Biography:Michael Houghton (virologist)
Sir Michael Houghton | |
|---|---|
 | |
| Born | 1949 (age 74–75) |
| Alma mater | University of East Anglia (BSc) King's College London (PhD) |
| Known for | Hepatitis C Hepatitis D |
| Awards | Karl Landsteiner Memorial Award (1992) Robert Koch Prize (1993) William Beaumont Prize (1994) Lasker Award (2000) Gairdner Foundation International Award (2013 – declined) Nobel Prize for Medicine (2020) |
| Scientific career | |
| Fields | Microbiology Virology |
| Institutions | University of Alberta Chiron Corporation |
| Thesis | RNA Polymerases and Transcription in the Chicken Oviduct (1977) |
| Doctoral advisor | James Chesterton |
| Website | apps |
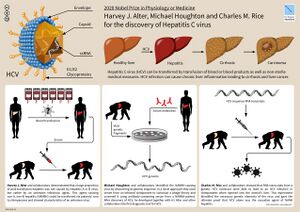
Sir Michael Houghton (born 1949) is a British scientist and Nobel Prize laureate. Along with Qui-Lim Choo, George Kuo and Daniel W. Bradley, he co-discovered Hepatitis C in 1989.[1] He also co-discovered the Hepatitis D genome in 1986.[2] The discovery of the Hepatitis C virus (HCV) led to the rapid development of diagnostic reagents to detect HCV in blood supplies, which has reduced the risk of acquiring HCV through blood transfusion from one in three to about one in two million.[3][4] It is estimated that antibody testing has prevented at least 40,000 new infections per year in the US alone and many more worldwide.[5]
Houghton is currently Canada Excellence Research Chair in Virology and Li Ka Shing Professor of Virology at the University of Alberta, where he is also director of the Li Ka Shing Applied Virology Institute.[6] He is the co-recipient of the 2020 Nobel Prize in Physiology or Medicine along with Harvey J. Alter and Charles M. Rice.[7][8]
Early life and education
Born in the United Kingdom in 1949, his father was a truck driver and union official.[5] He was educated at Alleyn's School.[9] At the age of 17 he became inspired to become a microbiologist after reading about Louis Pasteur.[10][11] Houghton won a scholarship to study at the University of East Anglia, graduating with a lower second class honours degree in biological sciences in 1972,[12] and subsequently completed his PhD degree in biochemistry at King's College London in 1977.[5][13]
Career
Houghton joined G. D. Searle & Company before moving to Chiron Corporation in 1982. It was at Chiron that Houghton together with colleagues Qui-Lim Choo and George Kuo, and Daniel W. Bradley from the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, first discovered evidence for HCV.[14]
Houghton was co-author of a series of seminal studies published in 1989 and 1990 that identified hepatitis C antibodies in blood, particularly among patients at higher risk of contracting the disease, including those who had received blood transfusions.[15][16][17][18] This work led to the development of a blood screening test in 1990; widespread blood screening that began in 1992 with the development of a more sensitive test has since virtually eliminated hepatitis C contamination of donated blood supplies in Canada.[19][20] In other studies published during the same period, Houghton and collaborators linked hepatitis C with liver cancer.[21][22][23]
In 2013, Houghton's team at the University of Alberta showed that a vaccine derived from a single strain of Hepatitis C was effective against all strains of the virus.[24][25] (As of 2020) the vaccine was in pre-clinical trials.[26]
Honours and awards
- 1992 – Karl Landsteiner Memorial Award[27]
- 1993 – Robert Koch Prize[28]
- 1994 – William Beaumont Prize[29]
- 2000 – Lasker Award[30]
- 2005 – Dale A. Smith Memorial Award[31]
- 2009 – Hepdart Lifetime Achievement Award[32]
- 2013 – He became the first person to decline the $100,000 Gairdner Foundation International Award stating "I felt that it would be unfair of me to accept this award without the inclusion of two colleagues, Dr. Qui-Lim Choo and Dr. George Kuo."[33][34]
- 2019 – Honorary doctorate of science from the University of East Anglia[35]
- 2020 – Nobel Prize in Physiology or Medicine[7]
- 2021 – Knighted in the 2021 Birthday Honours for services to medicine.[36]
References
- ↑ "Isolation of a cDNA clone derived from a blood-borne non-A, non-B viral hepatitis genome". Science 244 (4902): 359–62. April 1989. doi:10.1126/science.2523562. PMID 2523562. Bibcode: 1989Sci...244..359C.
