Chemistry:Rhodium(III) chloride
| |

| |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| Other names
Rhodium trichloride
| |
| Identifiers | |
| |
3D model (JSmol)
|
|
| ChemSpider | |
| EC Number |
|
PubChem CID
|
|
| RTECS number |
|
| UNII | |
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| RhCl3 | |
| Molar mass | 209.26 g/mol |
| Appearance | dark red solid deliquescent |
| Density | 5.38 g/cm3, solid |
| Melting point | ca. 450 °C (842 °F; 723 K) |
| Boiling point | 717 °C (1,323 °F; 990 K) |
| insoluble | |
| Solubility | soluble in hydroxide and cyanide solutions, also soluble in aqua regia |
| Acidity (pKa) | acidic in solution |
| −-7.5·10−6 cm3/mol | |
| Structure | |
| Monoclinic, mS16 | |
| C12/m1, No. 12 | |
| octahedral | |
| Thermochemistry | |
Std enthalpy of
formation (ΔfH⦵298) |
−234 kJ/mol |
| Hazards | |
| Safety data sheet | ICSC 0746 |
| Flash point | Nonflammable |
| Lethal dose or concentration (LD, LC): | |
LD50 (median dose)
|
>500 mg/kg (rat, oral) 1302 mg/kg (rat, oral)[1] |
| Related compounds | |
Other anions
|
Rhodium(III) fluoride Rhodium(III) bromide Rhodium(III) iodide |
Other cations
|
Cobalt(II) chloride Iridium(III) chloride |
Related compounds
|
Ruthenium(III) chloride Palladium(II) chloride |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa). | |
| Infobox references | |
Rhodium(III) chloride refers to inorganic compounds with the formula RhCl3(H2O)n, where n varies from 0 to 3. These are diamagnetic solids featuring octahedral Rh(III) centres. Depending on the value of n, the material is either a dense brown solid or a soluble reddish salt. The soluble trihydrated (n = 3) salt is widely used to prepare compounds used in homogeneous catalysis, notably for the industrial production of acetic acid and hydroformylation.[2]
Structures
Rhodium trichloride and its various hydrates can be considered the default halides of rhodium. By contrast, its lighter congener cobalt does not form a stable trichloride, mainly being available as cobalt(II) chloride.
Anhydrous rhodium(III) chloride
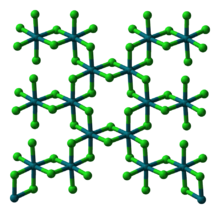
Anhydrous rhodium chloride is a dense red-brown solid. According to X-ray crystallography, tt crystallises in the motif seen also for YCl3 and AlCl3 (see image in upper right). The metal centres are octahedral, and the halides are doubly bridging. The octahedral molecular geometry adopted by RhCl3 is characteristic of most rhodium(III) complexes.[3] The anhydrous material is insoluble in common solvents and, for that reason, of little value in the laboratory.
Hydrates and aqueous solutions
Although hydrated rhodium trichloride is widely marketed and often used, the structure of this red solid has not been elucidated crystallographically. This reddish solid (see picture in box) is often described as RhCl3(H2O)3, but this composition has not been confirmed crystallographically.
Aqueous solutions of "rhodium trichloride hydrate" have been characterized by 103Rh NMR spectroscopy. Several species are detected, the proportions of which change with time and depend on the concentration of chloride. The relative distribution of these species determines the colour of the solutions, which can range from yellow (the hexaaquo ion) to "raspberry-red". Some of these species are the aquo complexes [Rh(H2O)6]3+, [RhCl(H2O)5]2+, cis- and trans-[RhCl2(H2O)4]+, and two isomers of [RhCl3(H2O)3].[4] These species have been separated by ion exchange chromatography and individually characterized by UV-vis spectroscopy.[5]
Preparation
RhCl3(H2O)3 is produced from salts such as Na3RhCl6, the latter being obtained in the purification of rhodium from the other platinum group metals such as platinum and iridium. The trisodium salt is converted to H3RhCl6 by ion exchange chromatography. Recrystallization of this acidic salt from water affords the hydrated trichloride, sometimes called "soluble rhodium trichloride."[6] Anhydrous RhCl3 is prepared by reaction of chlorine with rhodium sponge metal at 200–300 °C.[7] Above 800 °C, the anhydrous chloride reverts to Rh metal and chlorine.[6]
Coordination complexes
Despite the complexity of its solutions, hydrated rhodium trichloride is the precursor to a wide variety of complexes prepared in high yields.These complexes generally arise by substitution reactions , whereby of water and chloride are replaced by more basic ligands as described in the sections below. These reactions are facilitated by the fact that hydrated rhodium trichloride is soluble in a range of polar organic solvents.
