Chemistry:Phenoxathiin
From HandWiki
| |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| Preferred IUPAC name
Phenoxathiine | |
| Other names
1,4-Dibenzothioxine
| |
| Identifiers | |
3D model (JSmol)
|
|
| ChemSpider | |
PubChem CID
|
|
| UNII | |
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| C12H8OS | |
| Molar mass | 200.26 g·mol−1 |
| Melting point | 52–56 °C (126–133 °F; 325–329 K)[1] |
| Boiling point | 150–152 °C (302–306 °F; 423–425 K)[1] (at 5 mmHg) |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa). | |
| Infobox references | |
Tracking categories (test):
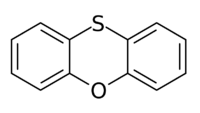
Phenoxathiin (dibenzooxathiane) C12H8OS is a heterocyclic compound of molecular weight 200.25632 g/mol with the CAS Registry Number 262-20-4.[2]
Diphenyl ether is a starting material in the production of phenoxathiin via the Ferrario reaction.[3] Phenoxathiin is used in polyamide and polyimide production.[4]
References
- ↑ 1.0 1.1 "Phenoxathiin". Sigma-Aldrich. http://www.sigmaaldrich.com/catalog/product/aldrich/218820?lang=en.
- ↑ The Chemistry of Phenoxathiin and its Derivatives. Clara L. Deasy Chem. Rev., 1943, 32 (2), pp 173–194 DOI: 10.1021/cr60102a001 Publication Date: April 1943
- ↑ Suter, C. M.; Maxwell, C. E. (1943). "Phenoxthin". Organic Syntheses. http://www.orgsyn.org/demo.aspx?prep=cv2p0485.; Collective Volume, 2, pp. 485
- ↑ Mitsuru Ueoda; Tatsuo Aizawa; Yoshio Imai (1977). "Preparation and properties of polyamides and polyimides containing phenoxathiin units". Journal of Polymer Science: Polymer Chemistry Edition 15 (11): 2739–2747. doi:10.1002/pol.1977.170151119.
External links
 |

