Chemistry:Serinol
From HandWiki
| |
| Identifiers | |
|---|---|
3D model (JSmol)
|
|
| ChEMBL | |
| ChemSpider | |
| EC Number |
|
PubChem CID
|
|
| UNII | |
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| C3H9NO2 | |
| Molar mass | 91.110 g·mol−1 |
| Appearance | colorless solid |
| Melting point | 128 °C (262 °F; 401 K) |
| Boiling point | 115–120 °C (239–248 °F; 388–393 K) 0.06 Torr |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa). | |
| Infobox references | |
Tracking categories (test):
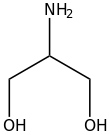
Serinol is the organic compound with the formula H
2NCH(CH
2OH)
2. A colorless solid, it is classified both as an amino alcohol and as a diol. It is structurally related to glycerol. Its name reflects the compound's relationship to the amino acid serine, from which it can be produced by hydrogenation. Other amino alcohols derived from amino acids: alaninol, leucinol, tyrosinol.
Biosynthetically, it is derived from dihydroxyacetone phosphate. It can be prepared in several steps starting with the condensation of nitromethane with two equivalents of formaldehyde.[1][2]
An N,O-protected form of serinol can be produced from serine.[3]
References
- ↑ Andreeßen, Björn; Steinbüchel, Alexander (2011). "Serinol: Small molecule - big impact". AMB Express 1 (1): 12. doi:10.1186/2191-0855-1-12. PMID 21906364.
- ↑ Baxter, Ellen W.; Reitz, Allen B. (2002). "Reductive Aminations of Carbonyl Compounds with Borohydride and Borane Reducing Agents". Organic Reactions. pp. 1–714. doi:10.1002/0471264180.or059.01. ISBN 0471264180.
- ↑ Dondoni, Alessandro; Perrone, Daniela (2000). "Synthesis of 1,1-Dimethylethyl (S)-4-Formyl-2,2-Dimethyl-3-Oxazolidinecarboxylate by Oxidation of the Alcohol". Organic Syntheses 77: 64. doi:10.15227/orgsyn.077.0064.
 |
