Chemistry:Bis(dimethylamino)methane
From HandWiki
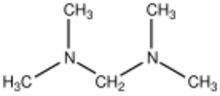
| |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| Other names
N,N,N',N'-tetramethylmethylenediamine
| |
| Identifiers | |
3D model (JSmol)
|
|
| ChemSpider | |
| EC Number |
|
PubChem CID
|
|
| UNII | |
| UN number | 1993 |
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| C5H14N2 | |
| Molar mass | 102.181 g·mol−1 |
| Appearance | colorless liquid |
| Density | 0.749 g/cm3 |
| Melting point | −12 °C (10 °F; 261 K) |
| Boiling point | 85 °C (185 °F; 358 K) |
| Hazards | |
| GHS pictograms |  
|
| GHS Signal word | Danger |
| H225, H314 | |
| P210, P233, P240, P241, P242, P243, P260, P264, P280, P301+330+331, P303+361+353, P304+340, P305+351+338, P310, P321, P363, P370+378, P403+235, P405, P501 | |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa). | |
| Infobox references | |
Bis(dimethylamino)methane is the organic compound with the formula [(CH3)2N]2CH2. It is classified as an aminal as well as a ditertiary amine, in fact the simplest. It is a colorless liquid that is widely available. It is prepared by the reaction of dimethylamine and formaldehyde:[1]
- 2 (CH3)2NH + CH2O → [(CH3)2N]2CH2 + H2O
It is used for the dimethylaminomethylation reactions, the reaction being initiated by the addition of a strong, anhydrous acid:[2]
- [(CH3)2N]2CH2 + H+ → (CH3)2NCH2+ + (CH3)2NH
Related reagents
- N,N,N′,N′-Tetramethylformamidinium chloride
- Eschenmoser's salt is used for similar applications.
References
- ↑ Gaudry, Michel; Jasor, Yves; Khac, Trung Bui (1979). "Regioselective Mannich Condensation with Dimethyl(Methylene)ammonium Trifluoroacetate: 1-(Dimethylamino)-4-methyl-3-pentanone". Org. Synth. 59: 153. doi:10.15227/orgsyn.059.0153.
- ↑ Allen J. Duplantier (2001). "Bis(dimethylamino)methane". EEROS, Encyclopedia of Reagents for Organic Synthesis. doi:10.1002/047084289X.rb143. ISBN 0471936235.
 |

