Chemistry:Muconic acid
| |
| Names | |
|---|---|
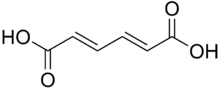
| IUPAC name
(2E,4E)-Hexa-2,4-dienedioic acid
| |
| Other names
(E,E)-Muconic acid
| |
| Identifiers | |
3D model (JSmol)
|
|
| ChEBI | |
| ChemSpider | |
| EC Number |
|
PubChem CID
|
|
| UNII | |
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| C6H6O4 | |
| Molar mass | 142.110 g·mol−1 |
| Appearance | Crystalline prisms |
| Density | 1.366 g/mL |
| Melting point | 194 to 195 °C (381 to 383 °F; 467 to 468 K) (cis,cis-form, prisms from ethanol), 301 °C (trans,trans-form, prisms from water), 190–191 °C (cis,trans-form, needles from hot water)[3] |
| Boiling point | 345 °C (653 °F; 618 K) |
| 1 g/L | |
| Hazards | |
| Main hazards | Irritant |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa). | |
| Infobox references | |
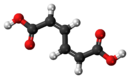
Muconic acid is a dicarboxylic acid. There are three isomeric forms designated trans,trans-muconic acid, cis,trans-muconic acid, and cis,cis-muconic acid which differ by the geometry around the double bonds. Its name is derived from mucic acid.
trans,trans-Muconic acid is a metabolite of benzene in humans. The determination of its concentration in urine is therefore used as a biomarker of occupational or environmental exposure to benzene.[4][5] Synthetically, trans,trans-muconic acid can be prepared from adipic acid.[6]
cis,cis-Muconic acid is produced by some bacteria by the enzymatic degradation of various aromatic chemical compounds.
The bioproduction of muconic acid is of interest because of its potential use as a platform chemical for the production of several valuable consumer bioplastics including nylon-6,6, polyurethane, and polyethylene terephthalate.[7]
See also
Notes
- ↑ Merck Index, 11th Edition, 6210
- ↑ Muconic acid at Sigma-Aldrich
- ↑ Merck Index, 12th Edition (1996), 6381, p.1079
- ↑ "A correlative study on red blood cell parameters and urine trans, trans-muconic acid in subjects with occupational benzene exposure". Toxicologic Pathology 35 (2): 268–9. 2007. doi:10.1080/01926230601156278. PMID 17366320.
- ↑ "Benzene exposure, assessed by urinary trans,trans-muconic acid, in urban children with elevated blood lead levels". Environ. Health Perspect. (Brogan &) 104 (3): 318–23. 1996. doi:10.2307/3432891. PMID 8919771.
- ↑ P. C. Guha; D. K. Sankaran (1946). "Muconic Acid". Organic Syntheses 26: 57–60. doi:10.15227/orgsyn.026.0057. PMID 20280761.
- ↑ "Metabolic engineering of muconic acid production in Saccharomyces cerevisiae.". Metab. Eng. 15: 55–66. 2013. doi:10.1016/j.ymben.2012.10.003. PMID 23164574.
 |