Chemistry:3-Nitroaniline
|
| |||
| Names | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| Preferred IUPAC name
3-Nitroaniline | |||
| Systematic IUPAC name
3-Nitrobenzenamine | |||
| Other names
meta-Nitroaniline
m-Nitroaniline | |||
| Identifiers | |||
3D model (JSmol)
|
|||
| ChEMBL | |||
| ChemSpider | |||
| EC Number |
| ||
PubChem CID
|
|||
| RTECS number |
| ||
| UNII | |||
| UN number | 1661 | ||
CompTox Dashboard (EPA)
|
|||
| |||
| |||
| Properties | |||
| C6H6N2O2 | |||
| Molar mass | 138.126 g·mol−1 | ||
| Appearance | Yellow solid | ||
| Density | 0.9011 | ||
| Melting point | 114 °C (237 °F; 387 K) | ||
| Boiling point | 306 °C (583 °F; 579 K) | ||
| 0.1 g/100 ml (20 °C) | |||
| Acidity (pKa) | 2.47 | ||
| -70.09·10−6 cm3/mol | |||
| Hazards | |||
| GHS pictograms |  
| ||
| GHS Signal word | Danger | ||
| H301, H311, H331, H373, H412 | |||
| P260, P261, P264, P270, P271, P273, P280, P301+310, P302+352, P304+340, P311, P312, P314, P321, P322, P330, P361, P363, P403+233, P405, P501 | |||
| Related compounds | |||
Related compounds
|
2-Nitroaniline, 4-Nitroaniline | ||
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa). | |||
| Infobox references | |||
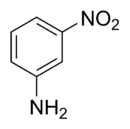
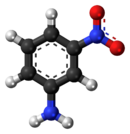
3-Nitroaniline is an organic compound with the formula H2NC6H4NO2. A yellow solid, it is a derivative of aniline, carrying a nitro functional group in position 3. It is an isomer of 2-nitroaniline and 4-nitroaniline. It is used as a precursor to dyes.[1]
Synthesis and applications
3-Nitroaniline is produced on a commercial scale by reduction of 1,3-dinitrobenzene with hydrogen sulfide:[1]
In principle it can also be prepared by nitration of benzamide followed by the Hofmann rearrangement of the resulting 3-nitrobenzamide. The reaction involves treating the 3-nitrobenzamide with sodium hypobromite or sodium hypochlorite to transform the amide group into an amine.
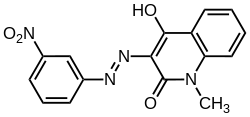
It is used as a chemical intermediate for azo coupling component 17 and the dyes disperse yellow 5 and acid blue 29. The chemical is changed to other substances (dyestuffs and m-nitrophenol) during the dyeing process.
References
- ↑ Jump up to: 1.0 1.1 Gerald Booth (2007). "Ullmann's Encyclopedia of Industrial Chemistry". Ullmann's Encyclopedia of Industrial Chemistry. Weinheim: Wiley-VCH. doi:10.1002/14356007.a17_411.
 |