Biology:Leiognathidae
| Leiognathidae | |
|---|---|
| |
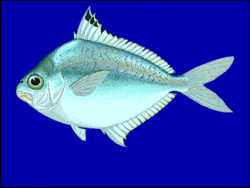
| Eubleekeria splendens | |
| Scientific classification | |
| Domain: | Eukaryota |
| Kingdom: | Animalia |
| Phylum: | Chordata |
| Class: | Actinopterygii |
| Order: | Perciformes |
| Suborder: | Percoidei |
| Family: | Leiognathidae T. N. Gill, 1893[2] |
| Genera | |
|
see text | |
Leiognathidae, the ponyfishes, slipmouths or slimys / slimies, are a small family of fishes in the order Perciformes.[3] They inhabit marine and brackish waters in the Indian and West Pacific Oceans. They can be used in the preparation of bagoong.
Characteristics
Ponyfishes are small and laterally compressed in shape, with a bland, silvery colouration. They are distinguished by highly extensible mouths, and the presence of a mechanism for locking the spines in the dorsal and anal fins. They also possess a highly integrated light organ in their throats that houses symbiotic bioluminescent bacteria that project light through the animal's underside.[4][5][6] Typically, the harbored bacterium is only Photobacterium leiognathi, but in the two ponyfish species Photopectoralis panayensis and Photopectoralis bindus, Photobacterium mandapamensis is also present.[7] Two of the most widely studied uses for luminescence in ponyfish are camouflage by ventral counterillumination[8][9] and species-specific sexual dimorphism.[5][6][10][11]
Although ponyfish seem quite ordinary and morphologically similar, their light organ systems are highly variable across species and often between sexes.[10][11]
Taxonomy
Leiognathidae is classified within the suborder Percoidei by the 5th edition of Fishes of the World, but they are placed in an unnamed clade which sits outside the superfamily Percoidea. This clade contains 7 families which appear to have some relationship to Acanthuroidei, Monodactylidae, and Priacanthidae.[12] Other authorities have placed the family in the order Chaetodontiformes alongside the family Chaetodontidae.[13]
Timeline of genera
<timeline> ImageSize = width:1000px height:auto barincrement:15px PlotArea = left:10px bottom:50px top:10px right:10px
Period = from:-65.5 till:10 TimeAxis = orientation:horizontal ScaleMajor = unit:year increment:5 start:-65.5 ScaleMinor = unit:year increment:1 start:-65.5 TimeAxis = orientation:hor AlignBars = justify
Colors =
#legends id:CAR value:claret id:ANK value:rgb(0.4,0.3,0.196) id:HER value:teal id:HAD value:green id:OMN value:blue id:black value:black id:white value:white id:cenozoic value:rgb(0.54,0.54,0.258) id:paleogene value:rgb(0.99,0.6,0.32) id:paleocene value:rgb(0.99,0.65,0.37) id:eocene value:rgb(0.99,0.71,0.42) id:oligocene value:rgb(0.99,0.75,0.48) id:neogene value:rgb(0.999999,0.9,0.1) id:miocene value:rgb(0.999999,0.999999,0) id:pliocene value:rgb(0.97,0.98,0.68) id:quaternary value:rgb(0.98,0.98,0.5) id:pleistocene value:rgb(0.999999,0.95,0.68) id:holocene value:rgb(0.999,0.95,0.88)
BarData=
bar:eratop bar:space bar:periodtop bar:space bar:NAM1 bar:NAM2
bar:space bar:period bar:space bar:era
PlotData=
align:center textcolor:black fontsize:M mark:(line,black) width:25 shift:(7,-4) bar:periodtop from: -65.5 till: -55.8 color:paleocene text:Paleocene from: -55.8 till: -33.9 color:eocene text:Eocene from: -33.9 till: -23.03 color:oligocene text:Oligocene from: -23.03 till: -5.332 color:miocene text:Miocene from: -5.332 till: -2.588 color:pliocene text:Plio. from: -2.588 till: -0.0117 color:pleistocene text:Pleist. from: -0.0117 till: 0 color:holocene text:H.
bar:eratop from: -65.5 till: -23.03 color:paleogene text:Paleogene from: -23.03 till: -2.588 color:neogene text:Neogene from: -2.588 till: 0 color:quaternary text:Q.
PlotData=
align:left fontsize:M mark:(line,white) width:5 anchor:till align:left
color:eocene bar:NAM1 from: -55.8 till: 0 text: Gazza color:oligocene bar:NAM2 from: -33.9 till: 0 text: Leiognathus
PlotData=
align:center textcolor:black fontsize:M mark:(line,black) width:25
bar:period from: -65.5 till: -55.8 color:paleocene text:Paleocene from: -55.8 till: -33.9 color:eocene text:Eocene from: -33.9 till: -23.03 color:oligocene text:Oligocene from: -23.03 till: -5.332 color:miocene text:Miocene from: -5.332 till: -2.588 color:pliocene text:Plio. from: -2.588 till: -0.0117 color:pleistocene text:Pleist. from: -0.0117 till: 0 color:holocene text:H.
bar:era from: -65.5 till: -23.03 color:paleogene text:Paleogene from: -23.03 till: -2.588 color:neogene text:Neogene from: -2.588 till: 0 color:quaternary text:Q.
