Chemistry:Dicumyl peroxide
| |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| Other names
DCUP
| |
| Identifiers | |
3D model (JSmol)
|
|
| ChEMBL | |
| ChemSpider | |
| EC Number |
|
PubChem CID
|
|
| RTECS number |
|
| UNII | |
| UN number | 3110 |
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| C18H22O2 | |
| Molar mass | 270.372 g·mol−1 |
| Appearance | colorless solid |
| Density | 1.062 g/cm3 |
| Melting point | 39 °C (102 °F; 312 K) |
| Hazards | |
| GHS pictograms |    
|
| GHS Signal word | Danger |
| H242, H315, H319, H360, H411 | |
| P203Script error: No such module "Preview warning".Category:GHS errors, P210, P234, P240, P264, P264+265Script error: No such module "Preview warning".Category:GHS errors, P273, P280, P302+352, P305+351+338, P318Script error: No such module "Preview warning".Category:GHS errors, P321, P332+317Script error: No such module "Preview warning".Category:GHS errors, P337+317Script error: No such module "Preview warning".Category:GHS errors, P362+364Script error: No such module "Preview warning".Category:GHS errors, P370+378, P391, P403, P405, P410, P411, P420, P501 | |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa). | |
| Infobox references | |
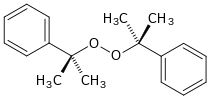
Dicumyl peroxide is an organic compound with the formula (C
6H
5CMe
2O)
2 (Me = CH3). Classified as a dialky peroxide, it is produced on a large scale industrially for use as an initiator for the production of low density polyethylene.
Production
It is synthesized as a by-product in the autoxidation of cumene, which mainly affords cumene hydroperoxide. Alternatively, it can be produced by the addition of hydrogen peroxide to α-methylstyrene.
Of the ca. 60,000 ton/y production of dialkyl peroxides, dicumyl peroxide is dominant.[2]
Properties
Dicumyl peroxide is relatively stable compound owing to the steric protection provided by the several substituents adjacent to the peroxide group. Upon heating, it breaks down by homolysis of the relatively weak O-O bond.
References
- ↑ "Dicumyl peroxide" (in en). https://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/compound/6641#section=Safety-and-Hazards.
- ↑ Klenk, Herbert; Götz, Peter H.; Siegmeier, Rainer; Mayr, Wilfried. "Ullmann's Encyclopedia of Industrial Chemistry". Ullmann's Encyclopedia of Industrial Chemistry. Weinheim: Wiley-VCH. doi:10.1002/14356007.a19_199.pub2.
 |

