Biology:LYPLAL1
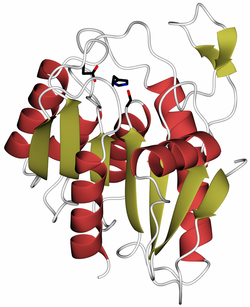 Crystal structure of human LYPLAL1, PDB code 3u0v. Alpha helices are in red, beta strands in gold, catalytic site residues in black. | |||||||||
| Identifiers | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Symbol | Lysophospholipase-like protein 1 | ||||||||
| Pfam | PF02230 | ||||||||
| InterPro | IPR029058 | ||||||||
| CATH | 3u0v | ||||||||
| SCOP2 | 3u0v / SCOPe / SUPFAM | ||||||||
| |||||||||
Lysophospholipase-like 1 is a protein in humans that is encoded by the LYPLAL1 gene. [1] The protein is a α/β-hydrolase of uncharacterized metabolic function. Genome-wide association studies in humans have linked the gene to fat distribution[2] and waist-to-hip ratio.[3] The protein's enzymatic function is unclear. LYPLAL1 was reported to act as a triglyceride lipase in adipose tissue[4] and another study suggested that the protein may play a role in the depalmitoylation of calcium-activated potassium channels.[5] However, LYPLAL1 does not depalmitoylate the oncogene Ras[6] and a structural and enzymatic study concluded that LYPLAL1 is generally unable to act as a lipase and is instead an esterase that prefers short-chain substrates, such as acetyl groups.[7] Structural comparisons have suggested that LYPLAL1 might be a protein deacetylase, but this has not been experimentally tested.[8]
Relationship to acyl-protein thioesterases
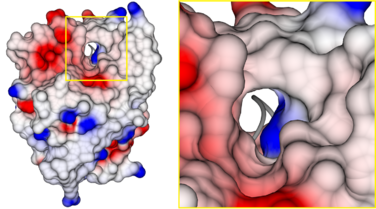
Sequence conservation and structural homology suggest a close relationship of LYPLAL1 proteins to acyl-protein thioesterases, and, therefore, it has been suggested that LYPLAL1 might be the third human acyl-protein thioesterase.[9] However, the major structural difference between both protein families has been established in the hydrophobic substrate binding tunnel, which has been identified in human acyl-protein thioesterases 1[10] and 2,[11] as well as in Zea mays acyl-protein thioesterase 2.[12] In LYPLAL1, this tunnel is closed due to a different loop conformation, changing the enzyme's substrate specificity to short acyl chains.[7]
References
- ↑ "Entrez Gene: Lysophospholipase-like 1". https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/sites/entrez?db=gene&cmd=retrieve&list_uids=127018.
- ↑ "Gene by sex interaction for measures of obesity in the framingham heart study". Journal of Obesity 2011: 329038. 2011. doi:10.1155/2011/329038. PMID 21253498.
- ↑ "Meta-analysis identifies 13 new loci associated with waist-hip ratio and reveals sexual dimorphism in the genetic basis of fat distribution". Nature Genetics 42 (11): 949–60. November 2010. doi:10.1038/ng.685. PMID 20935629.
- ↑ "Adipocyte triglyceride lipase expression in human obesity". American Journal of Physiology. Endocrinology and Metabolism 293 (4): E958-64. October 2007. doi:10.1152/ajpendo.00235.2007. PMID 17609260.
- ↑ "Distinct acyl protein transferases and thioesterases control surface expression of calcium-activated potassium channels". The Journal of Biological Chemistry 287 (18): 14718–25. April 2012. doi:10.1074/jbc.M111.335547. PMID 22399288.
- ↑ "Chemical-biological exploration of the limits of the Ras de- and repalmitoylating machinery". ChemBioChem 13 (7): 1017–23. May 2012. doi:10.1002/cbic.201200078. PMID 22488913.
- ↑ 7.0 7.1 "Crystal structure of the predicted phospholipase LYPLAL1 reveals unexpected functional plasticity despite close relationship to acyl protein thioesterases". Journal of Lipid Research 53 (1): 43–50. January 2012. doi:10.1194/jlr.M019851. PMID 22052940.
- ↑ "Structural and chemical biology of deacetylases for carbohydrates, proteins, small molecules and histones". Communications Biology 1: 217. 2018. doi:10.1038/s42003-018-0214-4. PMID 30534609.
- ↑ "Protein acyl thioesterases (Review)". Molecular Membrane Biology 26 (1): 32–41. January 2009. doi:10.1080/09687680802629329. PMID 19115143.
- ↑ "Crystal structure of the human acyl protein thioesterase I from a single X-ray data set to 1.5 A". Structure 8 (11): 1137–46. November 2000. doi:10.1016/s0969-2126(00)00529-3. PMID 11080636.
- ↑ "Molecular Mechanism for Isoform-Selective Inhibition of Acyl Protein Thioesterases 1 and 2 (APT1 and APT2)". ACS Chemical Biology 11 (12): 3374–3382. December 2016. doi:10.1021/acschembio.6b00720. PMID 27748579.
- ↑ "A hydrophobic anchor mechanism defines a deacetylase family that suppresses host response against YopJ effectors". Nature Communications 8 (1): 2201. December 2017. doi:10.1038/s41467-017-02347-w. PMID 29259199. Bibcode: 2017NatCo...8.2201B.
Further reading
 |