</timeline>
Genera
The following genera are classified within the Leiognathidae:[3][14]
- Aurigequula Fowler, 1918
- Equulites Fowler, 1904
- Eubleekeria Fowler, 1904
- Gazza Rüppell, 1835
- Karalla Chakrabarty & Sparks, 2008
- Leiognathus Lacepède, 1802
- Nuchequula Whitley, 1932
- Photolateralis Sparks & Chakrabarty, 2015[15]
- Photopectoralis Sparks, Dunlap & Smith, 2005
- Secutor Gistel, 1848
References
- ↑ Sepkoski, J. (2002). "A compendium of fossil marine animal genera". Bulletins of American Paleontology 364: 560. http://strata.ummp.lsa.umich.edu/jack/showgenera.php?taxon=611&rank=class.
- ↑ Richard van der Laan; William N. Eschmeyer; Ronald Fricke (2014). "Family-group names of Recent fishes". Zootaxa 3882 (2): 001–230. doi:10.11646/zootaxa.3882.1.1. PMID 25543675. https://biotaxa.org/Zootaxa/article/view/zootaxa.3882.1.1/10480.
- ↑ 3.0 3.1 Froese, Rainer, and Daniel Pauly, eds. (2015). "Leiognathidae" in FishBase. February 2015 version.
- ↑ Johnson, G.D.; Gill, A.C. (1998). Paxton, J.R.. ed. Encyclopedia of Fishes. San Diego: Academic Press. p. 186. ISBN 978-0-12-547665-2.
- ↑ 5.0 5.1 Haneda, Y.; Tsuji, F.I. (1976). "Luminescent systems of pony fishes". Journal of Morphology 150 (2): 539–552. doi:10.1002/jmor.1976.150.2.539.
- ↑ 6.0 6.1 McFall-Ngai, M.J.; Dunlap, P.V. (1984). "External and internal sexual dimorphism in leiognathid fishes: Morphological evidence for sex-specific bioluminescent signaling" (in en). Journal of Morphology 182 (1): 71–83. doi:10.1002/jmor.1051820105. ISSN 1097-4687. PMID 6492170.
- ↑ Kaeding, A.J.; Ast, J.C.; Pearce, M.M.; Urbanczyk, H.; Kimura, S.; Endo, H.; Nakamura, M.; Dunlap, P.V. (2007). "Phylogenetic Diversity and Cosymbiosis in the Bioluminescent Symbioses of "Photobacterium mandapamensis"" (in en). Applied and Environmental Microbiology 73 (10): 3173–3182. doi:10.1128/AEM.02212-06. ISSN 0099-2240. PMID 17369329. Bibcode: 2007ApEnM..73.3173K.
- ↑ Hastings, J.W. (1971). "Light to Hide by: Ventral Luminescence to Camouflage the Silhouette" (in en). Science 173 (4001): 1016–1017. doi:10.1126/science.173.4001.1016. ISSN 0036-8075. PMID 17796582. Bibcode: 1971Sci...173.1016W.
- ↑ McFall-Ngai, M.J.; Morin, J.G. (1991). "Camouflage by Disruptive Illumination in Leiognathids, a Family of Shallow-Water, Bioluminescent Fishes" (in en). Journal of Experimental Biology 156 (1): 119–137. doi:10.1242/jeb.156.1.119. ISSN 0022-0949. http://jeb.biologists.org/content/156/1/119.
- ↑ 10.0 10.1 Sparks, J.S.; Dunlap, P.V.; Smith, W.L. (2005). "Evolution and diversification of a sexually dimorphic luminescent system in ponyfishes (Teleostei: Leiognathidae), including diagnoses for two new genera" (in en). Cladistics 21 (4): 305–327. doi:10.1111/j.1096-0031.2005.00067.x. ISSN 1096-0031. PMID 34892969. https://deepblue.lib.umich.edu/bitstream/2027.42/72092/1/j.1096-0031.2005.00067.x.pdf.
- ↑ 11.0 11.1 Chakrabarty, P.; Davis, M.P.; Smith, W.L.; Berquist, R.; Gledhill, K.M.; Frank, L.R.; Sparks, J.S. (2011). "Evolution of the light organ system in ponyfishes (Teleostei: Leiognathidae)" (in en). Journal of Morphology 272 (6): 704–721. doi:10.1002/jmor.10941. ISSN 1097-4687. PMID 21433053.
- ↑ J. S. Nelson; T. C. Grande; M. V. H. Wilson (2016). Fishes of the World (5th ed.). Wiley. pp. 453. ISBN 978-1-118-34233-6. https://sites.google.com/site/fotw5th/.
- ↑ R. Betancur-Rodriguez; E. Wiley; N. Bailly; A. Acero; M. Miya; G. Lecointre; G. Ortí (2017). "Phylogenetic Classification of Bony Fishes – Version 4". BMC Evolutionary Biology 17 (162): 162. doi:10.1186/s12862-017-0958-3. PMID 28683774.
- ↑ Eschmeyer, William N.; Fricke, Ron; van der Laan, Richard, eds. "Genera in the family Leiognathidae". California Academy of Sciences. http://researcharchive.calacademy.org/research/ichthyology/catalog/fishcatget.asp?tbl=genus&family=Leiognathidae.
- ↑ Sparks, J.S.; Chakrabarty, P. (2015). "Description of a new genus of ponyfishes (Teleostei: Leiognathidae), with a review of the current generic-level composition of the family". Zootaxa 3947 (2): 181–190. doi:10.11646/zootaxa.3947.2.2. PMID 25947728.
Wikidata ☰ Q634284 entry
 |

