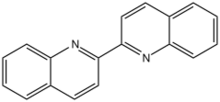
Chemistry:2,2'-Biquinoline
From HandWiki
| |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| Preferred IUPAC name
2,2′-Biquinoline | |
| Other names
2,2′-Biquinolyl; 2-Quinolin-2-ylquinoline; Cuproin
| |
| Identifiers | |
3D model (JSmol)
|
|
| ChemSpider | |
| EC Number |
|
PubChem CID
|
|
| UNII | |
CompTox Dashboard (EPA)
|
|
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| C18H12N2 | |
| Molar mass | 256.308 g·mol−1 |
| Appearance | White solid |
| Density | 1.374 g/cm3[1] |
| Melting point | 194.5 °C (382.1 °F; 467.6 K) |
| Hazards | |
| GHS pictograms | 
|
| GHS Signal word | Warning |
| H315, H319, H335 | |
| P261, P264, P271, P280, P302+352, P304+340, P305+351+338, P312, P321, P332+313, P337+313, P362, P403+233, P405, P501 | |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa). | |
| Infobox references | |
2,2′-Biquinoline is an organic compound with the formula (C9H6N)2. It is one of several biquinolines. It is prepared by reductive coupling of 2-chloroquinoline.[2] It is a colorimetric indicator for organolithium compounds.[3]
Ligand properties
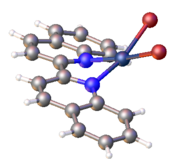
Structure of PdBr2(2,2'-biquinoline).[4]
2,2′-Biquinoline is a bidentate ligand. Unlike the related complexes of 2,2′-bipyridine, the metal does not typically occupy the plane of the biquinoline.
References
- ↑ Folting, K.; Merritt, L. L. (1977). "2,2'-Biquinolyl". Acta Crystallographica Section B 33 (11): 3540–3542. doi:10.1107/S0567740877011406.
- ↑ Nelson, Todd D.; Crouch, R. David (2004). "Cu, Ni, and Pd Mediated Homocoupling Reactions in Biaryl Syntheses: The Ullmann Reaction". Organic Reactions 15: 265–555. doi:10.1002/0471264180.or063.03. ISBN 0471264180.
- ↑ Watson, Spencer Charles; Eastham, Jerome F. (1967). "Colored Indicators for Simple Direct Titration of Magnesium and Lithium Reagents". Journal of Organometallic Chemistry 9: 165–8. doi:10.1016/S0022-328X(00)92418-5.
- ↑ Ha, Kwang (2012). "(2,2′-Biquinoline-κ2-N,N′)dibromidopalladium(II)". Acta Crystallographica Section E 68 (5): m618. doi:10.1107/S1600536812015425. PMID 22590118.
 |

