Biology:Monorhaphis
| Monorhaphididae chuni | |
|---|---|
| |
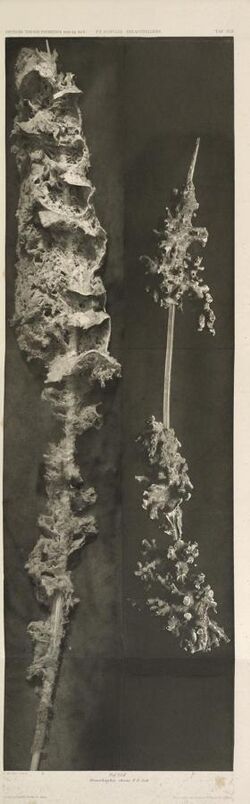
| Two black and white photographs of M. chuni | |
| Scientific classification | |
| Domain: | Eukaryota |
| Kingdom: | Animalia |
| Phylum: | Porifera |
| Class: | Hexactinellida |
| Order: | Amphidiscosida |
| Family: | Monorhaphididae Iijima, 1927 |
| Genus: | Monorhaphis Schulze, 1904 |
| Species: | M. chuni
|
| Binomial name | |
| Monorhaphis chuni Schulze, 1904
| |
| Synonyms[1] | |
|
Species synonymy
| |
Monorhaphis is a monotypic genus of siliceous deep sea Hexactinellid sponges. The single species is the type species Monorhaphis chuni, a sponge known for creating a single giant basal spicule (G.B.S.) to anchor the sponge in the sediments. The species was described by Franz Eilhard Schulze in 1904 from specimens collected by the German Deep Sea Expedition in 1898–1899.[2] Monorhaphis is also the only genus in the monotypic family Monorhaphididae.
One study provides substantial evidence that an individual of this deep-sea sponge, that forms giant spicules up to 3 meters long, is about 11,000 years old.[3]
Five other individuals collected from depths of 1,100 to 2,100 meters at three widely separated locations in the western Pacific Ocean were estimated to be 6,000 to 18,000 (±1,000) years old and grew radially at about 140 μm per 1,000 years.[4] The samples were shown to record deep ocean silica geochemistry throughout their lives.
References
- ↑ "Monorhaphis chuni Schulze, 1904". World Porifera database. World Register of Marine Species. http://www.marinespecies.org/aphia.php?p=taxdetails&id=171556.
- ↑ Xiaohong, Wang; Schröder; Müller, E.G. (2009). "Giant Siliceous Spicules from the Deep-sea Glass Sponge Monorhaphis chuni". in Jeon, Kwang W.. International Review of Cell and Molecular Biology, Vol. 273. London: Academic. pp. 69–115. ISBN 978-0-12-374804-1.
- ↑ Jochum KP, Wang X, Vennemann TW, Sinha B, Müller WEG. Silieous deep-sea sponge Monorhaphis chuni: A potential paleoclimate archive in ancient animals. Chem Geol. 2010;300–301:143–151.
- ↑ Jochum, KP; Schuessler, JA; Wang, XH (2017). "Whole‐Ocean Changes in Silica and Ge/Si Ratios During the Last Deglacial Deduced From Long‐Lived Giant Glass Sponges". Geophysical Research Letters 44 (22): 11,555-11,564. doi:10.1002/2017GL073897. Bibcode: 2017GeoRL..4411555J. http://gfzpublic.gfz-potsdam.de/pubman/item/escidoc:2797894.
Wikidata ☰ {{{from}}} entry
 |


