Chemistry:Cyclooctadecanonaene
| |||
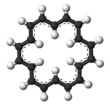
 "Herringbone" crystal structure of [18]annulene
| |||
| Names | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| Preferred IUPAC name
(1Z,3E,5E,7Z,9E,11E,13Z,15E,17E)-Cyclooctadeca-1,3,5,7,9,11,13,15,17-nonaene | |||
| Identifiers | |||
3D model (JSmol)
|
|||
| ChemSpider | |||
PubChem CID
|
|||
| |||
| |||
| Properties | |||
| C18H18 | |||
| Molar mass | 234.3 g·mol−1 | ||
| Appearance | red-brown crystals | ||
| Density | 1.134 g/cm3 (calc.)[1] | ||
| Structure[1] | |||
| monoclinic, P21/a | |||
a = 1.4984 (5) nm, b = 0.4802(2) nm, c = 1.0260(3) nm α = 90°, β = 111.52(1)°, γ = 90°
| |||
Formula units (Z)
|
2 | ||
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa). | |||
| Infobox references | |||
Cyclooctadecanonaene or [18]annulene is an organic compound with chemical formula C18H18. It belongs to the class of highly conjugated compounds known as annulenes and is aromatic. The usual isomer that [18]annulene refers to is the most stable one, containing six interior hydrogens and twelve exterior ones, with the nine formal double bonds in the cis,trans,trans,cis,trans,trans,cis,trans,trans configuration. It is reported to be a red-brown crystalline solid.
Aromaticity
Notably, [18]annulene is the first annulene after benzene ([6]annulene) to be fully aromatic: its π-system contains 4n + 2 electrons (n = 4), and it is large enough to comfortably accommodate six hydrogen atoms in its interior, allowing it to adopt a planar shape, thus satisfying Hückel's rule. The discovery of aromatic stabilization for [18]annulene is historically significant for confirming earlier theoretical predictions based on molecular orbital theory, since simple versions of valence bond theory did not readily explain the 4n + 2 rule.
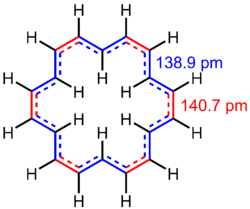
The 1H NMR of this compound exhibits the hallmarks of a system with an aromatic ring current, with the 12H signal of the exterior hydrogens at 9.25 ppm, while the 6H signal of the interior hydrogens resonates at a remarkable −2.9 ppm in THF-d8 at −60 °C. On the other hand, a single signal at 5.45 ppm (the weighted average of the two individual signals) is observed at 120 °C. This is consistent with rapid exchange of the exterior and interior hydrogens at that temperature. The bond lengths in [18]annulene are in between those of single and double carbon–carbon bond, with two bond lengths observed crystallographically: 138.9 pm (concave edges) and 140.7 pm (convex edges). These bond lengths are indicative of significant delocalization. The favorability of delocalization is, in turn, interpreted as evidence for aromaticity. For comparison, these values are close to the bond length of benzene (140 pm).[2]
Based on the enthalpy of hydrogenation, the overall resonance energy has been estimated to be 37 kcal/mol.[3] This is about the same as that of benzene; however, this energy is spread out over 18 atoms instead of 6, so [18]annulene experiences a weaker stabilization than benzene. In terms of reactivity, it is somewhat more air- and light-stable than [14]annulene and [10]annulene, which are, respectively, weakly aromatic and nonaromatic due to transannular interactions. Nevertheless, it rapidly undergoes electrophilic additions, much like other polyenes, and attempts to effect Friedel-Crafts-type reactions on [18]annulene failed.[4]
Despite the usual interpretation of [18]annulene as an 18-electron aromatic system, a 2014 theoretical study suggested that [18]annulene may be thought of as having only three completely delocalized π bonds associated with its aromaticity, while the other six π bonds represent conjugated three-center-two-electron ("3c-2e") π bonds on the periphery of the molecule.[5]
Synthesis
The compound was first synthesised by Franz Sondheimer.[6] The original synthesis started by the Eglinton reaction of the di-alkyne 1,5-hexadiyne with copper(II) acetate in pyridine to give the trimer, followed by deprotonation and isomerization with potassium tert-butoxide in tert-butanol and was concluded with hydrogen organic reduction with the Lindlar catalyst.[7]
See also
- Superbenzene
References
- ↑ 1.0 1.1 Gorter, S.; Rutten-Keulemans, E.; Krever, M.; Romers, C.; Cruickshank, D. W. J. (1995). "[18]-Annulene, C18H18, structure, disorder and Hückel's 4 n + 2 rule". Acta Crystallographica Section B Structural Science 51 (6): 1036–1045. doi:10.1107/S0108768195004927. Bibcode: 1995AcCrB..51.1036G.
- ↑ Jux, Norbert; R. Schleyer, Paul v; Majetich, George; Meyer, Karsten; Hampel, Frank; W. Heinemann, Frank; V. Nizovtsev, Alexey; Lungerich, Dominik (2016). "[18]Annulene put into a new perspective" (in en). Chemical Communications 52 (25): 4710–4713. doi:10.1039/C6CC01309K. PMID 26953607.
- ↑ Oth, Jean F. M.; Bünzli, Jean-Claude; De Julien De Zélicourt, Yves (1974-11-06). "The Stabilization Energy of [18] Annulene. A thermochemical determination". Helvetica Chimica Acta 57 (7): 2276–2288. doi:10.1002/hlca.19740570745. ISSN 0018-019X.
- ↑ Sondheimer, F.; Wolovsky, R.; Amiel, Y. (1962). "Unsaturated Macrocyclic Compounds. XXIII. The Synthesis of the Fully Conjugated Macrocyclic Polyenes Cyclooctadecanonaene ([18]Annulene), Cyclotetracosadodecaene ([24]Annulene), and Cyclotriacontapentadecaene ([30]Annulene).". J. Am. Chem. Soc. 68 (2): 274–284. doi:10.1021/ja00861a030.
- ↑ Ivanov, A.; Boldyrev. A (2014). "Deciphering aromaticity in porphyrinoids via adaptive natural density partitioning". Org. Biomol. Chem. 12 (32): 6145–6150. doi:10.1039/C4OB01018C. PMID 25002069.
- ↑ In the literature and some internet references, Sondheimer is sometimes misspelled as Sandheimer.
- ↑ Stöckel, K.; Sondheimer, F. (1988). "[18]Annulene". Organic Syntheses. http://www.orgsyn.org/demo.aspx?prep=cv6p0068.; Collective Volume, 6, pp. 68
 |