- ↑ Wang, KS; Choo, QL; Weiner, AJ; Ou, JH; Najarian, RC; Thayer, RM; Mullenbach, GT; Denniston, KJ et al. (9 October 1986). "Structure, sequence and expression of the hepatitis delta (delta) viral genome". Nature 323 (6088): 508–14. doi:10.1038/323508a0. PMID 3762705. Bibcode: 1986Natur.323..508W.
- ↑ "Opinion: Nobel-worthy discovery right in our backyard". http://www.chrcrm.org/en/node/6048.
- ↑ Semeniuk, Ivan (20 March 2013). "Science world abuzz as virologist turns down Gairdner award". https://www.theglobeandmail.com/technology/science/science-world-abuzz-as-virologist-turns-down-gairdner-award/article10052360/.
- ↑ 5.0 5.1 5.2 Thompson, Gilbert (2014). Pioneers of Medicine Without a Nobel Prize. p. 209. ISBN 978-1-78326-386-8. https://books.google.com/books?id=_dK3CgAAQBAJ&q=%22Pioneers+of+Medicine+Without+a+Nobel+Prize%22+%22houghton%22&pg=PA206.
- ↑ "MMI Faculty – Michael Houghton, PhD". http://www.mmi.med.ualberta.ca/staff_students/michael_houghton.php.
- ↑ 7.0 7.1 "Press release: The Nobel Prize in Physiology or Medicine 2020". Nobel Foundation. https://www.nobelprize.org/prizes/medicine/2020/press-release/.
- ↑ Wu, Katherine J.; Victor, Daniel (5 October 2020). "Nobel Prize in Medicine Awarded to Scientists Who Discovered Hepatitis C Virus – Harvey J. Alter, Michael Houghton and Charles M. Rice were jointly honored for their decisive contribution to the fight against blood-borne hepatitis, a major global health problem.". The New York Times. https://www.nytimes.com/2020/10/05/health/nobel-prize-medicine-hepatitis-c.html.
- ↑ "Congratulations to a Nobel Prize Laureate". https://www.alleyns.org.uk/alumni-development/news-events/news-detail/~board/alumni-and-development/post/congratulations-to-alumnus-professor-michael-houghton-2020-nobel-prize-laureate.
- ↑ "Michael Houghton, PhD". http://www.chrcrm.org/en/rotm/michael-houghton-phd.
- ↑ "Eureka moments in research". http://www.aihealthsolutions.ca/news-and-events/media-centre/eureka-moments-in-research/.
- ↑ "Nobelist: keep faith, because Covid vaccine is just round corner". 21 October 2020. https://www.timeshighereducation.com/news/nobelist-keep-faith-because-covid-vaccine-just-round-corner.
- ↑ Boyer, J.L; Blum, H.E; Maier, K.P; Sauerbruch, T.; Stalder, G.A (31 March 2001). Liver Cirrhosis and Its Development – Google Books. ISBN 978-0-7923-8760-2. https://books.google.com/books?id=n5P696E7T0wC&q=dr+Michael+Houghton&pg=PA344. Retrieved 12 January 2014.
- ↑ Houghton, M (2009). "The long and winding road leading to the identification of the hepatitis C virus.". J. Hepatol. 51 (5): 939–948. doi:10.1016/j.jhep.2009.08.004. PMID 19781804.
- ↑ Kuo, G; Choo, Q-L; Alter, HJ; Gitnick, GI; Redeker, AG; Purcell, RH; Miyamura, T; Dienstag, JL et al. (1989). "An assay for circulating antibodies to a major etiologic virus of human non-A, non-B hepatitis.". Science 244 (4902): 362–364. doi:10.1126/science.2496467. PMID 2496467. Bibcode: 1989Sci...244..362K.
- ↑ Esteban, JI; Viladomiu, L; Bonzalez, A; Roget, M; Genesca, J; Guardia, J; Esteban, R; Lopez-Talavera, JC et al. (1989). "Hepatitis C virus antibodies among risk groups in Spain.". Lancet 334 (8658): 294–297. doi:10.1016/s0140-6736(89)90485-6. PMID 2569102.
- ↑ Van Der Poel, CL; Ressink, HW; Lelie, PN; Leentvaar-Kuypers, A; Choo, Q-L; Kuo, G; Houghton, M (1989). "Anti-hepatitis C antibodies and non-A, non-B post-transfusion hepatitis in the Netherlands.". Lancet 334 (8658): 297–298. doi:10.1016/s0140-6736(89)90486-8. PMID 2569103.
