Chemistry:Dicarbonyl(acetylacetonato)rhodium(I)
From HandWiki
| |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| Other names
Rhodium acetylacetonate dicarbonyl
| |
| Identifiers | |
3D model (JSmol)
|
|
| ChemSpider | |
PubChem CID
|
|
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| C7H7O4Rh | |
| Molar mass | 258.034 g·mol−1 |
| Appearance | green solid |
| Density | 1.95 g/cm3 |
| Melting point | 155 °C (311 °F; 428 K) |
| Structure[1] | |
| triclinic | |
| P1 | |
a = 6.5189 Å, b = 7.7614 Å, c = 9.205 Å α = 106.04°, β = 91.15°, γ = 100.21° at 20°C
| |
Lattice volume (V)
|
439.3 Å3 |
Formula units (Z)
|
2 |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa). | |
| Infobox references | |
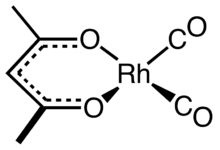
Dicarbonyl(acetylacetonato)rhodium(I) is an organorhodium compound with the formula Rh(O2C5H7)(CO)2. The compound consists of two CO ligands and an acetylacetonate. It is a dark green solid that dissolves in acetone and benzene, giving yellow solutions. The compound is used as a precursor to homogeneous catalysts.[2]
It is prepared by treating rhodium carbonyl chloride with sodium acetylacetonate in the presence of base:[3]
- [(CO)2RhCl]2 + 2 NaO2C5H7 → 2 Rh(O2C5H7)(CO)2 + 2 NaCl
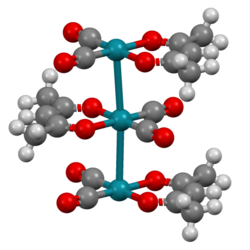
The complex adopts square planar molecular geometry. The molecules stack with Rh---Rh distances of about 326 pm. As such, it is representative of a linear chain compound.[1]
References
- ↑ 1.0 1.1 Huq, Fazlul; Skapski, Andrzej C. (1974). "Refinement of the Crystal Structure of Acetylacetonatodicarbonylrhodium(I)". Journal of Crystal and Molecular Structure 4 (6): 411–418. doi:10.1007/BF01220097.
- ↑ Zacuto, Michael J.; Leighton, James L. (2002). "Dicarbonyl(acetylacetonato) Rhodium(I)". Encyclopedia of Reagents for Organic Synthesis. doi:10.1002/047084289X.rn00024. ISBN 0471936235.
- ↑ Bonati, F.; Wilkinson, G. (1964). "Dicarbonyl-β-diketonato- and Related Complexes of Rhodium(I)". J. Chem. Soc.: 3156–3160. doi:10.1039/JR9640003156.
 |