Chemistry:α-Methylstyrene
From HandWiki
|
| |||
| Names | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| Preferred IUPAC name
(Prop-1-en-2-yl)benzene | |||
| Other names
2-Phenylpropene; 2-Phenylpropylene; 1-Methyl-1-phenylethylene; 1-Methyl-1-phenylethene; 1-Phenyl-1-methylethylene; 1-Phenyl-1-methylethene; (1-Methylethenyl)benzene; β-Phenylpropene; β-Phenylpropylene; α-Methylstyrol; α-Methylvinylbenzene; Isopropenylbenzene
| |||
| Identifiers | |||
3D model (JSmol)
|
|||
| Abbreviations | AMS | ||
| ChEBI | |||
| ChEMBL | |||
| ChemSpider | |||
| EC Number |
| ||
| KEGG | |||
PubChem CID
|
|||
| RTECS number |
| ||
| UNII | |||
| UN number | 2303 | ||
| |||
| |||
| Properties | |||
| C9H10 | |||
| Molar mass | 118.179 g·mol−1 | ||
| Appearance | Colorless liquid | ||
| Density | 0.91 g/cm3 | ||
| Melting point | −24 °C (−11 °F; 249 K) | ||
| Boiling point | 165 to 169 °C (329 to 336 °F; 438 to 442 K) | ||
| Insoluble | |||
| Vapor pressure | 2 mmHg (20 °C)[1] | ||
| -80.1·10−6 cm3/mol | |||
| Hazards | |||
| GHS pictograms |   
| ||
| GHS Signal word | Warning | ||
| H226, H319, H335, H411 | |||
| P210, P233, P240, P241, P242, P243, P261, P264+265Script error: No such module "Preview warning".Category:GHS errors, P271, P273, P280, P303+361+353, P304+340, P305+351+338, P319Script error: No such module "Preview warning".Category:GHS errors, P337+317Script error: No such module "Preview warning".Category:GHS errors, P370+378, P391, P403+233, P403+235, P405, P501 | |||
| NFPA 704 (fire diamond) | |||
| Flash point | 45 °C (113 °F; 318 K) | ||
| Explosive limits | 1.9–6.1%[1] | ||
| Lethal dose or concentration (LD, LC): | |||
LD50 (median dose)
|
4900 mg/kg (oral, rat)[2] | ||
| NIOSH (US health exposure limits): | |||
PEL (Permissible)
|
C 100 ppm (480 mg/m3)[1] | ||
REL (Recommended)
|
TWA 50 ppm (240 mg/m3) ST 100 ppm (485 mg/m3)[1] | ||
IDLH (Immediate danger)
|
700 ppm[1] | ||
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa). | |||
| Infobox references | |||
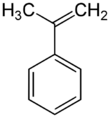
α-Methylstyrene (AMS) is an organic compound with the formula C6H5C(CH3)=CH2. It is a colorless oil.[4]
Synthesis and reactions
AMS is a precursor to plasticizers, resins, and polymers.[5]
AMS and acetophenone are byproducts formed in a variation of the cumene process. It can also be produced by dehydrogenation of cumene.
The homopolymer obtained from this monomer, poly(α-methylstyrene), is unstable, being characterized by a low ceiling temperature of 65 C.[6][7]
Side Effects in Humans
The American Conference of Governmental Industrial Hygienists (2009) defined occupational exposure limits of 10 ppm for airborne concentrations of a-methylstyrene.[8] based on allergic reactions, and effects on the central nervous system.[8][9]
References
- ↑ 1.0 1.1 1.2 1.3 1.4 NIOSH Pocket Guide to Chemical Hazards. "#0429". National Institute for Occupational Safety and Health (NIOSH). https://www.cdc.gov/niosh/npg/npgd0429.html.
- ↑ "alpha-Methyl styrene". Immediately Dangerous to Life and Health Concentrations (IDLH). National Institute for Occupational Safety and Health (NIOSH). https://www.cdc.gov/niosh/idlh/98839.html.
- ↑ "alpha-Methylstyrene" (in en). https://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/compound/7407#section=Safety-and-Hazards.
- ↑ James, Denis H.; Castor, William M. (2007). "Ullmann's Encyclopedia of Industrial Chemistry". Ullmann's Encyclopedia of Industrial Chemistry. Weinheim: Wiley-VCH. doi:10.1002/14356007.a25_329.pub2.
- ↑ "What is alpha-methylstyrene (AMS)?". http://www.sunocochemicals.com/products/alphaf.htm.
- ↑ Stevens, Malcolm P. (1999). "6". Polymer Chemistry an Introduction (3rd ed.). New York: Oxford University Press. pp. 193–194. ISBN 978-0-19-512444-6.
- ↑ Jones, G. R.; Wang, H. S.; Parkatzidis, K.; Whitfield, R.; Truong, N. P.; Anastasaki, A. (2023). "Reversed Controlled Polymerization (RCP): Depolymerization from Well-Defined Polymers to Monomers". Journal of the American Chemical Society 145 (18): 9898–9915. doi:10.1021/jacs.3c00589. PMID 37127289.
- ↑ 8.0 8.1 Morgan, D. L.; Mahler, J. F.; Kirkpatrick, D. T.; Price, H. C.; O'Connor, R. W.; Wilson, R. E.; Moorman, M. P. (February 1999). "Characterization of inhaled alpha-methylstyrene vapor toxicity for B6C3F1 mice and F344 rats". Toxicological Sciences 47 (2): 187–194. doi:10.1093/toxsci/47.2.187. ISSN 1096-6080. PMID 10220856.
- ↑ "α-METHYL STYRENE†". OSHA. https://www.osha.gov/chemicaldata/776.
 |