Biology:Hazel grouse
| Hazel grouse | |
|---|---|

| |
| Scientific classification | |
| Domain: | Eukaryota |
| Kingdom: | Animalia |
| Phylum: | Chordata |
| Class: | Aves |
| Order: | Galliformes |
| Family: | Phasianidae |
| Genus: | Tetrastes |
| Species: | T. bonasia
|
| Binomial name | |
| Tetrastes bonasia | |
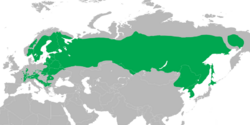
| |
| Range of T. bonasia | |
| Synonyms[2] | |
The hazel grouse (Tetrastes bonasia), sometimes called the hazel hen, is one of the smaller members of the grouse family of birds. It is a sedentary species, breeding across the Palearctic as far east as Hokkaido, and as far west as eastern and central Europe, in dense, damp, mixed coniferous woodland, preferably with some spruce. The bird is sometimes referred to as "rabchick" (from рябчик) by early 20th century English speaking travellers to Russia.[3]
Description
This is a relatively small grouse at 35–39 cm (14–15 in) length. The plumage of this plump bird is finely patterned, but it essentially has grey upperparts, brown wings and chestnut flecked white underparts.
The male has a short erectile crest and a white-bordered black throat. The female has a shorter crest and lacks the black color on the throat. In flight, this species shows a black-tipped grey tail.
The male has a high-pitched ti-ti-ti-ti-ti call, and the female a liquid tettettettettet. These calls, along with the burr of the flying birds' wings, are often the only indication of this grouse's presence, since its shyness and dense woodland habitat make it difficult to see.
Taxonomy
The hazel grouse has 11 recognized subspecies:[4]
- T. b. amurensis (Riley, 1925)
- T. b. bonasia (Linnaeus, 1758)
- T. b. griseonota (Salomonsen, 1947)
- T. b. kolymensis (Buturlin, 1916)
- T. b. rhenanus (Kleinschmidt, 1917)
- T. b. rupestris (Brehm & CL, 1831)
- T. b. schiebeli (Kleinschmidt, 1943)
- T. b. sibiricus (Buturlin, 1916)
- T. b. styriacus (von Jordans & Schiebel, 1944)
- T. b. vicinitas (Riley, 1915)
- T. b. yamashinai (Momiyama, 1928)
Feeding
This bird feeds on the ground, taking mainly plant food, supplemented by insects when breeding.
Breeding
The nest is on the ground, and 3–6 eggs is the normal clutch size. The female incubates the eggs and cares for the chicks alone, as is typical with gamebirds.
References
- ↑ BirdLife International (2016). "Bonasa bonasia". IUCN Red List of Threatened Species 2016: e.T22679494A85936486. doi:10.2305/IUCN.UK.2016-3.RLTS.T22679494A85936486.en. https://www.iucnredlist.org/species/22679494/85936486. Retrieved 4 June 2022.
- ↑ Peterson, Alan P.. "Birds of the World — current valid scientific avian names". http://www.zoonomen.net/avtax/frame.html.
- ↑ "Chapter XXIV". http://digital.library.upenn.edu/women/bryant/russia/russia-XXIV.html.
- ↑ Gill, Frank; Donsker, David; Rasmussen, Pamela, eds. (July 2021). "Pheasants, partridges, francolins". IOC World Bird List Version 11.2. International Ornithologists' Union. Retrieved 13 October 2021.
External links
- BirdLife species factsheet for Bonasa bonasia
- "Tetrastes bonasia". Avibase. https://avibase.bsc-eoc.org/species.jsp?lang=EN&avibaseid=.
- "Hazel grouse media". Internet Bird Collection. http://www.hbw.com/ibc/species/hazel-grouse-bonasa-bonasia.
- Hazel grouse photo gallery at VIREO (Drexel University)
Wikidata ☰ Q182761 entry
 |






