Chemistry:1,2-Diiodoethylene
From HandWiki
| |||
| |||
| Names | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| Preferred IUPAC name
1,2-Diiodoethene | |||
| Other names
1,2-Diiodoethylene
sym-Diiodoethylene | |||
| Identifiers | |||
| |||
3D model (JSmol)
|
|||
| ChemSpider | |||
| EC Number |
| ||
PubChem CID
|
|||
| |||
| |||
| Properties | |||
| C2H2I2 | |||
| Molar mass | 279.847 g/mol | ||
| Melting point | 73.4 °C (164.1 °F; 346.5 K) | ||
| Boiling point | 196 to 197 °C (385 to 387 °F; 469 to 470 K) | ||
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa). | |||
| Infobox references | |||
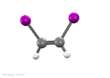
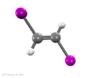
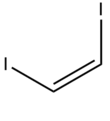
1,2-Diiodoethylene, also known as 1,2-diiodoethene, is an organoiodide with the molecular formula C2H2I2. It can exist as either of two geometric isomers, cis-1,2-diiodoethylene or trans-1,2-diiodoethylene.
E-Z relative stability
Like most cis-trans compounds, the Z isomer (cis) is less stable than the E isomer (trans) by 2 kcal/mol.[citation needed]
See also
References
 |