Chemistry:Pyrimidone
From HandWiki
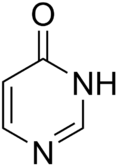
| |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| Preferred IUPAC name
1H-Pyrimidin-6-one | |
| Other names
Hydroxypyrimidine; Pyrimidinone
| |
| Identifiers | |
3D model (JSmol)
|
|
| ChemSpider | |
PubChem CID
|
|
| |
| Properties | |
| C4H4N2O | |
| Molar mass | 96.089 g·mol−1 |
| Appearance | White to light yellow powder |
| Melting point | 163 to 168 °C (325 to 334 °F; 436 to 441 K) |
| Hazards | |
| Main hazards | Respiratory system, eye, skin irritation |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa). | |
| Infobox references | |
Tracking categories (test):
Pyrimidone is the name given to either of two heterocyclic compounds with the formula C4H4N2O: 2-pyrimidone and 4-pyrimidone. The compounds can also be called 2-hydroxypyrimidine or 4-hydroxypyrimidine respectively, based on a substituted pyrimidine, or 1,3-diazine, ring.
Derivatives
Derivatives of pyrimidone are the basis of many other biological molecules, including:
- Nucleobases, such as cytosine
- Barbiturates, such as metharbital
- Antiulcer drugs including temelastine, icotidine, donetidine, and lupitidine.
This article does not cite any external source. HandWiki requires at least one external source. See citing external sources. (2021) (Learn how and when to remove this template message) |
 |