Chemistry:Bromopyruvic acid
| |
| |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| Preferred IUPAC name
3-Bromo-2-oxopropanoic acid | |
| Other names
Bromopyruvate
3-Bromopyruvic acid 3-Bromopyruvate 3-BrPA 3BP 3-Br-Pyr | |
| Identifiers | |
3D model (JSmol)
|
|
| ChEBI | |
| ChEMBL | |
| ChemSpider | |
| EC Number |
|
PubChem CID
|
|
| UNII | |
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| C3H3BrO3 | |
| Molar mass | 166.958 g·mol−1 |
| Appearance | white solid |
| Melting point | 79 to 82 °C (174 to 180 °F; 352 to 355 K) (hydrate) |
| Hazards | |
| GHS pictograms | 
|
| GHS Signal word | Danger |
| H290, H314 | |
| P260, P264, P280, P301+330+331, P303+361+353, P304+340, P305+351+338, P310, P321, P363, P405, P501 | |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa). | |
| Infobox references | |
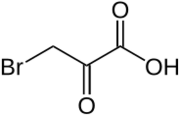
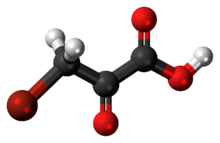
Bromopyruvic acid is the organic compound with the formula BrCH2COCO2H. This colorless solid is the brominated derivative of pyruvic acid. It bears structural similarity to lactic acid and pyruvic acid. It has been investigated as a metabolic poison and an anticancer agent.[1] Like other α-bromoketones, it is a strong alkylating agent.
Research
The pyruvate transporter system can be used to deliver bromopyruvate inside trypanosomal cells. Once intracellular, the primary target of 3BP is glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate dehydrogenase, which is highly sensitive to inhibition by bromopyruvate.[2] The pyruvate transporter system, which is known to be overexpressed in cancer cells, was later identified to be a monocarboxylate transporter called monocarboxylate transporter 1.[3]
References
- ↑ Peter L. Pedersen (2012). "3-Bromopyruvate (3BP) A Fast Acting, Promising, Powerful, Specific, and Effective "Small Molecule" Anti-Cancer Agent Taken from Labside to Bedside: Introduction to a Special Issue". J. Bioenerg. Biomembr. 44 (1): 1–6. doi:10.1007/s10863-012-9425-4. PMID 22382780.
- ↑ Barnard, JP; Reynafarje, B; Pedersen, PL (1993). "Glucose catabolism in African trypanosomes. Evidence that the terminal step is catalyzed by a pyruvate transporter capable of facilitating uptake of toxic analogs". The Journal of Biological Chemistry 268 (5): 3654–3661. doi:10.1016/S0021-9258(18)53743-1. PMID 8429041.
- ↑ Liu, Zhe; Sun, Yiming; Hong, Haiyu; Zhao, Surong; Zou, Xue; Ma, Renqiang; Jiang, Chenchen; Wang, Zhiwei et al. (2015-08-15). "3-bromopyruvate enhanced daunorubicin-induced cytotoxicity involved in monocarboxylate transporter 1 in breast cancer cells". American Journal of Cancer Research 5 (9): 2673–2685. ISSN 2156-6976. PMID 26609475.
External links
- Mathupala, Saroj P.; Ko, Young H.; Pedersen, Peter L. (2010). "The pivotal roles of mitochondria in cancer: Warburg and beyond and encouraging prospects for effective therapies". Biochimica et Biophysica Acta (BBA) - Bioenergetics 1797 (6–7): 1225–1230. doi:10.1016/j.bbabio.2010.03.025. PMID 20381449.
- Mathupala, Saroj P.; Ko, Young H.; Pedersen, Peter L. (2009). "Hexokinase-2 bound to mitochondria: Cancer's stygian link to the "Warburg effect" and a pivotal target for effective therapy". Seminars in Cancer Biology 19 (1): 17–24. doi:10.1016/j.semcancer.2008.11.006. PMID 19101634.
- Ko, Young H.; Smith, Barbara L.; Wang, Yuchuan; Pomper, Martin G.; Rini, David A.; Torbenson, Michael S.; Hullihen, Joanne; Pedersen, Peter L. (2004). "Advanced cancers: Eradication in all cases using 3-bromopyruvate therapy to deplete ATP". Biochemical and Biophysical Research Communications 324 (1): 269–75. doi:10.1016/j.bbrc.2004.09.047. PMID 15465013.
- Mathupala, S P; Ko, Y H; Pedersen, P L (2006). "Hexokinase II: Cancer's double-edged sword acting as both facilitator and gatekeeper of malignancy when bound to mitochondria". Oncogene 25 (34): 4777–86. doi:10.1038/sj.onc.1209603. PMID 16892090.
- The cancer cell's "power plants" as promising therapeutic targets: An overview, by Peter Pederson
 |

