Biology:Ornithine decarboxylase
| Ornithine decarboxylase | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
 Ornithine decarboxylase dimer, Human | |||||||||
| Identifiers | |||||||||
| EC number | 4.1.1.17 | ||||||||
| CAS number | 9024-60-6 | ||||||||
| Databases | |||||||||
| IntEnz | IntEnz view | ||||||||
| BRENDA | BRENDA entry | ||||||||
| ExPASy | NiceZyme view | ||||||||
| KEGG | KEGG entry | ||||||||
| MetaCyc | metabolic pathway | ||||||||
| PRIAM | profile | ||||||||
| PDB structures | RCSB PDB PDBe PDBsum | ||||||||
| Gene Ontology | AmiGO / QuickGO | ||||||||
| |||||||||
| ornithine decarboxylase | |
|---|---|
| Identifiers | |
| Symbol | ODC1 |
| NCBI gene | 4953 |
| HGNC | 8109 |
| OMIM | 165640 |
| RefSeq | NM_002539 |
| UniProt | P11926 |
| Other data | |
| EC number | 4.1.1.17 |
| Locus | Chr. 2 p25 |
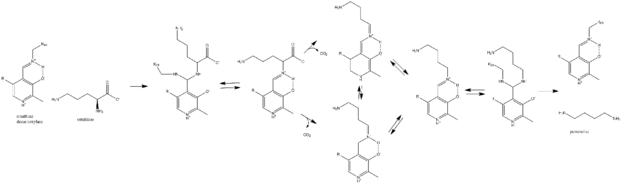
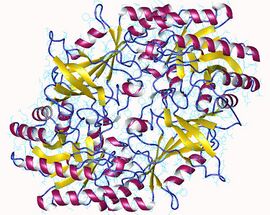
The enzyme ornithine decarboxylase (EC 4.1.1.17, ODC) catalyzes the decarboxylation of ornithine (a product of the urea cycle) to form putrescine. This reaction is the committed step in polyamine synthesis.[1] In humans, this protein has 461 amino acids and forms a homodimer.[2]
In humans, ornithine decarboxylase (ODC) is expressed by the gene ODC1. The protein ODC is sometimes referred to as "ODC1" in research pertaining to humans and mice, but certain species such as Drosophila (dODC2),[3] species of Solanaceae plant family (ODC2),[4] and the lactic acid bacteria Paucilactobacillus wasatchensis (odc2)[5] have been shown to have a second ODC gene.
Reaction mechanism
Lysine 69 on ornithine decarboxylase (ODC) binds the cofactor pyridoxal phosphate to form a Schiff base.[6] Ornithine displaces the lysine to form a Schiff base attached to orthonine, which decarboxylates to form a quinoid intermediate. This intermediate rearranges to form a Schiff base attached to putrescine, which is attacked by lysine to release putrescine product and reform PLP-bound ODC.[7] This is the first step and the rate-limiting step in humans for the production of polyamines, compounds required for cell division.
Spermidine synthase can then catalyze the conversion of putrescine to spermidine by the attachment of an aminopropyl moiety.[8] Spermidine is a precursor to other polyamines, such as spermine and its structural isomer thermospermine.
Structure
270px|thumb|right|3D crystal structure of ornithine decarboxylase.[9]
The active form of ornithine decarboxylase is a homodimer. Each monomer contains a barrel domain, consisting of an alpha-beta barrel, and a sheet domain, composed of two beta-sheets. The domains are connected by loops. The monomers connect to each other via interactions between the barrel of one monomer and the sheet of the other. Binding between monomers is relatively weak, and ODC interconverts rapidly between monomeric and dimeric forms in the cell.[1]
The pyridoxal phosphate cofactor binds lysine 69 at the C-terminus end of the barrel domain. The active site is at the interface of the two domains, in a cavity formed by loops from both monomers.[1]
Function
The ornithine decarboxylation reaction catalyzed by ornithine decarboxylase is the first and committed step in the synthesis of polyamines, particularly putrescine, spermidine and spermine. Polyamines are important for stabilizing DNA structure, the DNA double strand-break repair pathway and as antioxidants. Therefore, ornithine decarboxylase is an essential enzyme for cell growth, producing the polyamines necessary to stabilize newly synthesized DNA. Lack of ODC causes cell apoptosis in embryonic mice, induced by DNA damage.[10]
Proteasomal degradation
ODC is the most well-characterized cellular protein subject to ubiquitin-independent proteasomal degradation. Although most proteins must first be tagged with multiple ubiquitin molecules before they are bound and degraded by the proteasome, ODC degradation is instead mediated by several recognition sites on the protein and its accessory factor antizyme. The ODC degradation process is regulated in a negative feedback loop by its reaction products.[11]
Until a report by Sheaff et al. (2000),[12] which demonstrated that the cyclin-dependent kinase (Cdk) inhibitor p21Cip1 is also degraded by the proteasome in a ubiquitin-independent manner, ODC was the only clear example of ubiquitin-independent proteasomal degradation.[13]
Clinical significance
ODC is a transcriptional target of the oncogene Myc[14] and is upregulated in a wide variety of cancers. The polyamine products of the pathway initialized by ODC are associated with increased cell growth and reduced apoptosis.[15] Ultraviolet light,[16] asbestos[17] and androgens released by the prostate gland[18] are all known to induce increased ODC activity associated with cancer. Inhibitors of ODC such as eflornithine have been shown to effectively reduce cancers in animal models,[19] and drugs targeting ODC are being tested for potential clinical use. The mechanism by which ODC promotes carcinogenesis is complex and not entirely known. Along with their direct effect on DNA stability, polyamines also upregulate gap junction genes[20] and downregulate tight junction genes. Gap junction genes are involved in communication between carcinogenic cells and tight junction genes act as tumor suppressors.[15]
Mutations of the ODC1 gene have been shown to cause Bachmann-Bupp syndrome (BABS), a rare neurometabolic disorder characterized by global developmental delay, alopecia, macrocephaly, dysmorphic features, and behavioral abnormalities.[21] BABS is typically caused by an autosomal dominant de novo ODC1 variant.[21]
ODC gene expression is induced by a large number of biological stimuli including seizure activity in the brain.[22] Inactivation of ODC by difluoromethylornithine (DMFO, eflornithine) is used to treat cancer and facial hair growth in postmenopausal females.
