Chemistry:Fluorescamine
From HandWiki
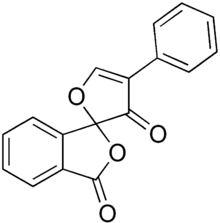
| |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| IUPAC name
4'-phenylspiro[2-benzofuran-3,2'-furan]-1,3'-dione
| |
| Other names
Fluram
| |
| Identifiers | |
3D model (JSmol)
|
|
| ChemSpider | |
| MeSH | D005450 |
PubChem CID
|
|
| UNII | |
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| C17H10O4 | |
| Molar mass | 278.26 g/mol |
| Melting point | 153 to 157 °C (307 to 315 °F; 426 to 430 K) |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa). | |
| Infobox references | |
Fluorescamine is a spiro compound that is not fluorescent itself, but reacts with primary amines to form highly fluorescent products, i.e. it is fluorogenic. It hence has been used as a reagent for the detection of amines and peptides.[2] 1-100 µg of protein and down to 10 pg of protein can be detected.[3][4] Once bound to protein the excitation wavelength is 381 nm (near ultraviolet) and the emission wavelength is 470 nm (blue).[5] This method is found to suffer from high blanks resulting from a high rate of hydrolysis due to requiring a large excess concentration.[6] Alternative methods are based on ortho-phthalaldehyde (OPA), Ellman's reagent (DTNB), or epicocconone.
Reaction
See also
References
- ↑ Fluram at Sigma-Aldrich
- ↑ Doetsch, Paul W.; Cassady, John M.; McLaughlin, Jerry L. (1980). "Cactus alkaloids : XL. Identification of mescaline and other β-phenethylamines in Pereskia, Pereskiopsis and Islaya by use of fluorescamine conjugates". Journal of Chromatography A 189: 79–85. doi:10.1016/S0021-9673(00)82285-2.
- ↑ Böhlen, Peter; Stein, Stanley; Dairman, Wallace; Udenfriend, Sidney (1973). "Fluorometric assay of proteins in the nanogram range". Archives of Biochemistry and Biophysics 155 (1): 213–220. doi:10.1016/S0003-9861(73)80023-2. PMID 4736505.
- ↑ protocol[|permanent dead link|dead link}}] by Fluoprobes
- ↑ Biotium. "Fluorescamine PRODUCT AND SAFETY DATA SHEET". Biotium. https://biotium.com/wp-content/uploads/2017/10/PI-90092.pdf.
- ↑ [1]
 |

