Chemistry:Phthalocyanine
| |
| |
| Names | |
|---|---|
Other names
| |
| Identifiers | |
3D model (JSmol)
|
|
| ChEBI | |
| ChemSpider | |
PubChem CID
|
|
| UNII | |
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| C32H18N8 | |
| Molar mass | 514.552 g·mol−1 |
| Hazards | |
| GHS pictograms |  [1] [1]
|
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa). | |
| Infobox references | |
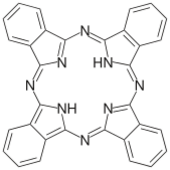
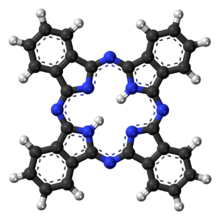
Phthalocyanine (H
2Pc) is a large, aromatic, macrocyclic, organic compound with the formula (C
8H
4N
2)
4H
2 and is of theoretical or specialized interest in chemical dyes and photoelectricity.
It is composed of four isoindole units[lower-alpha 1] linked by a ring of nitrogen atoms. (C
8H
4N
2)
4H
2 = H
2Pc has a two-dimensional geometry and a ring system consisting of 18 π-electrons. The extensive delocalization of the π-electrons affords the molecule useful properties, lending itself to applications in dyes and pigments. Metal complexes derived from Pc2−, the conjugate base of H
2Pc, are valuable in catalysis, organic solar cells, and photodynamic therapy.
Properties
Phthalocyanine and derived metal complexes (MPc) tend to aggregate and, thus, have low solubility in common solvents.[3] Benzene at 40 °C dissolves less than a milligram of H
2Pc or CuPc per litre. H
2Pc and CuPc dissolve easily in sulfuric acid due to the protonation of the nitrogen atoms bridging the pyrrole rings. Many phthalocyanine compounds are, thermally, very stable and do not melt but can be sublimed. CuPc sublimes at above 500 °C under inert gases (nitrogen, CO
2).[4] Substituted phthalocyanine complexes often have much higher solubility.[5] They are less thermally stable and often can not be sublimed. Unsubstituted phthalocyanines strongly absorb light between 600 and 700 nm, thus these materials are blue or green.[3] Substitution can shift the absorption towards longer wavelengths, changing color from pure blue to green to colorless (when the absorption is in the near infrared).
There are many derivatives of the parent phthalocyanine, where either carbon atoms of the macrocycle are exchanged for nitrogen atoms or the peripheral hydrogen atoms are substituted by functional groups like halogens, hydroxyl, amine, alkyl, aryl, thiol, alkoxy and nitrosyl groups. These modifications allow for the tuning of the electrochemical properties of the molecule such as absorption and emission wavelengths and conductance.[6]
History
In 1907, an unidentified blue compound, now known to be phthalocyanine, was reported.[7] In 1927, Swiss researchers serendipitously discovered copper phthalocyanine, copper naphthalocyanine, and copper octamethylphthalocyanine in an attempted conversion of o-dibromobenzene into phthalonitrile. They remarked on the enormous stability of these complexes but did not further characterize them.[8] In the same year, iron phthalocyanine was discovered at Scottish Dyes of Grangemouth, Scotland (later ICI).[9] It was not until 1934 that Sir Patrick Linstead characterized the chemical and structural properties of iron phthalocyanine.[10]
Synthesis
Phthalocyanine is formed through the cyclotetramerization of various phthalic acid derivatives including phthalonitrile, diiminoisoindole, phthalic anhydride, and phthalimides.[11] Alternatively, heating phthalic anhydride in the presence of urea yields H
2Pc.[12] Using such methods, approximately 57,000 tonnes (63,000 Imperial tons) of various phthalocyanines were produced in 1985.[12] More often, MPc is synthesized rather than H
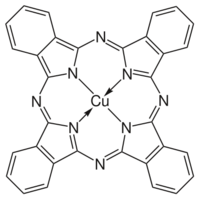
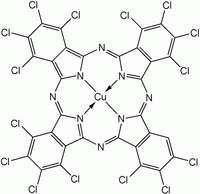
2Pc due to the greater research interest in the former. To prepare these complexes, the phthalocyanine synthesis is conducted in the presence of metal salts. Two copper phthalocyanines are shown in the figure below.
Halogenated and sulfonated derivatives of copper phthalocyanines are commercially important as dyes. Such compounds are prepared by treating CuPc with chlorine, bromine or oleum.
