Chemistry:2,2′-Bipyridine
| |
| |
| |

| |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| Preferred IUPAC name
2,2′-Bipyridine | |
| Other names
Bipyridyl
Dipyridyl Bipy Bpy Dipy | |
| Identifiers | |
3D model (JSmol)
|
|
| 113089 | |
| ChEBI | |
| ChEMBL | |
| ChemSpider | |
| EC Number |
|
| 3720 936807 | |
PubChem CID
|
|
| RTECS number |
|
| UNII | |
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| C10H8N2 | |
| Molar mass | 156.188 g·mol−1 |
| Appearance | Colorless solid |
| Melting point | 70 to 73 °C (158 to 163 °F; 343 to 346 K) |
| Boiling point | 273 °C (523 °F; 546 K) |
| Structure | |
| 0 D | |
| Hazards | |
| Main hazards | toxic |
| GHS pictograms |  
|
| GHS Signal word | Danger |
| H301, H302, H311, H312, H319, H412 | |
| P264, P270, P273, P280, P301+310, P301+312, P302+352, P305+351+338, P312, P321, P322, P330, P337+313, P361, P363, P405, P501 | |
| Lethal dose or concentration (LD, LC): | |
LD50 (median dose)
|
15-78 mg/kg (oral, rat); 20-140 mg/kg (oral, mouse) |
| Related compounds | |
Related compounds
|
4,4′-Bipyridine Pyridine Phenanthroline 3-Pyridylnicotinamide Terpyridine Biphenyl |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa). | |
| Infobox references | |
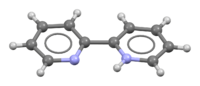
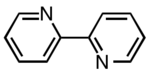
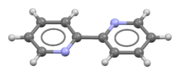
2,2′-Bipyridine (bipy or bpy, pronounced /ˈbɪpiː/) is an organic compound with the formula C10H8N2. This colorless solid is an important isomer of the bipyridine family. It is a bidentate chelating ligand, forming complexes with many transition metals. Ruthenium and platinum complexes of bipy exhibit intense luminescence, which may have practical applications.
Preparation, structure, and general properties
2,2'-Bipyridine was first prepared by decarboxylation of divalent metal derivatives of pyridine-2-carboxylate:[1]
- M(O2CC5H4N)2 → (C5H4N)2 + 2 CO2 + ...
It is prepared by the dehydrogenation of pyridine using Raney nickel:[2]
- 2 C5H5N → (C5H4N)2 + H2
Substituted 2,2'-bipyridines
Unsymmetrically substituted 2,2'-bipyridines can be prepared by cross coupling reaction of 2-pyridyl and substituted pyridyl reagents.[3]
Structure
Although bipyridine is often drawn with its nitrogen atoms in cis conformation, the lowest energy conformation both in solid state and in solution is in fact coplanar, with nitrogen atoms in trans position.[4] Monoprotonated bipyridine adopts a cis conformation.[5]
Reactions
A large number of complexes of 2,2'-bipyridine have been described. It binds metals as a chelating ligand, forming a 5-membered chelate ring.
See also
References
- ↑ Constable; Housecroft (2019). "The Early Years of 2,2'-Bipyridine—A Ligand in its Own Lifetime". Molecules 24 (21): 3951. doi:10.3390/molecules24213951. PMID 31683694.
- ↑ Sasse, W. H. F. (1966). "2,2′-Bipyridine". Organic Syntheses 46: 5. http://www.orgsyn.org/demo.aspx?prep=cv5p0102.; Collective Volume, 5, pp. 102
- ↑ Liu, Tiandong; Fraser, Cassandra L. (2012). "Discussion Addendum for: Synthesis of 4-, 5-, and 6-Methyl-2,2'-bipyridine by a Negishi Cross-Coupling Strategy: 5-Methyl-2,2'-bipyridine". Organic Syntheses 89: 76. doi:10.15227/orgsyn.089.0076.
- ↑ Merritt, L. L.; Schroeder, E. (1956). "The Crystal Structure of 2,2′-Bipyridine". Acta Crystallographica 9 (10): 801–804. doi:10.1107/S0365110X56002175.
- ↑ Göller, A.; Grummt, U.-W. (2000). "Torsional barriers in biphenyl, 2,2′-bipyridine and 2-phenylpyridine". Chemical Physics Letters 321 (5–6): 399–405. doi:10.1016/S0009-2614(00)00352-3. Bibcode: 2000CPL...321..399G.
 |