Biology:Duodenojejunal flexure
| Duodenojejunal flexure | |
|---|---|
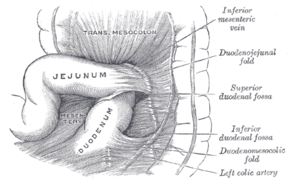 Superior and inferior duodenal fossæ. | |
 Small intestine | |
| Details | |
| Identifiers | |
| Latin | flexura duodenojejunalis |
| Anatomical terminology | |
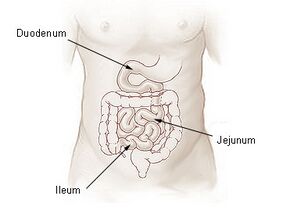
The duodenojejunal flexure or duodenojejunal junction, also known as the angle of Treitz,[1][2] is the border between the duodenum and the jejunum.
Structure
The ascending portion of the duodenum ascends on the left side of the aorta, as far as the level of the upper border of the second lumbar vertebra. At this point, it turns abruptly forward to merge with the jejunum, forming the duodenojejunal flexure. This forms the beginning of the jejunum.[3] The duodenojejunal flexure is surrounded by the suspensory muscle of the duodenum.[4]:274 It is retroperitoneal, so is less mobile than the jejunum that comes after it, helping to stabilise the jejunum.[5]
The duodenojejunal flexure lies in front of the left psoas major muscle, the left renal artery, and the left renal vein. It is covered in front, and partly at the sides, by peritoneum continuous with the left portion of the mesentery.
Clinical significance
The ligament of Treitz, a peritoneal fold, from the right crus of diaphragm, is an identification point for the duodenojejunal flexure during abdominal surgery.[6]:85
Additional images
Front of abdomen, showing surface markings for duodenum, pancreas, and kidneys.
See also
References
- ↑ Bracale, Umberto et.al. Laparoscopic segmental resection for tumours of the Angle of Treitz: a challenging but feasible surgical option. Results from a retrospective case-series analysis. Updates Surg. 2021; 73(1): 179–186. doi: 10.1007/s13304-020-00910-7
- ↑ Lissauer et.al. Neonatology at a Glance. John Wiley & Sons, 2020, p.125.
- ↑ Federle, Michael P.; Rosado-de-Christenson, Melissa L.; Raman, Siva P. et al., eds. (2017-01-01), "Small Intestine" (in en), Imaging Anatomy: Chest, Abdomen, Pelvis (Second Edition) (Elsevier): pp. 636–665, doi:10.1016/B978-0-323-47781-9.50031-3, ISBN 978-0-323-47781-9, http://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/B9780323477819500313, retrieved 2021-01-26
- ↑ Drake, Richard L.; Vogl, Wayne; Tibbitts, Adam W.M. Mitchell; illustrations by Richard; Richardson, Paul (2005). Gray's anatomy for students. Philadelphia: Elsevier/Churchill Livingstone. ISBN 978-0-8089-2306-0.
- ↑ Schneider, Armin; Feussner, Hubertus (2017-01-01), Schneider, Armin; Feussner, Hubertus, eds., "Chapter 2 - Anatomy, Physiology, and Selected Pathologies of the Gastrointestinal Tract" (in en), Biomedical Engineering in Gastrointestinal Surgery (Academic Press): pp. 11–39, ISBN 978-0-12-803230-5, http://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/B9780128032305000026, retrieved 2021-01-26
- ↑ Jacob, S. (2007) Chapter 4: Abdomen; Human anatomy, A clinically-orientated approach.
External links
- Anatomy figure: 37:06-04 at Human Anatomy Online, SUNY Downstate Medical Center - "The large intestine."
- Anatomy photo:39:07-0105 at the SUNY Downstate Medical Center - "Intestines and Pancreas: The Duodenum"
- Anatomy image:8155 at the SUNY Downstate Medical Center
 |