Oxygen and nitrogen-based ligands
Evidence for the affinity of rhodium chlorides for oxygen-based ligands is provided by the chloro-aquo complexes discussed above. Rhodium trichloride reacts with acetylacetone to give rhodium acetylacetonate.
Aqueous solutions of rhodium trichloride react with ammonia to give the salt pentamminerhodium chloride, [RhCl(NH3)5]Cl2. As for other metal-ammine complexes, the term "ammine" refers to ammonia bound to a metal ion as a ligand. Zinc reduction of this cation followed by the addition of sulfate gives the colourless hydride complex [HRh(NH3)5]SO4.[8] Some rhodium ammine chlorides are used in the purification of rhodium from its ores.[9]
Upon boiling in a mixture of ethanol and pyridine (py), hydrated rhodium trichloride converts to trans-[RhCl2(py)4)]Cl. In the absence of a reductant, the reaction affords fac-[RhCl3(py)3], analogous to the thioether derivatives.[3] Oxidation of aqueous ethanolic solution of pyridine and RhCl3(H2O)3 by air affords a blue paramagnetic oxygen-bridged compound, [Cl(py)4Rh-O2-Rh(py)4Cl]5+.[10]
Thioethers and tertiary phosphines
Rhodium(III) also forms a range of complexes with soft Lewis bases, such as thioethers, phosphines, and arsines. Such ligands form Rh(III) complexes, but unlike the "hard" N- and O-based ligands, these complexes often can be reduced to Rh(I) derivatives. The reactions are facilitated by the solubility of rhodium trichloride in alcohols, which also dissolve the organic ligands. Thus, ethanolic solutions of hydrated rhodium trichloride react with diethyl sulfide:
- "RhCl
3(H
2O)
3" + 3 S(C
2H
5)
2 → RhCl
3(S(C
2H
5)
2)
3 + 3H
2O
This complex has been used as source of anhydrous rhodium trichloride that is soluble in lipophilic solvents. Both fac and mer stereoisomers of such complexes have been isolated.[3]
Reaction of RhCl3(H2O)3 under mild conditions with tertiary phosphines affords adducts akin to the aforementioned thioether complexes. When these reactions are conducted in boiling ethanol solution, reduction occurs, leading to rhodium(I) derivatives. A famous derivative is [RhCl(PPh3)3] known as Wilkinson's catalyst. Either the ethanol solvent or the phosphine serves as reductant:[11][12]
- "RhCl
3(H
2O)
3" + 3 P(C
6H
5)
3 + CH
3CH
2OH → RhCl(P(C
6H
5)
3)
3 + 3 H
2O + 2 HCl + CH
3CHO - "RhCl
3(H
2O)
3" + 4 P(C
6H
5)
3 → RhCl(P(C
6H
5)
3)
3 + 2 H
2O + 2 HCl + OP(C
6H
5)
3
Alkenes and carbon monoxide
Unlike most other air-stable metal salts, hydrated rhodium trichloride reacts under mild conditions (near room temperature, one atmosphere) with carbon monoxide and many olefins. This behavior opens the doors to extensive inventory of organorhodium compounds. Most of these substrates cause reduction of rhodium(III) to rhodium(I). The resulting Rh(I) complexes engage the carbon-based ligands by pi-backbonding.
