper-award.html.
- ↑ Elias James Corey and John Dombrowski Roberts (1995). "John Clark Sheehan". National Academy of Sciences. http://www.nasonline.org/publications/biographical-memoirs/memoir-pdfs/sheehan-john.pdf.
- ↑ Corey, E. J.; Roberts, J. D.. "Biographical Memoirs: John Clark Sheehan. The National Academies Press". http://www.nap.edu/readingroom.php?book=biomems&page=jsheehan.html. Retrieved April 6, 2009.
- ↑ 4.0 4.1 Sheehan, John C (1982). The Enchanted Ring: The Untold Story of Penicillin. Cambridge, Massachusetts: MIT Press. ISBN 0-262-19204-7. OCLC 8170304. https://archive.org/details/enchantedringunt0000shee.
- ↑ "Professor John C. Sheehan Dies At 76". Massachusetts Institute of Technology News Office. April 1, 1992. http://web.mit.edu/newsoffice/1992/sheehan-0401.html. Retrieved March 30, 2009.
- ↑ "Penicillin Synthesis". Time magazine. March 18, 1957. http://www.time.com/time/magazine/article/0,9171,809227,00.html. Retrieved March 30, 2009.
- ↑ Saxon, Wolfgang (24 March 1992). "John Clark Sheehan, 76, Chemist Who First Synthesized Penicillin". The New York Times. https://www.nytimes.com/1992/03/24/us/john-clark-sheehan-76-chemist-who-first-synthesized-penicillin.html. Retrieved March 30, 2009.
 |
