Biology:Pink-necked green pigeon
| Pink-necked green pigeon | |
|---|---|

| |
| Male in Kent Ridge Park, Singapore | |

| |
| Female in Kent Ridge Park, Singapore | |
| Scientific classification | |
| Domain: | Eukaryota |
| Kingdom: | Animalia |
| Phylum: | Chordata |
| Class: | Aves |
| Order: | Columbiformes |
| Family: | Columbidae |
| Genus: | Treron |
| Species: | T. vernans
|
| Binomial name | |
| Treron vernans (Linnaeus, 1771)
| |
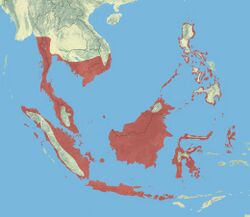
| |
| approximate distribution | |
| Synonyms | |
| |
The pink-necked green pigeon (Treron vernans) is a species of bird of the pigeon and dove family, Columbidae. It is a common species of Southeast Asia, found from Myanmar and Vietnam south through to the major islands of Indonesia and the Philippines (where it is called "punay"). It is a medium-sized pigeon with predominantly green plumage; only the male has the pink neck that gives the species its name. The species lives in a wide range of forested and human-modified habitats and is particularly found in open habitats. Its diet is dominated by fruit, in particular figs. Pairs lay two eggs in a flimsy twig nest in a tree, shrub, or hedge, and work together to incubate the eggs and raise the chicks. The species is thought to be an important disperser of fruit seeds. The species has adapted well to human changes to the environment, and can be found in crowded cities as long as fruiting trees are present.
Taxonomy
Carl Linnaeus described the pink-necked green pigeon as Columba vernans in 1771.[2] Its specific name, vernans, is derived from the Latin word vernantis for "brilliant" or "flourishing".[3] It was later moved to the green pigeon genus Treron. Within that genus the species is most closely related to the similar looking orange-breasted green pigeon of India and Southeast Asia. The species has had up to nine subspecies described, along with the nominate race, but among the important ornithological checklists the International Ornithological Congress' (IOC) Birds of the World, the Howard and Moore Complete Checklist of the Birds of the World and The Clements Checklist of Birds of the World do not accept any described subspecies as valid and all treat the species as monotypic.[4][5][6] Only the Handbook of the Birds of the World's HBW Alive lists any subspecies, with the proviso that the difference between them is in many cases clinal and further research is necessary to determine if any of them are valid.[7]
"Pink-necked green pigeon" has been designated as the official common name for the species by the IOC.[4] It is also known as the pink-necked pigeon.[7]
Description
The pink-necked green pigeon is a medium-sized pigeon, measuring 25 to 30 cm (9.8–11.8 in) in length and weighing around 105–160 g (3.7–5.6 oz). The species has sexually dimorphic plumage. The male has a grey head, pinkish neck and upper breast, and the rest of the breast is orange. The back is olive green and the wings are green with black primaries and yellow edging on the tertiaries which create a yellow bar across the wing in flight. The belly is yellowish with grey flanks, and the tail is grey with a black band at the end, and a chestnut uppertail coverts. The female is smaller overall, has a yellowish belly, throat and face, and greenish crown and back of the neck, although is otherwise similar to the male. The legs are pink or reddish, and the bill is white, pale blue green or grey. Juvenile birds look similar to females but are greyer above.[7]
Pigeons in the genus Treron are unusual in the family for not having cooing calls, instead making whistling and quacking noises,[8] but some cooing notes have been recorded for the pink-necked green pigeon, as the male makes a tri-syballic whistling call ending in a coo.[7] It is also reported to make a rasping krrak krrak... call,[9] but the species is generally held to not be particularly vocal, usually only calling in communal roosts and when it finds food.[7]
Distribution and habitat
