Chemistry:List of aminorex analogues
This is a list of aminorex analogues. Aminorex itself is a stimulant drug with a 5-phenyl-2-amino-oxazoline structure. It was developed in the 1960s as an anorectic,[1][2][3] but withdrawn from sale after it was discovered that extended use produced pulmonary hypertension, often followed by heart failure, which resulted in a number of deaths.[4] A designer drug analogue 4-methylaminorex appeared on the illicit market in the late 1980s but did not attract significant popularity due to its steep dose-response curve and tendency to produce seizures.[5][6][7][8] Pemoline, the 4-keto derivative of aminorex, had been discovered several years earlier,[9] and derivatives of this type appeared to be effective stimulants with comparatively low toxicity.[10][11] Pemoline was sold for around 25 years as a therapy for ADHD and relief of fatigue, before being withdrawn from the market in 2005 because of rare but serious cases of liver failure.[12][13][14][15] More recently in around 2014 another derivative 4,4'-dimethylaminorex started to be sold illicitly, but again swiftly lost popularity due to a spate of fatal overdose cases.[16][17][18] A number of related compounds are known, and new derivatives have continued to appear on the designer drug market.[19][20][21][22][23][24]
List of substituted aminorex derivatives
| Structure | Common name | Chemical name | CAS number |
|---|---|---|---|
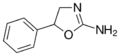
|
Aminorex | 5-phenyl-4,5-dihydro-1,3-oxazol-2-amine | 2207-50-3 |
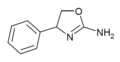
|
Rexamino | 4-phenyl-4,5-dihydro-1,3-oxazol-2-amine | 52883-35-9 |
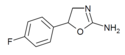
|
4'-Fluoroaminorex (4'-FAR) | 5-(4-fluorophenyl)-4,5-dihydro-1,3-oxazol-2-amine | 2967-77-3 |
| Clominorex | 5-(4-chlorophenyl)-4,5-dihydro-1,3-oxazol-2-amine | 3876-10-6 | |
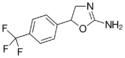
|
Fluminorex | 5-[4-(trifluoromethyl)phenyl]-4,5-dihydro-1,3-oxazol-2-amine | 720-76-3 |
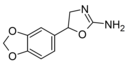
|
Methylenedioxyaminorex | 5-(3,4-methylenedioxyphenyl)-4,5-dihydro-1,3-oxazol-2-amine | 3865-98-3 |
|
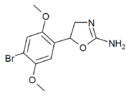
2C-B-aminorex (2C-B-AR) | 5-(2,5-dimethoxy-4-bromophenyl)-4,5-dihydro-1,3-oxazol-2-amine | |
|
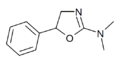
N,N-Dimethylaminorex (N,N-DMAR) | N,N-dimethyl-5-phenyl-4,5-dihydro-1,3-oxazol-2-amine | 32968-41-5 |
|
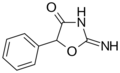
Pemoline | 2-amino-5-phenyl-1,3-oxazol-4(5H)-one | 2152-34-3 |
|
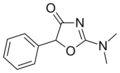
Thozalinone | 2-(dimethylamino)-5-phenyl-1,3-oxazol-4(5H)-one | 655-05-0 |
|
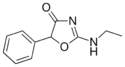
Fenozolone | 2-ethylamino-5-phenyl-1,3-oxazol-4-one | 15302-16-6 |
|
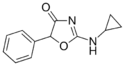
Cyclazodone | 2-(cyclopropylamino)-5-phenyl-1,3-oxazol-4-one | 14461-91-7 |
|
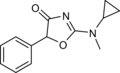
N-Methylcyclazodone | 2-(cyclopropyl(methyl)amino)-5-phenyl-1,3-oxazol-4-one | 14461-92-8 |
|
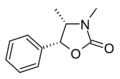
Ephedroxane [25] | (4S,5R)-3,4-dimethyl-5-phenyl-1,3-oxazolidin-2-one | 16251-46-0 |
|
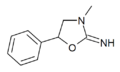
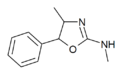
3-Methylaminorex | 3-methyl-5-phenyl-2-oxazolidinimine | 75343-73-6 |
