Chemistry:Isovanillin
From HandWiki
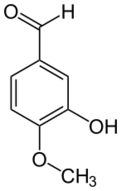
| |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| Preferred IUPAC name
3-Hydroxy-4-methoxybenzaldehyde[1] | |
| Other names
5-Formylguaiacol
3-Hydroxy-p-anisaldehyde | |
| Identifiers | |
3D model (JSmol)
|
|
| 1073021 | |
| ChEBI | |
| ChEMBL | |
| ChemSpider | |
| EC Number |
|
| MeSH | Isovanillin |
PubChem CID
|
|
| RTECS number |
|
| UNII | |
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| C8H8O3 | |
| Molar mass | 152.149 g·mol−1 |
| Appearance | Translucent crystals |
| Melting point | 113 to 116 °C (235 to 241 °F; 386 to 389 K) |
| Boiling point | 179 °C (354 °F; 452 K) at 15 mmHg |
| log P | 1.25 |
| Acidity (pKa) | 9.248 |
| Related compounds | |
Related compounds
|
Anisaldehyde |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa). | |
| Infobox references | |
Tracking categories (test):
Isovanillin is a phenolic aldehyde, an organic compound and isomer of vanillin.[2] It is a selective inhibitor of aldehyde oxidase. It is not a substrate of that enzyme, and is metabolized by aldehyde dehydrogenase into isovanillic acid, which could make it a candidate drug for use in alcohol aversion therapy.[3] Isovanillin can be used as a precursor in the chemical total synthesis of morphine.[4][5] The proposed metabolism of isovanillin (and vanillin) in rat has been described in literature,[6] and is part of the WikiPathways[7] machine readable pathway collection.
See also
References
- ↑ "Isovanillin". The PubChem Project. National Center for Biotechnology Information. https://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/summary/summary.cgi?cid=12127.
- ↑ "isovanillin - Compound Summary (CID 12127)". https://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/summary/summary.cgi?cid=12127&loc=ec_rcs#safety.
- ↑ Georgios Panoutsopoulos; Christine Beedham (2005). "Enzymatic Oxidation of Vanillin, Isovanillin and Protocatechuic Aldehyde with Freshly Prepared Guinea Pig Liver Slices". Cell Physiol Biochem 15 (1–4): 89–98. doi:10.1159/000083641. PMID 15665519. http://content.karger.com/produktedb/produkte.asp?doi=83641.
- ↑ Uchida, Kenji; Yokoshima, Satoshi; Kan, Toshiyuki; Fukuyama, Tohru (2006). "Total Synthesis of (±)-Morphine". Organic Letters 8 (23): 5311–5313. doi:10.1021/ol062112m. PMID 17078705.
- ↑ Uchida, Kenji; Yokoshima, Satoshi; Kan, Toshiyuki; Fukuyama, Tohru (2009). "Total Synthesis of (±)-Morphine". Heterocycles 77 (2): 1219–1234. doi:10.3987/COM-08-S(F)103. PMID 17078705. http://www.heterocycles.jp/newlibrary/libraries/search. Retrieved 27 December 2013.
- ↑ Strand, L. P.; Scheline, R. R. (January 1975). "The metabolism of vanillin and isovanillin in the rat". Xenobiotica; the Fate of Foreign Compounds in Biological Systems 5 (1): 49–63. doi:10.3109/00498257509056093. ISSN 0049-8254. PMID 1154798.
- ↑ "Vanillin and isovanillin metabolism". 2019-10-31. https://www.wikipathways.org/index.php/Pathway:WP4501.
 |