Applications
At the initial discovery of Pc, its uses were primarily limited to dyes and pigments.[13] Modification of the substituents attached to the peripheral rings allows for the tuning of the absorption and emission properties of Pc to yield differently colored dyes and pigments. There has since been significant research on H2Pc and MPc resulting in a wide range of applications in areas including photovoltaics, photodynamic therapy, nanoparticle construction, and catalysis.[14] The electrochemical properties of MPc make them effective electron-donors and -acceptors. As a result, MPc-based organic solar cells with power conversion efficiencies at or below 5% have been developed.[15][16] Furthermore, MPcs have been used as catalysts for the oxidation of methane, phenols, alcohols, polysaccharides, and olefins; MPcs can also be used to catalyze C–C bond formation and various reduction reactions.[17] Silicon and zinc phthalocyanines have been developed as photosensitizers for non-invasive cancer treatment.[18]
Various MPcs have also shown the ability to form nanostructures which have potential applications in electronics and biosensing.[19][20][21] Phthalocyanine is also used on some recordable DVDs.[22]
Toxicity and hazards
No evidence has been reported for acute toxicity or carcinogenicity of phthalocyanine compounds. The -1">50 (rats, oral) is 10 g/kg.[12]
Related compounds
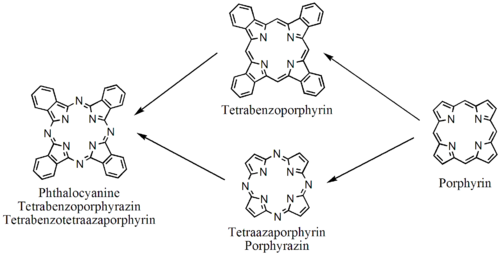
Phthalocyanines are structurally related to other tetrapyrrole macrocyles including porphyrins and porphyrazines. They feature four pyrrole-like subunits linked to form a 16 membered inner ring composed of alternating carbon and nitrogen atoms. Structurally larger analogues include naphthalocyanines. The pyrrole-like rings within H
2Pc are closely related to isoindole. Both porphyrins and phthalocyanines function as planar tetradentate dianionic ligands that bind metals through four inwardly projecting nitrogen centers. Such complexes are formally derivatives of Pc2−, the conjugate base of H
2Pc.
Footnotes
References
- ↑ "Pigment blue 16". U.S. National Institute of Health. https://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/compound/5282330.
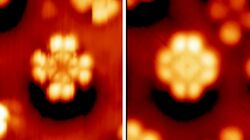
- ↑ Iannuzzi, Marcella; Tran, Fabien; Widmer, Roland; Dienel, Thomas; Radican, Kevin; Ding, Yun; Hutter, Jürg; Gröning, Oliver (2014). "Site-selective adsorption of phthalocyanine on h-BN/Rh(111) nanomesh". Physical Chemistry Chemical Physics 16 (24): 12374–12384. doi:10.1039/C4CP01466A. PMID 24828002. Bibcode: 2014PCCP...1612374I.
- ↑ 3.0 3.1 Ghani, Fatemeh; Kristen, Juliane; Riegler, Hans (2012-02-09). "Solubility properties of unsubstituted metal phthalocyanines in different types of solvents". Journal of Chemical & Engineering Data 57 (2): 439–449. doi:10.1021/je2010215. ISSN 0021-9568.
- ↑ Wagner, Hans J.; Loutfy, Rafik O.; Hsiao, Cheng-Kuo (1982-10-01). "Purification and characterization of phthalocyanines". Journal of Materials Science 17 (10): 2781–2791. doi:10.1007/bf00644652. ISSN 0022-2461. Bibcode: 1982JMatS..17.2781W.
- ↑ Nemykin, Victor N.; Lukyanets, Evgeny A. (2010-02-18). "Synthesis of substituted phthalocyanines". Arkivoc 2010 (1): 136. doi:10.3998/ark.5550190.0011.104.
- ↑ Siles, P.F.; Hahn, T.; Salvan, G.; Knupfer, M.; Zhu, F.; Zahn, D.R.T.; Schmidt, O.G. (2016-04-21). "Tunable charge transfer properties in metal-phthalocyanine heterojunctions". Nanoscale 8 (16): 8607–8617. doi:10.1039/c5nr08671j. ISSN 2040-3372. PMID 27049842. Bibcode: 2016Nanos...8.8607S.
- ↑ Braun, A.; Tcherniac, J. (1907). "Über die Produkte der Einwirkung von Acetanhydrid auf Phthalamid" (in DE). Berichte der Deutschen Chemischen Gesellschaft 40 (2): 2709–2714. doi:10.1002/cber.190704002202. https://books.google.com/books?id=0DBEAQAAMAAJ&pg=PA2709. Retrieved 2015-09-15.
- ↑ de Diesbach, Henri; von der Weid, Edmond (1927). "Quelques sels complexes des o-dinitriles avec le cuivre et la pyridine" (in FR). Helvetica Chimica Acta 10: 886–888. doi:10.1002/hlca.192701001110.
