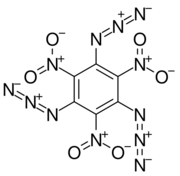
Chemistry:1,3,5-Triazido-2,4,6-trinitrobenzene
| |
| |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| Preferred IUPAC name
1,3,5-Triazido-2,4,6-trinitrobenzene | |
| Identifiers | |
3D model (JSmol)
|
|
| Abbreviations | TATNB |
| ChemSpider | |
| MeSH | C043826 |
PubChem CID
|
|
| UNII | |
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| C6N12O6 | |
| Molar mass | 336.144 g·mol−1 |
| Appearance | yellow crystals[1] |
| Melting point | 131 °C[2] |
| Structure[1] | |
| monoclinic | |
| P21/c, No. 14 | |
| Thermochemistry[1] | |
Std enthalpy of
formation (ΔfH⦵298) |
765.8 kJ/mol |
Std enthalpy of
combustion (ΔcH⦵298) |
3200 kJ/mol |
| Explosive data | |
| Detonation velocity | 7350 m/s |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa). | |
| Infobox references | |
1,3,5-Triazido-2,4,6-trinitrobenzene, also known as TATNB (triazidotrinitrobenzene) and TNTAZB (trinitrotriazidobenzene), is an aromatic high explosive composed of a benzene ring with three azido groups (-N3) and three nitro groups (-NO2) alternating around the ring, giving the chemical formula C6(N3)3(NO2)3. Its detonation velocity is 7,350 meters per second, which is comparable to TATB (triaminotrinitrobenzene).
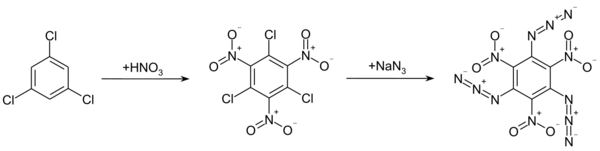
Preparation
The compound was first synthesized in 1924 by Oldřich Turek.[3] It can be prepared by the reaction of 1,3,5-trichloro-2,4,6-trinitrobenzene with sodium azide. 1,3,5-trichloro-2,4,6-trinitrobenzene is obtained from the nitration of 1,3,5-trichlorobenzene with nitric acid and sulfuric acid.[3]
Another route uses the nitration of 1,3,5-triazido-2,4-dinitrobenzene.[1]
Properties
Chemical Properties
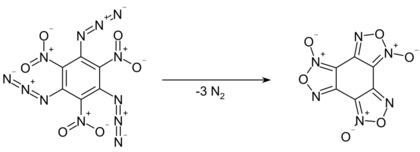
Even at low temperatures, the compound slowly decomposes by giving off nitrogen gas, converting into benzotrifuroxan. This reaction proceeds quantitatively within 14 hours at 100 °C.[3] As a solution in m-xylene, first order kinetics were observed for the decomposition, with a half-life of 340 minutes at 70 °C, 89 minutes at 80 °C, and 900 seconds at 100 °C.[4]
The compound explodes if rapidly heated above 168 °C.[1]
References
- ↑ 1.0 1.1 1.2 1.3 1.4 Adam, David; Karaghiosoff, Konstantin; Klapötke, Thomas M.; Holl, Gerhard; Kaiser, Manfred (2002). "Triazidotrinitro Benzene: 1,3,5-(N3)3-2,4,6-(NO2)3C6". Propellants Explos. Pyrotech. 27 (1): 7–11. doi:10.1002/1521-4087(200203)27:1<7::AID-PREP7>3.0.CO;2-J.
- ↑ Burov, Yu. M.; Nazin, G. M.; Manelis, G. B. (1999). "Retardation of Monomolecular Reactions in the Solid Phase". Russian Chemical Bulletin 48 (7): 1250–1254. doi:10.1007/BF02495284.
- ↑ 3.0 3.1 3.2 Matyáš, Robert; Pachman, Jiří (2013). Primary Explosives. Springer Science & Business Media. pp. 118–121. ISBN 9783642284366.
- ↑ Korsunskii, B. L.; Apina, T. A. (1971). "Kinetics of the Thermal Decomposition of 1,3,5-Triazido-2,4,6-trinitrobenzene in Solution". Bulletin of the Academy of Sciences of the USSR, Division of Chemical Science 20 (9): 1971–1973. doi:10.1007/BF00854439.
 |