- ↑ Alter, HJ; Purcell, RH; Shih, JW; Melpolder, JC; Houghton, M; Choo, Q-L; Kuo, G (1989). "Detection of antibody to hepatitis C virus in prospectively followed transfusion recipients with acute and chronic non-A, non-B hepatitis". N. Engl. J. Med. 321 (22): 1494–1500. doi:10.1056/nejm198911303212202. PMID 2509915.
- ↑ Cha, T-A; Kolberg, J; Irvine, B; Stempien, M; Beall, E; Yano, M; Choo, Q-L; Houghton, M et al. (1991). "Use of a signature nucleotide sequence of hepatitis C virus for detection of viral RNA in human serum and plasma". J. Clin. Microbiol. 29 (11): 2528–2534. doi:10.1128/JCM.29.11.2528-2534.1991. PMID 1663510.
- ↑ Bresters, D; Cuypers, HT; Reesink, HW; Schaasberg, WP; van der Poel, CL; Mauser-Bunschoten, EP; Houghton, M; Choo, Q-L et al. (1992). "Enhanced sensitivity of a second generation ELISA for antibody to hepatitis C virus.". Vox Sang. 62 (4): 213–217. doi:10.1111/j.1423-0410.1992.tb01201.x. PMID 1379394.
- ↑ Hasan, F; Jeffers, L; de Medina, M; Reddy, R; Parker, T; Schiff, E; Houghton, M; Choo, Q-L et al. (1989). "Hepatitis C HCV associated hepatocellular carcinoma.". Hepatology 10 (4): 589–91. doi:10.1002/hep.1840100432. PMID 2169456.
- ↑ De Bisceglie, AM; Alter, H; Kuo, G; Houghton, M; Hoofnagle, JH (1989). "Detection of antibody to hepatitis C virus in patients with various chronic liver diseases.". Hepatology 10 (4): 581. doi:10.1002/hep.1840100432.
- ↑ Saito, I; Miyamura, T; Ohbayashi, A; Harada, H; Katayama, T; Kikuchi, S; Watanabe, Y; Koi, S et al. (1990). "Hepatitis C virus infection is associated with the development of hepatocellular carcinoma.". Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 87 (17): 6547–6549. doi:10.1073/pnas.87.17.6547. PMID 2168552. Bibcode: 1990PNAS...87.6547S.
- ↑ Law, JL; Chen, C; Wong, J; Hockman, D; Santer, DM; Frey, SE; Belshe, RB; Wakita, T et al. (19 March 2013). "A hepatitis C virus (HCV) vaccine comprising envelope glycoproteins gpE1/gpE2 derived from a single isolate elicits broad cross-genotype neutralizing antibodies in humans.". PLOS ONE 8 (3): e59776. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0059776. PMID 23527266. Bibcode: 2013PLoSO...859776L.
- ↑ Houghton, M; Law, J; Tyrrell, DL (2013). "An inactivated hepatitis C virus vaccine on the horizon?". Gastroenterology 145 (2): 285–288. doi:10.1053/j.gastro.2013.06.029. PMID 23806539.
- ↑ "University of Alberta virologist awarded Nobel Prize in Physiology or Medicine" (in en). https://www.eurekalert.org/pub_releases/2020-10/uoaf-uoa100520.php.
- ↑ Karl Landsteiner Memorial Award 1992
- ↑ Robert Koch Prize 1993
- ↑ William Beaumont Prize 1994
- ↑ Albert Lasker Clinical Medical Research Award 2000
- ↑ "List of Past AABB Award Recipients". aabb.org. http://www.aabb.org/about/awards/Pages/recipientspast.aspx.
- ↑ "The William H. Prusoff HEP DART Lifetime Achievement Award". https://www.virology-education.com/event/previous/hep-dart-2019/awards/.
- ↑ "World-renowned virologist named recipient of Gairdner Award". 22 March 2013. http://www.folio.ualberta.ca/article.cfm?v=104208&i=104377&a=3.
- ↑ Boesveld, Sarah (20 March 2013). "Edmonton scientist turns down $100,000 'baby Nobel' because it shut out colleagues". http://news.nationalpost.com/2013/03/20/team-player-edmonton-scientist-turns-down-100000-baby-nobel-because-it-shut-out-colleagues/.
- ↑ "A Titanic actor, climate change trailblazer and banking boss: Meet UEA's newest honorary graduates". 11 June 2019. https://www.edp24.co.uk/news/education/meet-university-of-east-anglia-honorary-gradutes-2019-1-6099335.
- ↑ No. 63377. 12 June 2021. p. B2. https://www.thegazette.co.uk/London/issue/63377/supplement/B2
External links
- Miss nobel-id as parameter