Chemistry:Rho kinase inhibitor
Rho-kinase inhibitors (rho-associated protein kinase inhibitor or ROCK inhibitor) are a series of compounds that target rho kinase (ROCK) and inhibit the ROCK pathway.[1] Clinical trials have found that inhibition of the ROCK pathway contributes to the cardiovascular benefits of statin therapy. Furthermore, ROCK inhibitors may have clinical applications for anti-erectile dysfunction, antihypertension, and tumor metastasis inhibition.[2] More recently they have been studied for the treatment of glaucoma[3] and as a therapeutic target for the treatment of cardiovascular diseases, including ischemic stroke.[4] While statin therapy has been demonstrated to reduce the risk of major cardiovascular events, including ischemic stroke,[5] the interplay between the ROCK pathway and statin therapy to treat and prevent strokes in older adults has not yet been proven.[4] On a cellular level, ROCK has multiple functions, including regulation of smooth muscle cell contraction, cell migration, and maintenance of cell viability and morphology, in part by regulating stress fibers and focal adhesions.[2] Particularly, ROCK inhibitor is used for cell culture practice, in part to limit cellular death and limited dedifferentiation,[6][7][8] and therefore widely adopted for induced pluripotent stem cells (iPSC) and embryonic stem cell cultures,[9] although studies have shown mixed results for other cells types.[10]
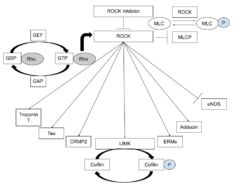
Molecular mechanism
Rho kinase inhibitors act on Rho kinase by altering the conformation of the protein, disrupting translocation to the plasma membrane, preventing ATP-dependent phosphorylation, and blocking RhoA binding to ROCK.[11] Some studies suggest that Rho kinase inhibitors also play a role in anti-angiogenesis by blocking ERK and Akt signaling pathways.[12][13] Rho kinase inhibitor also functions by blocking rho-mediated dephosphorylation of MLC20.[14]
Examples
A number of Rho kinase inhibitors are known.[15][16][17]
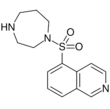
- AT-13148[18]
- BA-210
- β-Elemene
- Belumosudil
- Chroman 1[19][20]
- DJ4, which is a selective multi-specific ATP competitive inhibitor of activity of ROCK1 (IC50 of 5 nM), ROCK2 (IC50 of 50 nM), MRCKα (IC50 of 10 nM) and MRCKβ (IC50 of 100 nM) kinases without affecting activity of PAK1 and DMPK at 5 μM concentrations in in vitro cell-free kinase activity assays.[21] DJ4 reduces stress fiber formation, and inhibits migration and invasion of melanoma (A375), breast (MD-MB-231), and non-small cell lung cancer (A549) cells independent of cell death induction.
- Fasudil, not currently approved by the U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA), but in Japan and China it is used for improvement and prevention of cerebral vasospasm and the cerebral ischemic symptoms subsequent to subarachnoid hemorrhage surgery.
- GSK-576371[22]
- GSK429286A, C21H16F4N4O2[23]
- H-1152 Inhibitor H-1152 is approximately 9 to 16 times more potent than Y-27632 and HA-1077 (Fasudil)[24]
- Hydroxyfasudil, an active metabolite of fasudil
- Ibuprofen
- LX-7101[25]
- Netarsudil, approved in United States for glaucoma and ocular hypertension.[26]
- RKI-1447, a potent small molecule inhibitor of ROCK1 and ROCK2.[27] Studies show that RKI-1447 could have anti-invasive and anti-tumor activities.
- Ripasudil, used in Japan for the treatment of glaucoma and ocular hypertension.
- TCS-7001
- Thiazovivin
- Verosudil (AR-12286) [28]
- Y-27632, the first small molecule ROCK inhibitor. It selectively inhibits ROCK1 with Ki of 140 nM.[29]
- Y-30141
- Y-33075
- Y-39983
References
- ↑ Liao, James K.; Seto, Minoru; Noma, Kensuke (July 2007). "Rho Kinase (ROCK) Inhibitors". Journal of Cardiovascular Pharmacology 50 (1): 17–24. doi:10.1097/FJC.0b013e318070d1bd. ISSN 0160-2446. PMID 17666911.
