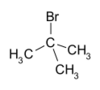
Chemistry:Tert-Butyl bromide
| |
| |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| Preferred IUPAC name
2-Bromo-2-methylpropane[1] | |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa). | |
| Infobox references | |
|Section1=! colspan=2 style="background: #f8eaba; text-align: center;" |Identifiers
|-
|
|
|-
|
|
|-
|
| 1730892 |-
| ChEMBL
|
|- | ChemSpider
|
|-
|
- 208-065-9
|-
|
|
|- | RTECS number
|
- TX4150000
|- | UNII
|
|- | UN number | 2342 |-
| colspan="2" |
- InChI=1S/C4H9Br/c1-4(2,3)5/h1-3H3
 Key: RKSOPLXZQNSWAS-UHFFFAOYSA-N
Key: RKSOPLXZQNSWAS-UHFFFAOYSA-N
|-
| colspan="2" |
- CC(C)(C)Br
|- |Section2=! colspan=2 style="background: #f8eaba; text-align: center;" |Properties
|-
|
| C4H9Br
|- | Molar mass
| 137.020 g·mol−1
|- | Appearance | Colorless liquid |-
| Density | 1.22 g mL−1 (at 20 °C)[2] |- | Melting point | −16.20 °C; 2.84 °F; 256.95 K
|- | Boiling point | 73.3 °C; 163.8 °F; 346.4 K
|-
| log P | 2.574 |-
|
constant (kH)
| 310 nmol Pa−1 kg−1 |-
|
| 1.4279 |- |Section3=! colspan=2 style="background: #f8eaba; text-align: center;" |Thermochemistry
|-
|
| 165.7 J K mol−1 |-
|
formation (ΔfH⦵298)
| −133.4 kJ mol−1 |- |Section4=! colspan=2 style="background: #f8eaba; text-align: center;" |Hazards
|-
| GHS pictograms
|  |-
| GHS Signal word
|DANGER
|-
| GHS Signal word
|DANGER
|-
|
| H225 |-
|
| P210 |-
| Flash point
| 16 °C (61 °F; 289 K)
|-
| colspan=2 style="text-align:left; background-color:#f1f1f1;" | Lethal dose or concentration (LD, LC): |-
|- style="background:#f4f4f4;"
| style="padding-left:1em;" |
|
- 1.25 g kg−1 (intraperitoneal, rat)
- 4.4 g kg−1 (intraperitoneal, mouse)
|-
|- |Section5=! colspan=2 style="background: #f8eaba; text-align: center;" |Related compounds
|-
|
|
- Bromoethane
- n-Propyl bromide
- 2-Bromopropane
- 1-Bromobutane
- 2-Bromobutane
|- }} tert-Butyl bromide (also referred to as 2-bromo-2-methylpropane) is an organic compound with the formula Me3CBr (Me = methyl). The molecule features a tert-butyl group attached to a bromide substituent. This organobromine compound is used as a standard reagent in synthetic organic chemistry. It is a colorless liquid.
Reactions
It is used to introduce tert-butyl groups. Illustrative is the tert-butylation of cyclopentadiene to give di-tert-butylcyclopentadiene:[3]
- C5H6 + 2 NaOH + 2 Me3CBr → (Me3C)2C5H4 + 2 NaBr + 2 H2O
Other aspects
tert-Butyl bromide used to study the massive deadenylation of adenine based-nucleosides induced by halogenated alkanes (alkyl halides) under physiological conditions. 2-Bromo-2-methylpropane causes the massive deguanylation of guanine based-nucleosides and massive deadenylation of adenine based-nucleosides.[4]
Phase transition from orthorhombic Pmn21 phase III at low temperatures (measurements from 95 K), to a disordered rhombohedral phase II at 205-213 K. Phase II can exist from 213-223 K, partly coincident with an FCC phase I, which can be observed between 210-250 K. Phase transitions have also been studied at high pressure (up to 300MPa)[5]
References
- ↑ "2-Bromo-2-methylpropane - Compound Summary". PubChem Compound. USA: National Center for Biotechnology Information. 26 March 2005. Identification. https://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/summary/summary.cgi?cid=10485&loc=ec_rcs. Retrieved 16 June 2012.
- ↑ CRC Handbook of Chemistry and Physics 65th Ed.
- ↑ Reiners, Matthias; Ehrlich, Nico; Walter, Marc D. (2018). "Synthesis of 1,3,5-Tri-tert-Butylcyclopenta-1,3-diene and Its Metal Complexes Na{1,2,4-(Me3C)3C5H2} and Mg{η5-1,2,4-(Me3C)3C5H2)2". Inorganic Syntheses 37: 199. doi:10.1002/9781119477822.ch8.
- ↑ “2-Bromo-2-Methylpropane 135615.” H2NC6H4CO2C2H5, Drugs, www.sigmaaldrich.com/catalog/product/aldrich/135615?lang=en®ion=US.
- ↑ “2-Bromo-2-Methylpropane Structures.” The Cambridge Crystallographic Data Centre (CCDC), www.ccdc.cam.ac.uk/structures/search?id=doi:10.5517/ccvcqmj&sid=DataCite
 |