ODC is also an enzyme indispensable to parasites like Trypanosoma, Giardia, and Plasmodium, a fact exploited by the drug eflornithine.[23]
Immunological significance
In antigen-activated T cells, ODC enzymatic activity increases after activation, which corresponds with increase in polyamine synthesis in T cells after activation.[24] As with ODC and cancer, MYC, also referred to as c-Myc for cellular Myc, is the master regulator of polyamine biosynthesis in T cells.[25]
A 2020 study by Wu et al. using T-cell specific ODC cKO mice showed that T cells can function and proliferate normally in vivo and other polyamine synthesis pathways can compensate for lack of ODC.[26] However, blocking polyamine synthesis via ODC with DMFO and polyamine uptake with AMXT 1501 depleted the polyamine pool and inhibited T-cell proliferation and suppressed T-cell inflammation.[26]
Recent studies have shown the importance of ODC and polyamine synthesis in T helper cell fate commitment.[27] A 2021 study by Puleston et al. showed that TH1 and TH2 cells express higher levels of ODC than regulatory T (Treg) cells and TH17 cells, which corresponded to higher levels of polyamine biosynthesis in TH1 and TH2.[28] A 2021 study by Wagner et al. showed a promotion of a Treg program in Odc1-/- mice.[29] They concluded that polyamine-related enzyme expression was enhanced in pathogenic TH17 and suppressed in Treg cells.[29]
References
- ↑ 1.0 1.1 1.2 "Structure of mammalian ornithine decarboxylase at 1.6 A resolution: stereochemical implications of PLP-dependent amino acid decarboxylases". Structure 7 (5): 567–581. May 1999. doi:10.1016/S0969-2126(99)80073-2. PMID 10378276.
- ↑ "Regulation of ornithine decarboxylase". The Journal of Biological Chemistry 281 (21): 14529–14532. May 2006. doi:10.1074/jbc.R500031200. PMID 16459331.
- ↑ "Isolation and characterization of the Drosophila ornithine decarboxylase locus: evidence for the presence of two transcribed ODC genes in the Drosophila genome". DNA and Cell Biology 12 (6): 499–508. 1993. doi:10.1089/dna.1993.12.499. PMID 8329117.
- ↑ "Ornithine decarboxylase genes contribute to S-RNase-independent pollen rejection". Plant Physiology 186 (1): 452–468. May 2021. doi:10.1093/plphys/kiab062. PMID 33576789.
- ↑ "Production of Putrescine and Cadaverine by Paucilactobacillus wasatchensis". Frontiers in Microbiology 13: 842403. 2022-03-03. doi:10.3389/fmicb.2022.842403. PMID 35308356.
- ↑ "Mechanism of formation of the internal aldimine in pyridoxal 5'-phosphate-dependent enzymes". Journal of the American Chemical Society 133 (39): 15496–15505. October 2011. doi:10.1021/ja204229m. PMID 21854048.
- ↑ "Characterization of the reaction mechanism for Trypanosoma brucei ornithine decarboxylase by multiwavelength stopped-flow spectroscopy". Biochemistry 36 (49): 15147–15155. December 1997. doi:10.1021/bi971652b. PMID 9398243.
- ↑ "Analysis of polyamines as markers of (patho)physiological conditions". Journal of Chromatography. B, Analytical Technologies in the Biomedical and Life Sciences 781 (1–2): 107–149. December 2002. doi:10.1016/S1570-0232(02)00669-4. PMID 12450656.
- ↑ PDB: 1d7k; "Crystal structure of human ornithine decarboxylase at 2.1 A resolution: structural insights to antizyme binding". Journal of Molecular Biology 295 (1): 7–16. January 2000. doi:10.1006/jmbi.1999.3331. PMID 10623504.; rendered via PyMOL.