- ↑ 2.0 2.1 "Rho kinase (ROCK) inhibitors". Journal of Cardiovascular Pharmacology 50 (1): 17–24. July 2007. doi:10.1097/FJC.0b013e318070d1bd. PMID 17666911.
- ↑ "An emerging treatment option for glaucoma: Rho kinase inhibitors". Clinical Ophthalmology 8: 883–90. 2014. doi:10.2147/OPTH.S41000. PMID 24872673.
- ↑ 4.0 4.1 "ROCK as a therapeutic target for ischemic stroke". Expert Review of Neurotherapeutics 17 (12): 1167–1177. December 2017. doi:10.1080/14737175.2017.1395700. PMID 29057688.
- ↑ "Clinical Effectiveness of Statin Therapy After Ischemic Stroke: Primary Results From the Statin Therapeutic Area of the Patient-Centered Research Into Outcomes Stroke Patients Prefer and Effectiveness Research (PROSPER) Study". Circulation 132 (15): 1404–13. October 2015. doi:10.1161/CIRCULATIONAHA.115.016183. PMID 26246175.
- ↑ "ROCK inhibitor prevents the dedifferentiation of human articular chondrocytes". Biochemical and Biophysical Research Communications 420 (1): 124–9. March 2012. doi:10.1016/j.bbrc.2012.02.127. PMID 22405765.
- ↑ "ROCK inhibition enhances aggrecan deposition and suppresses matrix metalloproteinase-3 production in human articular chondrocytes". Connective Tissue Research 55 (2): 89–95. April 2014. doi:10.3109/03008207.2013.852544. PMID 24111521.
- ↑ "RhoA/ROCK Pathway Activation is Regulated by AT1 Receptor and Participates in Smooth Muscle Migration and Dedifferentiation via Promoting Actin Cytoskeleton Polymerization". International Journal of Molecular Sciences 21 (15): 5398. July 2020. doi:10.3390/ijms21155398. PMID 32751352.
- ↑ "ROCK inhibition enhances the recovery and growth of cryopreserved human embryonic stem cells and human induced pluripotent stem cells". Molecular Reproduction and Development 76 (8): 722–32. August 2009. doi:10.1002/mrd.21021. PMID 19235204.
- ↑ "Minimal Sustainability of Dedifferentiation by ROCK Inhibitor on Rat Nucleus Pulposus Cells In Vitro". Spine Surgery and Related Research 3 (4): 385–391. 2019. doi:10.22603/ssrr.2019-0019. PMID 31768460.
- ↑ Yamaguchi, Hiroto; Kasa, Miyuki; Amano, Mutsuki; Kaibuchi, Kozo; Hakoshima, Toshio (2006-03-01). "Molecular Mechanism for the Regulation of Rho-Kinase by Dimerization and Its Inhibition by Fasudil" (in en). Structure 14 (3): 589–600. doi:10.1016/j.str.2005.11.024. ISSN 0969-2126. PMID 16531242.
- ↑ Hata, Yasuaki; Miura, Muneki; Nakao, Shintaro; Kawahara, Shuhei; Kita, Takeshi; Ishibashi, Tatsuro (2008-02-01). "Antiangiogenic properties of fasudil, a potent Rho-Kinase inhibitor" (in en). Japanese Journal of Ophthalmology 52 (1): 16–23. doi:10.1007/s10384-007-0487-5. ISSN 1613-2246. PMID 18369695. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10384-007-0487-5.
- ↑ Khalil, Raouf A. (2010) (in en). Rho Kinase in Vascular Smooth Muscle. Morgan & Claypool Life Sciences. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK54588/.
