Chemistry:Glycol nucleic acid
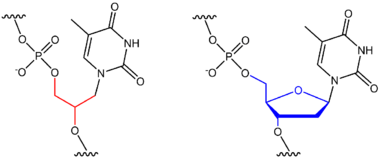
Glycol nucleic acid (GNA), sometimes also referred to as glycerol nucleic acid, is a nucleic acid similar to DNA or RNA but differing in the composition of its sugar-phosphodiester backbone, using propylene glycol in place of ribose or deoxyribose.[1] GNA is chemically stable but not known to occur naturally. However, due to its simplicity, it might have played a role in the evolution of life.
The 2,3-dihydroxypropyl nucleoside analogues were first prepared by Ueda et al. (1971). Soon thereafter it was shown that phosphate-linked oligomers of the analogues do in fact exhibit hypochromicity in the presence of RNA and DNA in solution (Seita et al. 1972). The preparation of the polymers was later described by Cook et al. (1995, 1999) and Acevedo and Andrews (1996). However the ability of GNA-GNA self-pairing was first reported by Zhang and Meggers in 2005.[1] Crystal structures of a GNA duplexes were subsequently reported by Essen and Meggers.[2][3]
DNA and RNA have a deoxyribose and ribose sugar backbone, respectively, whereas GNA's backbone is composed of repeating glycol units linked by phosphodiester bonds. The glycol unit has just three carbon atoms and still shows Watson–Crick base pairing. The Watson–Crick base pairing is much more stable in GNA than its natural counterparts DNA and RNA as it requires a high temperature to melt a duplex of GNA. It is possibly the simplest of the nucleic acids, making it a hypothetical precursor to RNA.
See also
References
- ↑ 1.0 1.1 "A simple glycol nucleic acid". Journal of the American Chemical Society 127 (12): 4174–5. March 2005. doi:10.1021/ja042564z. PMID 15783191. https://pubs.acs.org/doi/10.1021/ja042564z.
- ↑ "Duplex structure of a minimal nucleic acid". Journal of the American Chemical Society 130 (26): 8158–9. July 2008. doi:10.1021/ja802788g. PMID 18529005.
- ↑ "Atomic resolution duplex structure of the simplified nucleic acid GNA". Chemical Communications 46 (7): 1094–6. February 2010. doi:10.1039/B916851F. PMID 20126724. http://xlink.rsc.org/?DOI=B916851F.
Further reading
- "A simple glycol nucleic acid". Journal of the American Chemical Society 127 (12): 4174–5. March 2005. doi:10.1021/ar900292q. PMID 15783191. https://pubs.acs.org/doi/abs/10.1021/ar900292q.
- "Condensation polymerization of nucleotide analogues.". Die Makromolekulare Chemie: Macromolecular Chemistry and Physics 154 (1): 255–61. April 1972. doi:10.1002/macp.1972.021540123.
- "Synthesis of N‐(2, 3‐dihydroxypropyl) derivatives of nucleic bases.". Journal of Heterocyclic Chemistry 8 (5): 827–9. October 1971. doi:10.1002/jhet.5570080527.
- "Synthesis of propane-2, 3-diol combinatorial monomers.". Tetrahedron Letters 37 (23): 3931–4. June 1996. doi:10.1016/0040-4039(96)00745-9.
- Cook PD, Acevedo OL, Davis PW, Ecker DJ, Hebert N, "Synthesis of acyclic oligonucleotides as antiviral and antiinflammatory agents and inhibitors of phospholipase A2.", WO patent 9518820, published 13 July 1995
- Cook PD, Acevedo OL, Davis PW, Ecker DJ, Hebert N, "Preparation of ethylene glycol phosphate linked oligodeoxyribonucleotides as phospholipase A2 inhibitors.", US patent 5886177, issued 23 March 1999, assigned to ISIS Pharmaceuticals Inc.
External links
- Simpler than DNA - Chemical & Engineering News
 |