Reaction of hydrated rhodium trichloride with olefins affords compounds of the type Rh2Cl2(alkene)4. Specifically, ethylene gives chlorobis(ethylene)rhodium dimer ([(C
2H
4)
2Rh(μ–Cl)]
2). With 1,5-cyclooctadiene, cyclooctadiene rhodium chloride dimer ([(C
8H
12)
2Rh(μ–Cl)]
2) is produced.[13]
When hydrated rhodium trichloride is treated with cyclopentadienes, organometallic half sandwich compounds can be produced. For example, treating hydrated rhodium trichloride with pentamethylcyclopentadiene in hot methanol leads to the precipitation of solid pentamethylcyclopentadienyl rhodium dichloride dimer:[14]
- 2 C
5(CH
3)
5H + 2 "RhCl
3(H
2O)
3" → [(C
5(CH
3)
5)RhCl
2]
2 + 2 HCl + 6 H
2O
A solution of hydrated rhodium trichloride in methanol reacts with carbon monoxide to produce H[RhCl2(CO)2], which contains the dicarbonyldichloridorhodate(I) anion. Further carbonylation in the presence of sodium citrate as a reductant leads to tetrarhodium dodecacarbonyl, Rh4(CO)12, a rhodium(0) cluster compound.[15] Solid RhCl3(H2O)3 reacts with flowing CO gives the volatile compound [(CO)2Rh(μ-Cl)]2.[16]
Numerous Rh-CO-phosphine complexes have been prepared in the course of extensive investigations on hydroformylation catalysis. RhCl(PPh3)3 reacts with CO to give trans-RhCl(CO)(PPh3)2, stoichiometrically analogous to but less nucleophilic than Vaska's complex. trans-RhCl(CO)(PPh3)2 reacts with a mixture of NaBH4 and PPh3 to give HRh(CO)(PPh3)3, a highly active catalyst for the hydroformylation of alkenes.[17]
Catalysis
Beginning especially in the 1960s, RhCl3(H2O)3 was demonstrated to be catalytically active for a variety of reactions involving CO, H2, and alkenes.[18] These compounds are fundamental petrochemical feedstocks, so their manipulation can be consequential. For example, RhCl3(H2O)3 was shown to dimerise ethylene to a mixture of cis and trans 2-butene:
- 2 CH
2=CH
2 → CH
3–CH
2–CH=CH
2
Ethylene dimerization was shown to involve catalysis by the aforementioned ethylene complexes. This and many related discoveries nurtured the then young field of homogeneous catalysis, wherein the catalysts are dissolved in the medium with the substrate. Previous to this era, most metal catalysts were "heterogeneous", i.e. the catalysts were solids and the substrates were either liquid or gases.
Another advance in homogeneous catalysis was the finding that PPh3-derived complexes were active catalytically as well as soluble in organic solvents,[17] The best known such catalyst being Wilkinson's catalyst that catalyzes the hydrogenation and isomerization of alkenes.[18]
The hydroformylation of alkenes is catalyzed by the related RhH(CO)(PPh3)3. Catalysis by rhodium is so efficient that it has significantly displaced the previous technology based on less expensive cobalt catalysts.
Safety
Rhodium(III) chloride is not listed under Annex I of Directive 67/548/EEC, but is usually classified as harmful, R22: Harmful if swallowed. Some Rh compounds have been investigated as anti-cancer drugs. It is listed in the inventory of the Toxic Substances Control Act (TSCA).
References
- ↑ "Rhodium (metal fume and insoluble compounds, as Rh)". Immediately Dangerous to Life and Health Concentrations (IDLH). National Institute for Occupational Safety and Health (NIOSH). https://www.cdc.gov/niosh/idlh/7440166.html.
- ↑ Greenwood, N. N.; Earnshaw, A. (1997). Chemistry of the Elements (2nd ed.). Oxford: Butterworth-Heinemann. ISBN 0-7506-3365-4.
- ↑ 3.0 3.1 3.2 Cotton, Simon A. (1997). Chemistry of the Precious Metals. Chapman & Hall. ISBN 0-7514-0413-6.
- ↑ Carr, Christopher; Glaser, Julius; Sandström, Magnus (1987). "103Rh NMR chemical shifts of all ten [RhCln(OH2)6−n]3−n complexes in aqueous solution". Inorg. Chim. Acta 131 (2): 153–156. doi:10.1016/S0020-1693(00)96016-X.
- ↑ Wolsey, Wayne C.; Reynolds, Charles A.; Kleinberg, Jacob (1963). "Complexes in the Rhodium(III)-Chloride System in Acid Solution". Inorg. Chem. 2 (3): 463–468. doi:10.1021/ic50007a009.
