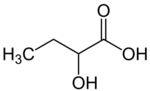
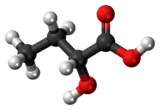
Chemistry:2-Hydroxybutyric acid
| |
| |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| Preferred IUPAC name
2-Hydroxybutanoic acid | |
| Other names
α-Hydroxybutyric acid
| |
| Identifiers | |
3D model (JSmol)
|
|
| ChEBI | |
| ChEMBL | |
| ChemSpider | |
| KEGG | |
| MeSH | 2-hydroxybutyric+acid |
PubChem CID
|
|
| UNII | |
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| C4H8O3 | |
| Molar mass | 104.105 g·mol−1 |
| Related compounds | |
Other anions
|
hydroxybutyrate |
Related carboxylic acids
|
propionic acid lactic acid 3-hydroxypropionic acid malonic acid butyric acid hydroxypentanoic acid |
Related compounds
|
erythrose threose 1,2-butanediol 1,3-butanediol 2,3-butanediol 1,4-butanediol |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa). | |
| Infobox references | |
2-Hydroxybutyric acid, is a hydroxybutyric acid with the hydroxyl group on the carbon adjacent to the carboxyl. It is a chiral compound having two enantiomers, D-2-hydroxybutyric acid and L-2-hydroxybutyric acid. Its conjugate base is known as alpha-hydroxybutyrate and α-hydroxybutyrate.
2-Hydroxybutyrate, the conjugate base of 2-hydroxybutyric acid, is produced in mammalian tissues (principally hepatic) that catabolize L-threonine or synthesize glutathione. Oxidative stress or detoxification demands can dramatically increase the rate of hepatic glutathione synthesis. Under such metabolic stress conditions, supplies of L-cysteine for glutathione synthesis become limiting, so homocysteine is diverted from the transmethylation pathway forming methionine into the transsulfuration pathway forming cystathionine. 2-Hydroxybutyrate is released as a byproduct when cystathionine is cleaved to cysteine that is incorporated into glutathione. Chronic shifts in the rate of glutathione synthesis may be reflected by urinary excretion of 2-hydroxybutyrate.
α-hydroxybutyrate may be useful as an early indicator of insulin resistance in non-diabetic subjects.[1] Moreover, elevated serum α-hydroxybutyrate predicts worsening glucose tolerance.[2]
References
- ↑ "alpha-hydroxybutyrate is an early biomarker of insulin resistance and glucose intolerance in a nondiabetic population". PLOS ONE 5 (5): 10883. 2010. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0010883. PMID 20526369. Bibcode: 2010PLoSO...510883G.
- ↑ "Early metabolic markers of the development of dysglycemia and type 2 diabetes and their physiological significance". Diabetes 62 (5): 1730–1737. 2013. doi:10.2337/db12-0707. PMID 23160532. PMC 3636608. http://diabetes.diabetesjournals.org/content/62/5/1730.long.
 |