The range of the pink-necked green pigeon extends from southern Myanmar, Thailand, Cambodia, and Vietnam south through the Malay Peninsula and across the Greater Sundas (and their surrounding islands), Bali, Lombok, Sumbawa, and as far east as the Moluccas as well as the Philippines. It occupies a variety of habitats, including primary forest, forest edge, secondary forest, and coastal mangroves.[7] It favours more open environments and where it is found in association with denser forest it is typically on the edges.[10] It is also readily found in human dominated environments such as gardens, plantations and farmland. It is more common in lowlands and close to the coast, but can be found up to 300 m (980 ft) in the Philippines,[7] 750 m (2,460 ft) in Borneo[10] and 1,200 m (3,900 ft) in Sulawesi. The species is recorded as non-migratory by the Handbook of the Birds of the World,[7] but other sources have described it as making local movements.[9] A related species, the thick-billed green pigeon, covers vast distances in search of fruit, and it is likely that the pink-necked green pigeon has a similar behaviour.[11]
After the main island of Krakatoa was obliterated in a volcanic eruption in 1883, leaving a handful of smaller islands, the pink-necked pigeon was observed on the first bird survey of these remnants. The survey was conducted in 1908, and at the time the pigeon was the only obligate frugivore (meaning it ate mostly fruit, as opposed to as part of a wider diet or opportunistically) that had established itself on the islands.[11][12] Within the archipelago it was able to colonise Anak Krakatau, a volcano that emerged from the sea from the caldera in 1927, within 36 years of the new island suffering a large eruption in 1952.[13] The delay between the island settling down and colonisation was likely due to the time taken for figs to become established on the island and begin fruiting.[14] It later became extinct on that island, due to a small population and predation.[15] The species has recently expanded its range, having colonised Flores at some time since 2000.[16]
Behaviour
The pink-necked green pigeon is primarily a frugivore, taking a range of fruits, particularly figs (Ficus). Fruit of other trees are taken as well, including Glochidion, Breynia, Vitex, Macaranga, Muntingia, Melastoma,[7] Oncosperma and Bridelia.[12] Shoots, buds and seeds are also taken, but much less commonly so, often by quite a substantial margin. In one study of the frugivores of Sulawesi 55 observations were made of this species feeding and every one was of it eating fruit, mostly figs.[17] The species feeds in the mid-canopy of the forest and rarely feeds in the understory or on the ground. It is described as being agile when clinging on fine branches to reach fruits at the end.[7] Like other members of the genus Treron, the gizzard is muscular and contains grit, which is used to grind and digest seeds inside fruit.[8] Studies of closely related species have found that not every individual has grit, and it is likely the same is true of this species.[11] It is social, feeding in small groups or, where an abundant source of food is found, quite large flocks of up to 70 birds. The species also roosts communally, and can form roosting flocks of hundreds of birds.[7]
There is no defined breeding season and it has been recorded breeding all year across its range. The task of building the nest is divided by sex, with the male being responsible for collecting the nesting material and the female building it. The nest itself is a simple and flimsy platform of twigs and finer material. Two eggs are laid, which are white and measure 26.8 mm–28.9 mm × 20.3 mm–21.8 mm (1.06 in–1.14 in × 0.80 in–0.86 in). The nest is placed in a tree, shrub or hedge, and can be quite close to the ground, ranging from 1 to 10 m (3.3–32.8 ft). The breeding biology of this species is virtually unknown,[7] with only a single breeding report from Singapore. In that report, the pair shared incubation duties, with the male incubating during the day and the female at night, with the incubation time being 17 days. On hatching the chicks are brooded continuously for the first few days of life, as with incubation the male broods during the day and the female at night. Chicks are near-naked and have brown skin with a few white pin feathers on hatching. Chicks leave the nest 10 days after hatching, but remain in the nesting area for a few days after hatching, and continue to be fed by their parents.[18]
