Chemistry:Benexate
From HandWiki
Short description: Chemical compound
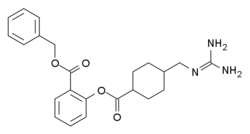 | |
| Clinical data | |
|---|---|
| AHFS/Drugs.com | International Drug Names |
| Routes of administration | Oral |
| ATC code |
|
| Legal status | |
| Legal status |
|
| Identifiers | |
| |
| CAS Number | |
| PubChem CID | |
| ChemSpider | |
| UNII | |
| ChEMBL | |
| Chemical and physical data | |
| Formula | C23H27N3O4 |
| Molar mass | 409.486 g·mol−1 |
| 3D model (JSmol) | |
| |
| |
| | |
Benexate (BEX) is an anti-ulcer agent used in the treatment of acid-related disorders. It is unique in its inability to form salts that are both non-bitter and soluble.[1][2]
Medical uses
Benexate is approved from treatment of gastric ulcer in Japan.[3]
Mechanism of action
The mechanism of action of benexate involves promotion of prostaglandin synthesis, protein secretion, and blood flow stimulation in the gastrointestinal tract.[4]
See also
References
- ↑ "Differential effect of benexate hydrochloride betadex on prostaglandin levels in stomach and inflammatory sites in rats". Japanese Journal of Pharmacology 72 (2): 183–190. 1996. doi:10.1254/jjp.72.183. PMID 8912919.
- ↑ "Studies of benexate CD: effect of inclusion compound formation on the antiulcer activity of benexate, the effective ingredient of benexate CD.". Folia Pharmacologica Japonica (91): 377–383. 1998.
- ↑ "Benexate". Inxight Drugs. National Center for Advancing Translational Sciences. https://drugs.ncats.io/drug/O3PR2X907M.
- ↑ "Benexate hydrochloride betadex modulates nitric oxide synthesis and cytokine expression in gastric ulcers". Experimental and Therapeutic Medicine 12 (2): 573–580. 2016. doi:10.3892/etm.2016.3384. PMID 27446246.
Further reading
- Rui Tamura, Mikiji Miyata, ed (2015). Advances in Organic Crystal Chemistry: Comprehensive Reviews 2015 (1st ed.). Springer Japan. doi:10.1007/978-4-431-55555-1. ISBN 978-4-431-55554-4. https://www.springer.com/gp/book/9784431555544.
 |
