Chemistry:Iron(II) fumarate
From HandWiki
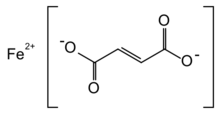
| |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| IUPAC name
Iron(2+) (2E)-but-2-enedioate
| |
| Other names
Ferrous fumarate; Feostat
| |
| Identifiers | |
3D model (JSmol)
|
|
| ChEMBL | |
| ChemSpider | |
PubChem CID
|
|
| UNII | |
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| C4H2FeO4 | |
| Molar mass | 169.901 g·mol−1 |
| Appearance | reddish-brown powder |
| Odor | odorless |
| Density | 2.435 g/cm3 (20 °C) |
| Melting point | 280 °C (536 °F; 553 K) |
| slightly soluble | |
| Pharmacology | |
| 1=ATC code }} | B03AA02 (WHO) |
| Hazards | |
| NFPA 704 (fire diamond) | |
| Lethal dose or concentration (LD, LC): | |
LD50 (median dose)
|
3850 mg/kg (oral, rat) |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa). | |
| Infobox references | |
Iron(II) fumarate, also known as ferrous fumarate, is the iron(II) salt of fumaric acid, occurring as a reddish-orange powder, used to supplement iron intake. It has the chemical formula C
4H
2FeO
4. Pure ferrous fumarate has an iron content of 32.87%, therefore one tablet of 300 mg iron fumarate will contain 98.6 mg of iron (548% Daily Value based on 18 mg RDI).
Iron supplement
Ferrous fumarate is often taken orally as an iron supplement to treat or prevent iron deficiency anemia.[1]
See also
References
- ↑ Santiago, Palacios (2012-05-02). "Ferrous versus Ferric Oral Iron Formulations for the Treatment of Iron Deficiency: A Clinical Overview" (in en). The Scientific World Journal 2012: e846824. doi:10.1100/2012/846824. ISSN 2356-6140. PMID 22654638.
 |


