Chemistry:SEP-363856
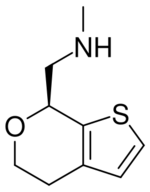
| |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| IUPAC name
(7S)-4,7-Dihydro-N-methyl-5H-thieno[2,3-c]pyran-7-methanamine
| |
| Other names
SEP-856
| |
| Identifiers | |
3D model (JSmol)
|
|
| ChemSpider | |
PubChem CID
|
|
| UNII | |
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| C9H13NOS | |
| Molar mass | 183.27 g·mol−1 |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa). | |
| Infobox references | |
SEP-363856 (also known as SEP-856)[1] is an investigational antipsychotic that is undergoing clinical trials for the treatment of schizophrenia and Parkinson's disease psychosis.[2] The medication is being developed by the pharmaceutical companies Sunovion Pharmaceuticals and PsychoGenics Inc.[2]
Research has shown that SEP-363856 results in a greater reduction from baseline in the PANSS total score than placebo.[3] Treatment with SEP-363856, as compared with placebo, was also associated with an improvement in sleep quality.[3]
Adverse effects
The adverse effect profile of SEP-363856 differs from that of other antipsychotics because its mechanism of action does not involve antagonism of dopamine receptors in the brain, which is responsible for the drug-induced movement disorders (like akathisia) that may occur with those agents.[4] Some adverse events reported in preliminary clinical trials are somnolence, agitation, nausea, diarrhea, and dyspepsia.[4]
Pharmacology
Mechanism of action
The mechanism of action of SEP-363856 in the treatment of schizophrenia is unclear. However, it is thought to be an agonist at the trace amine-associated receptor 1 (TAAR1) and serotonin-1A receptor (5-HT1A) receptors.[5] This mechanism of action is unique among available antipsychotics, which generally antagonize dopamine receptors (especially dopamine receptor D2).[6][7]
Pharmacokinetics
The precise pharmacokinetic profile of SEP-363856 has not been reported, though the developer has suggested that the pharmacokinetic data supports once daily dosing.[5]
Research
As of 2018, Sunovion, the maker of another antipsychotic called lurasidone (Latuda), is conducting clinical trials on SEP-363856 in partnership with the preclinical research company PsychoGenics.[2][8][9] The U.S. Food and Drug Administration has granted SEP-363856 the breakthrough therapy designation.[5][10] In addition to schizophrenia, SEP-363856 is also being studied for the treatment of psychosis associated with Parkinson's disease.[10]
See also
References
- ↑ "SEP 363856 - AdisInsight". Adis International Ltd.. https://adisinsight.springer.com/drugs/800036955. Retrieved 29 December 2018.
- ↑ 2.0 2.1 2.2 Brooks, Megan. "New Psychotropic Drug for Schizophrenia Promising in Early Testing". Reuters Health Information. https://www.medscape.com/viewarticle/906892?src=wnl_edit_tpal&uac=194606CT&impID=1846550&faf=1. Retrieved 29 December 2018.
- ↑ 3.0 3.1 Koblan, Kenneth S.; Kent, Justine; Hopkins, Seth C.; Krystal, John H.; Cheng, Hailong; Goldman, Robert; Loebel, Antony (2020-04-16). "A Non–D2-Receptor-Binding Drug for the Treatment of Schizophrenia". New England Journal of Medicine 382 (16): 1497–1506. doi:10.1056/NEJMoa1911772. ISSN 0028-4793. PMID 32294346. https://doi.org/10.1056/NEJMoa1911772.
- ↑ 4.0 4.1 Brooks, Megan. "'Game Changer' for Schizophrenia on the Horizon?". WebMD LLC. https://www.medscape.com/viewarticle/913348. Retrieved 21 June 2019.
- ↑ 5.0 5.1 5.2 "Sunovion and PsychoGenics Announce that SEP-363856 Has Received FDA Breakthrough Therapy Designation for the Treatment of People with Schizophrenia". Bloomberg L.P.. https://www.bloomberg.com/press-releases/2019-05-10/sunovion-and-psychogenics-announce-that-sep-363856-has-received-fda-breakthrough-therapy-designation-for-the-treatment-of-people. Retrieved 21 June 2019.
- ↑ Koblan, Kenneth; Hopkins, Seth; Justine, Kent; Hailong, Cheng; Goldman, Robert; Loebel, Antony (2019). "O12.5. Efficacy and Safety of Sep-363856, A Novel Psychotropic Agent with a Non-D2 Mechanism of Action, in the Treatment of Schizophrenia: A 4-Week, Randomized, Placebo-Controlled Trial". Schizophrenia Bulletin 45: S199. doi:10.1093/schbul/sbz021.269.
- ↑ Dedic, Nina; Jones, Philip G.; Hopkins, Seth C.; Lew, Robert; Shao, Liming; Campbell, John E.; Spear, Kerry L.; Large, Thomas H. et al. (2019). "SEP-363856, a Novel Psychotropic Agent with a Unique, Non-D2 Receptor Mechanism of Action". Journal of Pharmacology and Experimental Therapeutics 371 (1): 1–14. doi:10.1124/jpet.119.260281. PMID 31371483.
- ↑ "Sunovion – Our Therapies". Sumitomo Dainippon Pharma Co., Ltd.. http://www.sunovion.us/our-therapies/. Retrieved 29 December 2018.
- ↑ "About Us". PsychoGenics. http://www.psychogenics.com/index.html. Retrieved 29 December 2018.
- ↑ 10.0 10.1 "Drug Receives FDA's Breakthrough Therapy Designation for Treating Individuals with Schizophrenia". Pharmacy & Healthcare Communications, LLC. https://www.pharmacytimes.com/resource-centers/mental-health/drug-receives-fdas-breakthrough-therapy-designation-for-treating-individuals-with-schizophrenia. Retrieved 21 June 2019.