Ecology

Like many fruit-eating pigeons, the pink-necked green pigeon is thought to be an important disperser of fruit seeds in forests and woodlands. The grinding gizzard was thought to mean the species was entirely a seed predator instead of a seed disperser but studies of closely related species have shown that not every bird crop contains grinding stones and some seeds could pass through, and the same is likely to be true of this species. The species is thought to be one of those responsible for helping the return of many of the Ficus species to the islands of Krakatoa after the obliteration of the original island in a volcanic eruption. It may not have been responsible for the first shrubby fig species, which may have been carried by generalists such as bulbuls, but once some fruiting figs had established on the island it could have been responsible for both bringing new species of Ficus to the islands and then moving the seeds between the islands. Its flight time to the islands of Krakatoa has been estimated at 48 minutes, far shorter than the estimated seed retention time in its gut of 60 to 480 minutes.[11]
The pink-necked pigeon has been reported being preyed upon by white-bellied sea-eagles, and peregrine falcons have been implicated in the localised extinction of the species on Anak Krakatau.[19]
Status
An adaptable species, T. vernans has fared well with human-made changes to its range. It has readily moved into cities and is common in Singapore's protected areas and even its gardens,[7] and has become more common over time.[20] In spite of suffering some hunting pressure in Thailand, Malaysia and Sumatra,[7] and being targeted by the cage bird trade,[21] it remains common there and across most of its range.[7] Because it is not considered to be in any danger of extinction it has been evaluated as least concern by the IUCN Red List of Threatened Species.[1]
References
- ↑ Jump up to: 1.0 1.1 BirdLife International (2016). "Treron vernans". IUCN Red List of Threatened Species 2016: e.T22691137A93303843. doi:10.2305/IUCN.UK.2016-3.RLTS.T22691137A93303843.en. https://www.iucnredlist.org/species/22691137/93303843. Retrieved 15 November 2021.
- ↑ Jump up to: 2.0 2.1 Linné, Car. A. (1771). "Regni Animalis Appendix. Aves". Mantissa Plantarum Altera. Holmia: Laurentius Salvius. p. 526. https://biodiversitylibrary.org/page/42945634.
- ↑ Jobling, J. A. (2018). "Key to Scientific Names in Ornithology" (in en). Lynx Edicions, Barcelona. https://www.hbw.com/dictionary/key-to-scientific-names-in-ornithology?name=vernans.
- ↑ Jump up to: 4.0 4.1 Gill, Frank; Donsker, David, eds (2019). "Pigeons". World Bird List Version 9.1. International Ornithologists' Union. https://www.worldbirdnames.org/bow/pigeons/.
- ↑ Dickinson, Edward; Christidis, Les (2014). "The Howard and Moore Complete Checklist of the Birds of the World version 4.0 (Downloadable checklist)". https://www.howardandmoore.org.
- ↑ Clements, J; Schulenberg, T; Iliff, M; Roberson, D; Fredericks, T; Sullivan, B; Wood, C (2018). "The eBird/Clements checklist of birds of the world: v2018". http://www.birds.cornell.edu/clementschecklist/download/.
- ↑ Jump up to: 7.00 7.01 7.02 7.03 7.04 7.05 7.06 7.07 7.08 7.09 7.10 7.11 7.12 7.13 7.14 Baptista, L.; Trail, P.; Horblit, H.; Kirwan, G. M.; Garcia, E. (2019). "Pink-necked Green-pigeon (Treron vernans)". in del Hoyo, Josep; Elliott, Andrew; Sargatal, Jordi et al.. Handbook of the Birds of the World Alive. Barcelona: Lynx Edicions. https://www.hbw.com/species/pink-necked-green-pigeon-treron-vernans.
- ↑ Jump up to: 8.0 8.1 Baptista, L.; Trail, P.; Horblit, H. (2019). "Pigeons, Doves (Columbidae)". in del Hoyo, Josep; Elliott, Andrew; Sargatal, Jordi et al.. Handbook of the Birds of the World Alive. Barcelona: Lynx Edicions. https://www.hbw.com/family/pigeons-doves-columbidae.
- ↑ Jump up to: 9.0 9.1 Robson, Craig (2005). Birds of Southeast Asia : Thailand, peninsular Malaysia, Singapore, Vietnam, Cambodia, Laos, Myanmar. Princeton and Oxford: Princeton University Press. p. 80. ISBN 978-0-691-12435-3.