- ↑ 6.0 6.1 Brauer, Georg, ed (1965). "Rhodium(III) Chloride". Handbook of Preparative Inorganic Chemistry. 2 (2nd ed.). New York: Academic Press. pp. 1587–1588. ISBN 9780323161299. https://books.google.com/books?id=Pef47TK5NfkC&pg=PA1587.
- ↑ Renner, Hermann; Schlamp, Günther; Kleinwächter, Ingo; Drost, Ernst; Lüschow, Hans M.; Tews, Peter; Panster, Peter; Diehl, Manfred et al. (2005). Ullmann's Encyclopedia of Industrial Chemistry. Weinheim: Wiley-VCH. doi:10.1002/14356007.a21_075. ISBN 3527306730.
- ↑ Osborn, J. A.; Thomas, K.; Wilkinson, G. (1972). "Pentaamminechlororhodium(III) Dichloride and Pentaamminehydridorhodium(III) Sulfate". Inorganic Syntheses. Inorganic Syntheses. 13. 213–215. doi:10.1002/9780470132449.ch43. ISBN 9780470132449.
- ↑ Benguerel, E.; Demopoulos, G. P.; Harris, G. B. (1996). "Speciation and Separation of Rhodium(III) from Chloride Solutions: A Critical Review". Hydrometallurgy 40 (1–2): 135–152. doi:10.1016/0304-386X(94)00086-I.
- ↑ Gillard, R. D.; Wilkinson, G. (1967). "trans ‐Dichlorotetra(pyridine)Rhodium(III) Salts". Inorganic Syntheses. Inorganic Syntheses. 10. 64–67. doi:10.1002/9780470132418.ch11. ISBN 9780470132418.
- ↑ Osborn, J. A.; Jardine, F. H.; Young, J. F.; Wilkinson, G. (1966). "The Preparation and Properties of Tris(triphenylphosphine)halogenorhodium(I) and Some Reactions Thereof Including Catalytic Homogeneous Hydrogenation of Olefins and Acetylenes and Their Derivatives". J. Chem. Soc. A 1966: 1711–1732. doi:10.1039/J19660001711.
- ↑ Osborn, J. A.; Wilkinson, G. (1967). "Tris(triphenylphosphine)halorhodium(I)". Inorganic Syntheses. Inorganic Syntheses. 10. 67–71. doi:10.1002/9780470132418.ch12. ISBN 9780470132418.
- ↑ Giordano, G.; Crabtree, R. H. (1979). "Di‐μ‐Chloro‐Bis(η 4 ‐1,5‐Cyclooctadlene) Dirhodium(I)". Inorganic Syntheses. Inorganic Syntheses. 28. 88–90. doi:10.1002/9780470132500.ch50. ISBN 9780470132500.
- ↑ White, C.; Yates, A.; Maitlis, Peter M. (2007). "(η5 -Pentamethylcyclopentadienyl)Rhodium and -Iridium Compounds". Inorganic Syntheses. Inorganic Syntheses. 29. 228–234. doi:10.1002/9780470132609.ch53. ISBN 9780470132609.
- ↑ Serp, P. H.; Kalck, P. H.; Feurer, R.; Morancho, R. (2007). "Tri(μ-carbonyl)Nonacarbonyltetrarhodium, Rh4 (μ-CO)3 (CO)9". Inorganic Syntheses. Inorganic Syntheses. 32. 284–287. doi:10.1002/9780470132630.ch45. ISBN 9780470132630.
- ↑ McCleverty, J. A.; Wilkinson, G. (1966). "Dichlorotetracarbonyldirhodium". Inorganic Syntheses. Inorganic Syntheses. 8. 211–214. doi:10.1002/9780470132395.ch56. ISBN 9780470132395.
- ↑ 17.0 17.1 Hartwig, John F. (2010). Organotransition Metal Chemistry: From Bonding to Catalysis. New York: University Science Books. ISBN 978-1-891389-53-5.
- ↑ 18.0 18.1 Bennett, Martin A.; Longstaff, P. A. (1965). "Complexes of Rhodium(I) with Triphenylphosphine". Chem. Ind. (London): 846.
External links
 |


