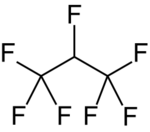
Chemistry:1,1,1,2,3,3,3-Heptafluoropropane
| |
| |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| Preferred IUPAC name
1,1,1,2,3,3,3-Heptafluoropropane | |
| Other names
Heptafluoropropane
Apaflurane HFC-227ea R-227ea HFC-227 FM-200 | |
| Identifiers | |
3D model (JSmol)
|
|
| ChEMBL | |
| ChemSpider | |
| KEGG | |
PubChem CID
|
|
| UNII | |
| UN number | UN3296 |
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| C3HF7 | |
| Molar mass | 170.03 g/mol |
| Density | 1.46 g/cm3 at -16 °C |
| Melting point | −131 °C (−204 °F; 142 K) |
| Boiling point | −16.4 °C (2.5 °F; 256.8 K) |
| Hazards | |
| NFPA 704 (fire diamond) | |
| Related compounds | |
Related compounds
|
1,1,1,2,2,3,3-Heptachloropropane |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa). | |
| Infobox references | |
1,1,1,2,3,3,3-Heptafluoropropane, also called heptafluoropropane, HFC-227ea (ISO name), HFC-227 or FM-200, as well as apaflurane (INN), is a colourless, odourless gaseous halocarbon commonly used as a gaseous fire suppression agent.
Chemistry
Its chemical formula is CF3-CHF-CF3, or C3HF7. With a boiling point of −16.4 °C, it is a gas at room temperature. It is slightly soluble in water (260 mg/L).
Use
HFC-227ea is used in fire suppression systems that protect data processing and telecommunication facilities, and in fire suppression of many flammable liquids and gases. HFC-227ea is categorized as a Clean Agent and is governed by NFPA 2001 - Standard for Clean Agent Fire Extinguishing Systems. Effective fire suppression requires introducing a concentration of the HFC-227ea agent between 6.25% and 9% depending on the hazard being suppressed. Its NOAEL for cardiac sensitization is 9%. The United States Environmental Protection Agency allows concentration of 9% volume in occupied spaces without mandated egress time, or up to 10.5% for a limited time. Most fire suppression systems are designed to provide concentration of 6.25-9%.
The HFC-227ea fire suppression agent was the first non-ozone-depleting replacement for Halon 1301.[citation needed] In addition, HFC-227ea leaves no residue on valuable equipment after discharge.[2]
HFC-227ea contains no chlorine or bromine atoms, presenting no ozone depletion effect. Its atmospheric lifetime is approximated between 31 and 42 years. It leaves no residue or oily deposits and can be removed by ventilation of the affected space.
As an aerosol propellant, HFC-227ea is used in pharmaceutical metered dose inhalers such as those used for dispensing asthma medication.
Safety
At high temperatures, heptafluoropropane will decompose and produce hydrogen fluoride. The decomposition produces a sharp, pungent odour, which can be perceived in concentrations far below a dangerous level. Other decomposition products include carbonyl fluoride, carbon monoxide and carbon dioxide. Prior to re-entry of a room where HFC-227ea system has been activated to suppress a fire, the atmosphere should be tested. An Acid Scavenging Additive added to heptafluoropropane reduces the amount of hydrogen fluoride. Contact with liquid HFC-227ea may cause frostbite.
Climate change considerations
Heptafluoropropane (HFC-227ea) contributes to climate change. It has a global warming potential (GWP) of 3,220 over 100 years.[3]
Due to its high GWP, the HFC-227ea has been included in the list of controlled substances of the Montreal Protocol (2016 Kigali amendment, in effect in January 2019).[4] Under EU regulations, production, imports and sales of HFC-227ea in spray cans such as freeze sprays or dusters have been prohibited since 2014, as the GWP is over the limit of 150 for these applications.[5][6][7]
Tradenames for HFC-227ea used as fire suppression agent
- FE-227 FM-200 (Dupont) (United States Environmental Protection Agency (EPA) SNAP Listed)[8]
- FITECH - 227 (Fitech Engineers)
- Solkaflam 227 (Solvay Fluor)
- MH-227 (Shanghai Waysmos) (United States Environmental Protection Agency (EPA) SNAP Listed)[8]
- Orient 227 (Orient Corporation) (United States Environmental Protection Agency (EPA) SNAP Listed)[8]
- SR-200 (SRI)
- NAF S 227(Safety High Tech)
See also
Other fire suppression agents:
- HFC-125
- ECARO-25
- Argonite
- FE-13
- FK-5-1-12
- Halon 1211
- Halon 1301
- FS49C2
- HFC-236fa
References
- Sinerji Fire Protection Product Page (Archived 2009-04-25)
- ↑ NIST datapage for heptafluoropropane
- ↑ "Fike FE-227 Product Page". http://fire-chief.com/fe227.asp.
- ↑ GOV.UK: Calculate the carbon dioxide equivalent quantity of an F gas. Retrieved on 2018-01-25.
- ↑ Montreal Protocol Section 1.1. including 2016 Kigali amendment.
- ↑ "Regulation (EU) No 517/2014 of the European Parliament and of the Council of 16 April 2014 on fluorinated greenhouse gases and repealing Regulation (EC) No 842/2006 — European Environment Agency" (in en). https://www.eea.europa.eu/policy-documents/regulation-eu-no-517-2014.
- ↑ "EU legislation to control F-gases" (in en). 2016-11-23. https://ec.europa.eu/clima/policies/f-gas/legislation_en.
- ↑ "ILT onderschept illegale spuitbussen in Rotterdamse haven - Nieuwsbericht - Inspectie Leefomgeving en Transport (ILT)" (in nl). Ministry of Infrastructure and Water Management. 2020-08-31. https://www.ilent.nl/actueel/nieuws/2020/08/31/ilt-onderschept-illegale-spuitbussen-in-rotterdamse-haven.
- ↑ 8.0 8.1 8.2 "Substitutes in Total Flooding Agents". United States Environmental Protection Agency. United States government. 20 November 2014. https://www.epa.gov/snap/substitutes-total-flooding-agents.
External links
- MSDS for heptafluoropropane
- MSDS for heptafluoropropane
- MSDS for heptafluoropropane
- SDS for (LUKE 227) heptafluoropropane
- SDS for Chemori 227
 |