|
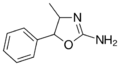
4-Methylaminorex (4-MAR) | 4-methyl-5-phenyl-4,5-dihydro-1,3-oxazol-2-amine | 3568-94-3 |
|
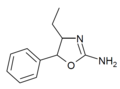
4-Ethylaminorex (4-EAR) | 4-ethyl-5-phenyl-4,5-dihydro-1,3-oxazol-2-amine | 1364933-63-0 |
|
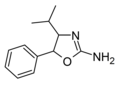
4-Isopropylaminorex | 4-isopropyl-5-phenyl-4,5-dihydro-1,3-oxazol-2-amine | |
|
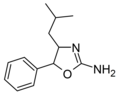
4-Isobutylaminorex | 4-(2-methylpropyl)-5-phenyl-4,5-dihydro-1,3-oxazol-2-amine | |
|
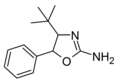
4-tert-butylaminorex | 4-(1,1-dimethylethyl)-5-phenyl-4,5-dihydro-1,3-oxazol-2-amine | |
|
4,N-Dimethylaminorex (4,N-DMAR) | 4,5-dihydro-N,4-dimethyl-5-phenyl-2-oxazolamine | 2207-49-0 |
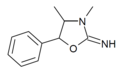
|
3,4-Dimethylaminorex (3,4-DMAR) | 3,4-dimethyl-5-phenyl-2-oxazolidinimine | 82485-31-2 |
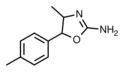
|
4,4'-Dimethylaminorex (4,4'-DMAR) | 4-methyl-5-(4-methylphenyl)-4,5-dihydro-1,3-oxazol-2-amine | 1445569-01-6 |
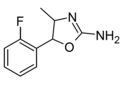
|
2'-Fluoro-4-methylaminorex (2F-MAR) | 4-methyl-5-(2-fluorophenyl)-4,5-dihydro-1,3-oxazol-2-amine | |
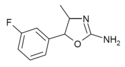
|
3'-Fluoro-4-methylaminorex (3F-MAR) | 4-methyl-5-(3-fluorophenyl)-4,5-dihydro-1,3-oxazol-2-amine | |
|
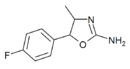
4'-Fluoro-4-methylaminorex (4F-MAR) | 4-methyl-5-(4-fluorophenyl)-4,5-dihydro-1,3-oxazol-2-amine | 1364933-64-1 |
|
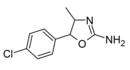
4'-Chloro-4-methylaminorex (4C-MAR) | 4-methyl-5-(4-chlorophenyl)-4,5-dihydro-1,3-oxazol-2-amine | |
|
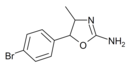
4'-Bromo-4-methylaminorex (4B-MAR) | 4-methyl-5-(4-bromophenyl)-4,5-dihydro-1,3-oxazol-2-amine | |
|
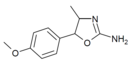
4'-Methoxy-4-methylaminorex (4'-MeO-4-MAR) | 4-methyl-5-(4-methoxyphenyl)-4,5-dihydro-1,3-oxazol-2-amine | 1445570-65-9 |
|
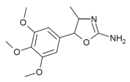
3',4',5'-Trimethoxy-4-methylaminorex (TM-4-MAR) | 4-methyl-5-(3,4,5-trimethoxyphenyl)-4,5-dihydro-1,3-oxazol-2-amine | 1445571-92-5 |
|
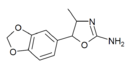
3',4'-Methylenedioxy-4-methylaminorex (MDMAR) | 4-methyl-5-(3,4-methylenedioyphenyl)-4,5-dihydro-1,3-oxazol-2-amine | 1445573-16-9 |
See also
- Berefrine
- List of methylphenidate analogues
- Substituted benzofuran
- Substituted cathinone
- Substituted phenylmorpholine
References
- ↑ Meschino JA, Poos GI. 2-amino-5,6-dihydro-4H-1,3-oxazines and a process for their preparation. US Patent 3115494, 1961
- ↑ Poos GI. 2-amino-5-aryloxazoline products. US Patent 3161650, 1962
- ↑ "2-Amino-5-aryl-2-oxazolines. Potent New Anorectic Agents". Journal of Medicinal Chemistry 6 (3): 266–272. May 1963. doi:10.1021/jm00339a011. PMID 14185981.
- ↑ "Aminorex and pulmonary hypertension. A review". Cor et Vasa 27 (2–3): 160–171. 1985. PMID 3928246.
- ↑ "A fatality involving U4Euh, a cyclic derivative of phenylpropanolamine". Journal of Forensic Sciences 33 (2): 549–553. March 1988. doi:10.1520/JFS11971J. PMID 3373171.
- ↑ "Neurochemical effects of an acute treatment with 4-methylaminorex: a new stimulant of abuse". European Journal of Pharmacology 180 (1): 103–111. May 1990. doi:10.1016/0014-2999(90)90597-y. PMID 1973111.