- ↑ "The discovery of a new pigment: The story of Monastral blue by Imperial Chemical Industries". http://www.colorantshistory.org/PhthaloDiscovery.html.
- ↑ Linstead, R.P. (1934-01-01). "212. Phthalocyanines. Part I. A new type of synthetic colouring matters". Journal of the Chemical Society. (resumed): 1016. doi:10.1039/jr9340001016. ISSN 0368-1769.
- ↑ Sakamoto, Keiichi; Ohno-Okumura, Eiko (2009-08-28). "Syntheses and functional properties of phthalocyanines". Materials 2 (3): 1127–1179. doi:10.3390/ma2031127. Bibcode: 2009Mate....2.1127S.
- ↑ 12.0 12.1 12.2 Löbbert, Gerd. "Ullmann's Encyclopedia of Industrial Chemistry". Ullmann's Encyclopedia of Industrial Chemistry. Weinheim: Wiley-VCH. doi:10.1002/14356007.a20_213.
- ↑ Dahlen, Miles A. (1939-07-01). "The phthalocyanines: A new class of synthetic pigments and dyes". Industrial & Engineering Chemistry 31 (7): 839–847. doi:10.1021/ie50355a012. ISSN 0019-7866.
- ↑ Claessens, Christian G.; Hahn, Uwe; Torres, Tomás (2008). "Phthalocyanines: From outstanding electronic properties to emerging applications". The Chemical Record 8 (2): 75–97. doi:10.1002/tcr.20139. ISSN 1528-0691. PMID 18366105.
- ↑ Kumar, Challuri Vijay; Sfyri, Georgia; Raptis, Dimitrios; Stathatos, Elias; Lianos, Panagiotis (2014-12-10). "Perovskite solar cell with low cost Cu-phthalocyanine as hole transporting material". RSC Advances 5 (5): 3786–3791. doi:10.1039/c4ra14321c. ISSN 2046-2069.
- ↑ Yuen, Avery P.; Jovanovic, Stephen M.; Hor, Ah-Mee; Klenkler, Richard A.; Devenyi, Gabriel A.; Loutfy, Rafik O.; Preston, John S. (2012). "Photovoltaic properties of M-phthalocyanine/fullerene organic solar cells". Solar Energy 86 (6): 1683–1688. doi:10.1016/j.solener.2012.03.019. Bibcode: 2012SoEn...86.1683Y.
- ↑ Sorokin, Alexander B. (2013-10-09). "Phthalocyanine metal complexes in catalysis". Chemical Reviews 113 (10): 8152–8191. doi:10.1021/cr4000072. ISSN 0009-2665. PMID 23782107.
- ↑ Miller, J.; Baron, E.; Scull, H.; Hsia, A.; Berlin, J.; Mccormick, T.; Colussi, V.; Kenney, M. et al. (2007). "Photodynamic therapy with the phthalocyanine photosensitizer Pc 4: The case experience with preclinical mechanistic and early clinical–translational studies". Toxicology and Applied Pharmacology 224 (3): 290–299. doi:10.1016/j.taap.2007.01.025. PMID 17397888.
- ↑ Karan, Santanu; Basak, Dhrubajyoti; Mallik, Biswanath (2007). "Copper phthalocyanine nanoparticles and nanoflowers". Chemical Physics Letters 434 (4–6): 265–270. doi:10.1016/j.cplett.2006.12.007. Bibcode: 2007CPL...434..265K.
- ↑ van Keuren, Edward; Bone, Alysia; Ma, Changbao (2008-06-01). "Phthalocyanine nanoparticle formation in supersaturated solutions". Langmuir 24 (12): 6079–6084. doi:10.1021/la800290s. ISSN 0743-7463. PMID 18479155.
- ↑ Lokesh, K.S.; Shivaraj, Y.; Dayananda, B.P.; Chandra, Sudeshna (2009). "Synthesis of phthalocyanine stabilized rhodium nanoparticles and their application in biosensing of cytochrome c". Bioelectrochemistry 75 (2): 104–109. doi:10.1016/j.bioelechem.2009.02.005. PMID 19303822.
- ↑ "Mitsui Gold Archival DVD-R and DVD+R". http://www.conservationresources.com/Main/section_6/section6_12.htm.
External links
- "Society of Porphyrins and Phthalocyanines". https://www.spp-jpp.org/.
- Wiki est. (2006-03-21) by Henry Rzepa. Sir Patrick Linstead: Phthalocyanines. Department of Chemistry. ChemWiki (video). U.K.: Imperial College.
- "Journal of Porphyrins and Phthalocyanines". http://www.worldscinet.com/jpp/.
- "ICI Grangemouth discovery". http://www.colorantshistory.org/PhthaloDiscovery.html.
 |