Chemistry:Spirotetramat
| |

| |
| Names | |
|---|---|
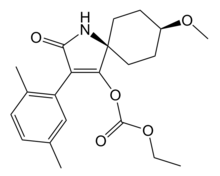
| IUPAC name
cis-3-(2,5-Xylyl)-4-(ethoxycarbonyloxy)-8-methoxy-1-azaspiro[4.5]dec-3-en-2-one
| |
| Other names
Spirotetramat, Movento, Ultor, cis-3-(2,5-dimethylphenyl)-8-methoxy-2-oxo-1-azaspiro[4.5]dec-3-en-4-yl ethyl carbonate
| |
| Identifiers | |
3D model (JSmol)
|
|
| EC Number |
|
PubChem CID
|
|
| UNII | |
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| C21H27NO5 | |
| Molar mass | 373.449 g·mol−1 |
| Density | 1.23 g/cm3 |
| Melting point | 142 °C (288 °F; 415 K) |
| Boiling point | 235 °C (455 °F; 508 K) (decomposes) |
| Practically insoluble (0.03 g/L at 20 °C and pH 7) | |
| Solubility in dichloromethane | Easily soluble |
| Acidity (pKa) | 6.9[1] |
| Hazards | |
| Main hazards | Irritant |
| GHS Signal word | Warning |
| H317, H319, H335, H361, H410 | |
| P201, P202, P261, P264, P271, P272, P273, P280, P281, P302+352, P304+340, P305+351+338, P308+313, P312, P321, P333+313, P337+313, P363, P391, P403+233, P405, P501 | |
| Flash point | Non-flammable |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa). | |
| Infobox references | |
Spirotetramat (ISO Name) is a keto-enol insecticide developed by Bayer CropScience under the brand names Movento[2] and Ultor.[3]
Mechanism
Spirotetramat is active against piercing-sucking insects, such as aphids, mites, and white flies, by acting as an ACC inhibitor, interrupting lipid biosynthesis in the insects. It is a systemic insecticide that penetrates plant leaves when sprayed on. It is ambimobile, being transported both upwards and downwards through vascular bundles.[4] In plants, it is hydrolyzed to the enol form by cleavage of the central ethoxycarbonyl group. This enol is more stable due to double bond being in a ring and the conjugation with the amide group and the benzene ring.
Regulation
Bayer obtained spirotetramat's first regulatory approval in Tunisia in 2007.[5][6] It was recognized by the European Union May 1, 2014.[7]
Toxicology and safety
Spirotetramat has moderate to low acute toxicity, is irritating to eyes and potentially sensitizing to skin. When tested on rats, it was not shown to be carcinogenic.[8] In Denmark, it is listed as harmful to aquatic invertebrates, but not dangerous to bees.[9]
References
- ↑ "Biological Buffers". http://www.sigmaaldrich.com/life-science/metabolomics/bioultra-reagents/biological-buffers.html.
- ↑ "Movento". https://www.cropscience.bayer.us/products/insecticides/movento.
- ↑ "US EPA, Pesticide Produce Label, ULTOR, 05/06/2011". https://www3.epa.gov/pesticides/chem_search/ppls/000264-01065-20110506.pdf.
- ↑ "Movento, an innovative ambimobile insecticide for sucking insect pest control in agriculture: Biological profile and field performance". Crop Protection 28 (10): 838–844. Oct 2009. doi:10.1016/j.cropro.2009.06.015.
- ↑ "Management of the tomato borer, Tuta absoluta in Tunisia with novel insecticides and plant extracts". EPPO Bulletin 42 (2): 291–296. 7 Aug 2012. doi:10.1111/epp.2572.
- ↑ Agropages: New insecticide spirotetramat granted first regulatory approval." (15 November 2007)
- ↑ COMMISSION IMPLEMENTING REGULATION (EU) No 1177/2013. (23 January 2018)
- ↑ "EPA Pesticide Fact Sheet, juni 2008". http://www.thebeeyard.org/wp-content/uploads/2010/03/plugin-spirotetramat.pdf.
- ↑ "Merit Gran - Produktoplysninger - Middeldatabasen". https://middeldatabasen.dk/product.asp?productID=61181.
 |