- ↑ Nagumo, Hiromitsu; Sasaki, Yasuharu; Ono, Yoshitaka; Okamoto, Hiroyuki; Seto, Minoru; Takuwa, Yoh (2000-01-01). "Rho kinase inhibitor HA-1077 prevents Rho-mediated myosin phosphatase inhibition in smooth muscle cells". American Journal of Physiology. Cell Physiology 278 (1): C57–C65. doi:10.1152/ajpcell.2000.278.1.C57. ISSN 0363-6143. PMID 10644512.
- ↑ You, Y., Zhu, K., Wang, J., Liang, Q., Li, W., Wang, L., ... & Shi, J. (2023). ROCK inhibitor: Focus on recent updates. Chinese Chemical Letters, 108336. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cclet.2023.108336
- ↑ "Exploring the potential of RhoA inhibitors to improve exercise-recoverable spinal cord injury: A systematic review and meta-analysis". Journal of Chemical Neuroanatomy 111: 101879. November 2020. doi:10.1016/j.jchemneu.2020.101879. ISSN 0891-0618. PMID 33197553.
- ↑ "Should we keep rocking? Portraits from targeting Rho kinases in cancer". Pharmacological Research 160: 105093. October 2020. doi:10.1016/j.phrs.2020.105093. PMID 32726671.
- ↑ "Rho Kinase Inhibition by AT13148 Blocks Pancreatic Ductal Adenocarcinoma Invasion and Tumor Growth". Cancer Research 78 (12): 3321–3336. June 2018. doi:10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-17-1339. PMID 29669760.
- ↑ Chroman 1, CAS No. : 1273579-40-0
- ↑ "A versatile polypharmacology platform promotes cytoprotection and viability of human pluripotent and differentiated cells". Nature Methods 18 (5): 528–541. May 2021. doi:10.1038/s41592-021-01126-2. PMID 33941937.
- ↑ "A novel selective multikinase inhibitor of ROCK and MRCK effectively blocks cancer cell migration and invasion". Cancer Letters 354 (2): 299–310. November 2014. doi:10.1016/j.canlet.2014.08.032. PMID 25172415.
- ↑ "Effects of a Rho kinase inhibitor on pressure overload induced cardiac hypertrophy and associated diastolic dysfunction". American Journal of Physiology. Heart and Circulatory Physiology 294 (4): H1804-14. April 2008. doi:10.1152/ajpheart.01078.2007. PMID 18245565.
- ↑ GSK429286A@pubchem
- ↑ Teixeira, C. E.; Jin, L.; Priviero, F. B.; Ying, Z.; Webb, R. C. (2007). "Comparative pharmacological analysis of Rho-kinase inhibitors and identification of molecular components of Ca2+ sensitization in the rat lower urinary tract". Biochemical Pharmacology 74 (4): 647–658. doi:10.1016/j.bcp.2007.06.004. PMID 17603024.
- ↑ "Design, synthesis and biological characterization of selective LIMK inhibitors". Bioorganic & Medicinal Chemistry Letters 25 (18): 4005–10. September 2015. doi:10.1016/j.bmcl.2015.07.009. PMID 26233434.
- ↑ "RHOPRESSA presribing information". U.S. Food and Drug Administration. https://www.accessdata.fda.gov/drugsatfda_docs/label/2017/208254lbl.pdf.
- ↑ "RKI-1447 is a potent inhibitor of the Rho-associated ROCK kinases with anti-invasive and antitumor activities in breast cancer". Cancer Research 72 (19): 5025–34. October 2012. doi:10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-12-0954. PMID 22846914.
- ↑ "Ocular hypotensive effect of the Rho kinase inhibitor AR-12286 in patients with glaucoma and ocular hypertension". American Journal of Ophthalmology 152 (5): 834–41.e1. November 2011. doi:10.1016/j.ajo.2011.04.012. PMID 21794845.
- ↑ "information of different kinds of ROCK inhibitor". selleckchemicals. http://www.selleckchem.com/pathways_ROCK.html.
Further reading
 |
