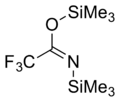
Chemistry:BSTFA
From HandWiki
| |||
| Names | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| IUPAC name
trimethylsilyl 2,2,2-trifluoro-N-trimethylsilylethanimidate
| |||
| Other names
BSTFA, N,O-Bis(trimethylsilyl)trifluoroacetamide
| |||
| Identifiers | |||
3D model (JSmol)
|
|||
| ChEBI | |||
| ChemSpider | |||
PubChem CID
|
|||
| |||
| |||
| Properties | |||
| C8H18F3NOSi2 | |||
| Molar mass | 257.403 g·mol−1 | ||
| Appearance | colourless liquid | ||
| Density | 0.96 | ||
| Melting point | −10 °C (14 °F; 263 K) | ||
| Boiling point | 45–55 °C (113–131 °F; 318–328 K) 14 mm Hg | ||
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa). | |||
| Infobox references | |||
Tracking categories (test):
N,O-Bis(trimethylsilyl)trifluoroacetamide (BSTFA) is an organosilicon compound. It is a colorless liquid that is very sensitive to traces of water or alcohols.
It is often used to convert hydroxyl groups to trimethylsilyl ether groups (Me = CH3):
- ROH + CF
3C(OSiMe
3)NSiMe
3 → CF
3C(O)NH(SiMe
3) + ROSiMe
3
These silylated derivatives are amenable to analysis or further manipulation. Siloxanes are invariably more volatile than their hydroxyl precursors, and thus they can be more easily analyzed with gas chromatography.[1]
This reagent was first reported in 1968.[2]
Related compound
- Bis(trimethylsilyl)acetamide, MeC(OSiMe
3)NSiMe
3
References
- ↑ Ito, Katsuji; Nakayama, Yuki (2001). "N,O-Bis(trimethylsilyl)trifluoroacetamide (BSTFA)". Encyclopedia of Reagents for Organic Synthesis. pp. 1–4. doi:10.1002/047084289X.rn01923. ISBN 9780470842898.
- ↑ Stalling DL, Gehrke CW, Zumwalt RW. A new silylation reagent for amino acids bis(trimethylsilyl)trifluoroacetamide (BSTFA). Biochemical and Biophysical Research Communications. 1968 May 23;31(4):616-22. PMID 5656249
 |