Chemistry:1,3-Diphenyltriazene
From HandWiki
| |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| Preferred IUPAC name
(1E)-1,3-Diphenyl-1-triazene | |
| Other names
Diazoaminobenzene
| |
| Identifiers | |
3D model (JSmol)
|
|
| ChEMBL | |
| ChemSpider | |
| EC Number |
|
PubChem CID
|
|
| UNII | |
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| C12H11N3 | |
| Molar mass | 197.241 g·mol−1 |
| Appearance | Pale yellow solid |
| Density | 1.29 g/cm3 |
| Melting point | 95–96[1] °C (203–205 °F; 368–369 K) |
| Boiling point | 180 °C (356 °F; 453 K) decomposes[2] |
| Hazards | |
| GHS pictograms | 
|
| GHS Signal word | Warning |
| H302, H312, H315, H319, H332, H335 | |
| P261, P264, P270, P271, P280, P301+312, P302+352, P304+312, P304+340, P305+351+338, P312, P321, P322, P330, P332+313, P337+313, P362, P363, P403+233, P405, P501 | |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa). | |
| Infobox references | |
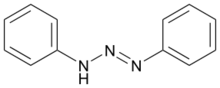
1,3-Diphenyltriazene is the organic compound with the formula PhN=N-N(H)Ph (Ph = C6H5). It is a prototypical triazene, i.e. a compound with the functional group RN=N-NR2. It is a pale yellow solid, prepared by the reaction of phenyldiazonium salts with aniline.[3] It is a planar molecule. The N-N distances are 1.287 and 1.337 Å.[4]
References
- ↑ William B. Smith, Oliver Chenpu Ho (April 1990). "Application of the isoamyl nitrite-diiodomethane route to aryl iodides" (in en). The Journal of Organic Chemistry 55 (8): 2543–2545. doi:10.1021/jo00295a056. ISSN 0022-3263. https://pubs.acs.org/doi/abs/10.1021/jo00295a056. Retrieved 2021-05-27.
- ↑ Shimura, Eiji. Preparation of electrophotographic toners using a foaming agent and an insulating substance. 1988. JP 63050863 A.
- ↑ Hartman, W. W.; Dickey, J. B. (1934). "Diazoaminobenzene". Organic Syntheses 14: 24. doi:10.15227/orgsyn.014.0024.
- ↑ Lego, Christian; Neumüller, Bernhard (2011). "Reaktionen von 1,3-Diphenyltriazenid mit Cu+ und Tl+". Zeitschrift für anorganische und allgemeine Chemie 637 (12): 1784–1789. doi:10.1002/zaac.201100227.
 |