- ↑ "The ornithine decarboxylase gene is essential for cell survival during early murine development". Molecular and Cellular Biology 21 (19): 6549–6558. October 2001. doi:10.1128/MCB.21.19.6549-6558.2001. PMID 11533243.
- ↑ "Determinants of proteasome recognition of ornithine decarboxylase, a ubiquitin-independent substrate". The EMBO Journal 22 (7): 1488–1496. April 2003. doi:10.1093/emboj/cdg158. PMID 12660156.
- ↑ "Proteasomal turnover of p21Cip1 does not require p21Cip1 ubiquitination". Molecular Cell 5 (2): 403–410. February 2000. doi:10.1016/S1097-2765(00)80435-9. PMID 10882081.
- ↑ "A proteasome howdunit: the case of the missing signal". Cell 101 (4): 341–344. May 2000. doi:10.1016/S0092-8674(00)80843-0. PMID 10830160.
- ↑ "The ornithine decarboxylase gene is a transcriptional target of c-Myc". Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America 90 (16): 7804–7808. August 1993. doi:10.1073/pnas.90.16.7804. PMID 8356088. Bibcode: 1993PNAS...90.7804B.
- ↑ 15.0 15.1 "Polyamines and cancer: old molecules, new understanding". Nature Reviews. Cancer 4 (10): 781–792. October 2004. doi:10.1038/nrc1454. PMID 15510159. https://www.escholarship.org/uc/item/1sc3c2gj.
- ↑ "A definitive role of ornithine decarboxylase in photocarcinogenesis". The American Journal of Pathology 159 (3): 885–892. September 2001. doi:10.1016/S0002-9440(10)61764-6. PMID 11549581.
- ↑ "Role of asbestos and active oxygen species in activation and expression of ornithine decarboxylase in hamster tracheal epithelial cells". Cancer Research 51 (1): 167–173. January 1991. PMID 1846307.
- ↑ "Comparison of androgen regulation of ornithine decarboxylase and S-adenosylmethionine decarboxylase gene expression in rodent kidney and accessory sex organs". Endocrinology 130 (3): 1131–1144. March 1992. doi:10.1210/endo.130.3.1537280. PMID 1537280.
- ↑ "Development of difluoromethylornithine (DFMO) as a chemoprevention agent". Clinical Cancer Research 5 (5): 945–951. May 1999. PMID 10353725.
- ↑ "Polyamines regulate gap junction communication in connexin 43-expressing cells". The Biochemical Journal 357 (Pt 2): 489–495. July 2001. doi:10.1042/0264-6021:3570489. PMID 11439099.
- ↑ 21.0 21.1 "Bachmann-Bupp Syndrome". GeneReviews. Seattle (WA): University of Washington, Seattle. 1993. http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK583220/. Retrieved 2023-06-28.
- ↑ "Ornithine decarboxylase induction and polyamine synthesis in the kindling of seizures: the effect of alpha-difluoromethylornithine". Epilepsy Research 11 (1): 3–7. March 1992. doi:10.1016/0920-1211(92)90015-L. PMID 1563337.
- ↑ "Targeting the polyamine biosynthetic enzymes: a promising approach to therapy of African sleeping sickness, Chagas' disease, and leishmaniasis". Amino Acids 33 (2): 359–366. August 2007. doi:10.1007/s00726-007-0537-9. PMID 17610127.
- ↑ "Role of Polyamines in Immune Cell Functions". Medical Sciences 6 (1): 22. March 2018. doi:10.3390/medsci6010022. PMID 29517999.
- ↑ "c-Myc and cancer metabolism". Clinical Cancer Research 18 (20): 5546–5553. October 2012. doi:10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-12-0977. PMID 23071356.
- ↑ 26.0 26.1 "De novo synthesis and salvage pathway coordinately regulate polyamine homeostasis and determine T cell proliferation and function". Science Advances 6 (51). December 2020. doi:10.1126/sciadv.abc4275. PMID 33328226. Bibcode: 2020SciA....6.4275W.
- ↑ "Polyamine: A metabolic compass for T helper cell fate direction". Cell 184 (16): 4109–4112. August 2021. doi:10.1016/j.cell.2021.07.012. PMID 34358466.
- ↑ "Polyamine metabolism is a central determinant of helper T cell lineage fidelity". Cell 184 (16): 4186–4202.e20. August 2021. doi:10.1016/j.cell.2021.06.007. PMID 34216540.
- ↑ 29.0 29.1 "Metabolic modeling of single Th17 cells reveals regulators of autoimmunity". Cell 184 (16): 4168–4185.e21. August 2021. doi:10.1016/j.cell.2021.05.045. PMID 34216539.
External links
- Ornithine decarboxylase at herkules.oulu.fi
- Ornithine+decarboxylase at the US National Library of Medicine Medical Subject Headings (MeSH)
 |