- ↑ Jump up to: 10.0 10.1 Myers, Susan (2009). Birds of Borneo : Brunei, Sabah, Sarawak, and Kalimantan. Princeton and Oxford: Princeton University Press. p. 97. ISBN 978-0-691-14350-7.
- ↑ Jump up to: 11.0 11.1 11.2 11.3 Thornton, Ian W. B.; Compton, Stephen G.; Wilson, Craig N. (1996). "The role of animals in the colonization of the Krakatau Islands by fig trees (Ficus species)". Journal of Biogeography 23 (4): 577–592. doi:10.1111/j.1365-2699.1996.tb00019.x. Bibcode: 1996JBiog..23..577T.
- ↑ Jump up to: 12.0 12.1 Whittaker, Robert J.; Jones, Stephen H. (1994). "The Role of Frugivorous Bats and Birds in the Rebuilding of a Tropical Forest Ecosystem, Krakatau, Indonesia". Journal of Biogeography 21 (3): 245. doi:10.2307/2845528. Bibcode: 1994JBiog..21..245W. https://zenodo.org/record/8205074.
- ↑ Thornton, I. W.; Zann, R. A.; Rawlinson, P. A.; Tidemann, C. R.; Adikerana, A. S.; Widjoya, A. H. (1 January 1988). "Colonization of the Krakatau Islands by vertebrates: equilibrium, succession, and possible delayed extinction.". Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences 85 (2): 515–518. doi:10.1073/pnas.85.2.515. PMID 3422440. Bibcode: 1988PNAS...85..515T.
- ↑ Compton, S. G.; Thornton, I. W. B.; New, T. R.; Underhill, L. (19 December 1988). "The Colonization of the Krakatau Islands by Fig Wasps and Other Chalcids (Hymenoptera, Chalcidoidea)". Philosophical Transactions of the Royal Society B: Biological Sciences 322 (1211): 459–470. doi:10.1098/rstb.1988.0138. Bibcode: 1988RSPTB.322..459C.
- ↑ Thornton, Ian (1994). "Figs, frugivores and falcons: an aspect of the assembly of mixed tropical forest on the emergent volcanic island, Anak Krakatau". South Australian Geographical Journal 93: 3–21.
- ↑ Schellekens, Mark; Trainor, Colin; Encallado, Juan; Imansyah, M Jeri (2009). "Status of the Pied Imperial Pigeon Ducula bicolour and Pink-necked Green-Pigeon Treron vernans on Flores, Nusa Tenggara". Kukila 14: 16–20. https://www.researchgate.net/publication/235688039.
- ↑ Walker, J. S. (2007). "Dietary specialization and fruit availability among frugivorous birds on Sulawesi". Ibis 149 (2): 345–356. doi:10.1111/j.1474-919X.2006.00637.x.
- ↑ Wee, Y. C. (2005). "Forging a closer relationship with Pink-necked Green-pigeons". Nature Watch 13 (3): 16–21. https://www.nss.org.sg/articles/f0766cb6-eForgingaCloserRelationship.pdf.
- ↑ Rawlinson, P; Zann, R; van Balen, S; Thornton, I (1992). "Colonization of the Krakatau Islands by Vertebrates". GeoJournal 28 (2, Krakatau – a Century of Change): 225–231. doi:10.1007/BF00177236.
- ↑ KwekYan, C; SiYang, T; Kurukulasuriya, B; YiFei, C; Rajathurai, L; Lim, H; Tan, H (2012). "Decadal changes in urban bird abundance in Singapore.". Raffles Bulletin of Zoology Supplement 25: 89–196. https://www.researchgate.net/publication/256094237.
- ↑ Shepherd, Chris (2006). "The bird trade in Medan, north Sumatra: an overview". BirdingASIA 5: 16–24. https://www.traffic.org/site/assets/files/5655/bird-trade-medan.pdf.
External links
Wikidata ☰ Q863151 entry
 |