- ↑ "Recreational use of aminorex and pulmonary hypertension". Chest 118 (5): 1496–1497. November 2000. doi:10.1378/chest.118.5.1496. PMID 11083709.
- ↑ "Rewarding properties of the stereoisomers of 4-methylaminorex: involvement of the dopamine system". Pharmacology, Biochemistry, and Behavior 81 (4): 715–724. August 2005. doi:10.1016/j.pbb.2005.04.020. PMID 15982727.
- ↑ Schmidt L, Scheffler H. Central nervous system stimulant. US Patent 2892753, 1957
- ↑ "Hardy RA, Howell CF, Quinones NQ. Method of producing central nervous system stimulation and anorexia. US Patent 3313688, 1964". https://patents.google.com/patent/US3313688.
- ↑ "Guidicelli DP, Najer H. 5-phenyl-2-cyclopropylamino-4-oxazolinone, and process for making the same. US Patent 3609159, 1967". https://patents.google.com/patent/US3609159.
- ↑ "Pemoline hepatotoxicity in children". The Journal of Pediatrics 132 (5): 894–897. May 1998. doi:10.1016/s0022-3476(98)70329-4. PMID 9602211.
- ↑ "Pemoline hepatotoxicity and postmarketing surveillance". Journal of the American Academy of Child and Adolescent Psychiatry 40 (6): 622–629. June 2001. doi:10.1097/00004583-200106000-00006. PMID 11392339.
- ↑ "A surveillance method for the early identification of idiosyncratic adverse drug reactions". Drug Safety 31 (2): 169–180. 2008. doi:10.2165/00002018-200831020-00006. PMID 18217792.
- ↑ "Risk Evaluation and Mitigation Strategies (REMS), Pemoline, and What Is a Signal?". Clinical Therapeutics 39 (4): 665–669. April 2017. doi:10.1016/j.clinthera.2017.03.008. PMID 28366595.
- ↑ "Characterization of a novel and potentially lethal designer drug (±)-cis-para-methyl-4-methylaminorex (4,4'-DMAR, or 'Serotoni')". Drug Testing and Analysis 6 (7–8): 684–695. 2014. doi:10.1002/dta.1668. PMID 24841869.
- ↑ "4,4'-DMAR: chemistry, pharmacology and toxicology of a new synthetic stimulant of abuse". Basic & Clinical Pharmacology & Toxicology 117 (1): 26–30. July 2015. doi:10.1111/bcpt.12399. PMID 25819702.
- ↑ "The psychostimulant (±)-cis-4,4'-dimethylaminorex (4,4'-DMAR) interacts with human plasmalemmal and vesicular monoamine transporters". Neuropharmacology 138: 282–291. August 2018. doi:10.1016/j.neuropharm.2018.06.018. PMID 29908239.
- ↑ "Stimulus properties of some analogues of 4-methylaminorex". Pharmacology, Biochemistry, and Behavior 51 (2–3): 375–378. 1995. doi:10.1016/0091-3057(94)00407-a. PMID 7667356.
- ↑ "The effects of aminorex and related compounds on brain monoamines and metabolites in CBA mice". The Journal of Pharmacy and Pharmacology 49 (1): 89–96. January 1997. doi:10.1111/j.2042-7158.1997.tb06758.x. PMID 9120777.
- ↑ "Synthesis, characterization, and monoamine transporter activity of the new psychoactive substance 3',4'-methylenedioxy-4-methylaminorex (MDMAR)". Drug Testing and Analysis 7 (7): 555–564. July 2015. doi:10.1002/dta.1732. PMID 25331619.
- ↑ "DARK Classics in Chemical Neuroscience: Aminorex Analogues". ACS Chemical Neuroscience 9 (10): 2484–2502. October 2018. doi:10.1021/acschemneuro.8b00415. PMID 30269490.
- ↑ "Characterization of a recently detected halogenated aminorex derivative: para-fluoro-4-methylaminorex (4'F-4-MAR)". Scientific Reports 9 (1): 8314. June 2019. doi:10.1038/s41598-019-44830-y. PMID 31165778. Bibcode: 2019NatSR...9.8314F.
- ↑ "Pharmacological characterization of the aminorex analogs 4-MAR, 4,4'-DMAR, and 3,4-DMAR". Neurotoxicology 72: 95–100. May 2019. doi:10.1016/j.neuro.2019.02.011. PMID 30776375.
- ↑ "Pharmacology of ephedroxanes". Journal of Ethnopharmacology 13 (2): 175–191. May 1985. doi:10.1016/0378-8741(85)90005-4. PMID 4021515.
 |

