Biology:Phosphonopyruvate decarboxylase
From HandWiki
| Phosphonopyruvate decarboxylase | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
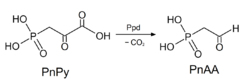 A reaction using Ppd as a catalyst | |||||||||
| Identifiers | |||||||||
| EC number | 4.1.1.82 | ||||||||
| Databases | |||||||||
| IntEnz | IntEnz view | ||||||||
| BRENDA | BRENDA entry | ||||||||
| ExPASy | NiceZyme view | ||||||||
| KEGG | KEGG entry | ||||||||
| MetaCyc | metabolic pathway | ||||||||
| PRIAM | profile | ||||||||
| PDB structures | RCSB PDB PDBe PDBsum | ||||||||
| |||||||||
The enzyme phosphonopyruvate decarboxylase (EC 4.1.1.82) catalyzes the chemical reaction
- 3-phosphonopyruvate [math]\displaystyle{ \rightleftharpoons }[/math] 2-phosphonoacetaldehyde + CO2
This enzyme belongs to the family of lyases, specifically the carboxy-lyases, which cleave carbon-carbon bonds. The systematic name of this enzyme class is 3-phosphonopyruvate carboxy-lyase (2-phosphonoacetaldehyde-forming). This enzyme is also called 3-phosphonopyruvate carboxy-lyase. This enzyme participates in aminophosphonate metabolism.
References
- "The phosphonopyruvate decarboxylase from Bacteroides fragilis". J. Biol. Chem. 278 (42): 41302–8. 2003. doi:10.1074/jbc.M305976200. PMID 12904299.
- "Interaction of inhibitors with phosphoenolpyruvate mutase: implications for the reaction mechanism and the nature of the active site". Biochemistry 33 (18): 5641–6. 1994. doi:10.1021/bi00184a037. PMID 8180189.
- "Studies on the biosynthesis of bialaphos. Biochemical mechanism of C-P bond formation: discovery of phosphonopyruvate decarboxylase which catalyzes the formation of phosphonoacetaldehyde from phosphonopyruvate". J. Antibiot. (Tokyo) 50 (3): 212–9. March 1997. doi:10.7164/antibiotics.50.212. PMID 9127192.
 |

