Chemistry:Germanium dibromide
From HandWiki
| |
| Identifiers | |
|---|---|
3D model (JSmol)
|
|
| ChemSpider | |
| EC Number |
|
PubChem CID
|
|
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| Br2Ge | |
| Molar mass | 232.438 g·mol−1 |
| Appearance | white to pale yellow solid[1] |
| Melting point | 120–125 °C[2] 143–144 °C (when heating rapidly)[1] |
| Hazards | |
| GHS pictograms | 
|
| GHS Signal word | Danger |
| H314 | |
| P260, P264, P280, P301+330+331, P302+361+354Script error: No such module "Preview warning".Category:GHS errors, P304+340, P305+354+338Script error: No such module "Preview warning".Category:GHS errors, P316Script error: No such module "Preview warning".Category:GHS errors, P321, P363, P405, P501 | |
| Related compounds | |
Other anions
|
Germanium difluoride Germanium dichloride Germanium diiodide |
Other cations
|
Tin dibromide Lead dibromide |
Related compounds
|
Germanium tetrabromide |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa). | |
| Infobox references | |
Germanium dibromide is a bromide of germanium with the chemical formula GeBr2.
Preparation
Germanium dibromide can be obtained by reducing germanium tetrabromide with germanium or zinc.[4][1]
Properties
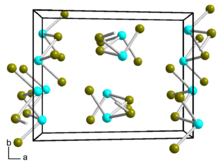
Germanium dibromide is a yellow-white solid that is soluble in ethanol and acetone. It disproportionates into germanium tetrabromide and germanium.[1][5] It hydrolyzes to germanium dihydroxide.[4] Germanium dibromide is monoclinic, space group P21/c (No. 14), lattice parameters a = 11.68 Å, b = 9.12 Å, c = 7.02 Å, and β = 101.9°.[6] It can react with cyclopentadienylsodium or cyclopentadienylthallium in ether solvent to form germanocene.[7]
References
- ↑ 1.0 1.1 1.2 1.3 Georg Brauer (Hrsg.), unter Mitarbeit von Marianne Baudler u. a.: Handbuch der Präparativen Anorganischen Chemie. 3., umgearbeitete Auflage. Band I, Ferdinand Enke, Stuttgart 1975, ISBN 3-432-02328-6, S. 724.
- ↑ Sigma-Aldrich Co., Germanium(II) bromide, 97%.
- ↑ "Germanium(II) bromide" (in en). https://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/compound/6327224#section=Safety-and-Hazards.
- ↑ 4.0 4.1 Holleman, Arnold Frederik; Wiberg, Egon (2001), Wiberg, Nils, ed., Inorganic Chemistry, San Diego/Berlin: Academic Press/De Gruyter, p. 959, ISBN 0-12-352651-5
- ↑ L. M. Dennis (1928-08-02), "Germanium. Zusammenfassung der Untersuchungen im Department of Chemistry, Cornell University, 1921-1927", Zeitschrift fÜr anorganische und allgemeine Chemie 174 (1): 97–141, doi:10.1002/zaac.19281740114
- ↑ Roland C. Rouse, Donald R. Peacor, Bruce R. Maxim (1977-01-01), "The crystal structure of germanium dibromide*", Zeitschrift für Kristallographie - Crystalline Materials 145 (3–4): 161–171, doi:10.1524/zkri.1977.145.3-4.161, ISSN 2194-4946, Bibcode: 1977ZK....145..161R
- ↑ John V. Scibelli, M. David. Curtis (February 1973). "Bis(.pi.-cyclopentadienyl)germanium(II)" (in en). Journal of the American Chemical Society 95 (3): 924–925. doi:10.1021/ja00784a051. ISSN 0002-7863. https://pubs.acs.org/doi/abs/10.1021/ja00784a051. Retrieved 2021-06-10.
 |
