Chemistry:Thianthrene
| |
| |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| Preferred IUPAC name
Thianthrene[1] | |
| Other names
Thianthren; 9,10-Dithiaanthracene; Di-o-phenylene disulfide
| |
| Identifiers | |
3D model (JSmol)
|
|
| ChEMBL | |
| ChemSpider | |
| EC Number |
|
PubChem CID
|
|
| UNII | |
| |
| |
| Properties[2] | |
| C12H8S2 | |
| Molar mass | 216.32 g·mol−1 |
| Melting point | 151 to 155 °C (304 to 311 °F; 424 to 428 K) |
| Boiling point | 364 to 366 °C (687 to 691 °F; 637 to 639 K) |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa). | |
| Infobox references | |
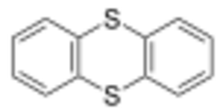
Thianthrene is a sulfur-containing heterocyclic chemical compound. It is a derivative of the parent heterocycle called dithiin. It is notable for its ease of oxidation.
Structure and synthesis
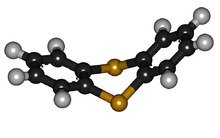
Like other 1,4-dithiins but unlike its oxygen analog dibenzodioxin, the shape of thianthrene is not planar. It is bent, with a fold angle of 128° between the two benzo groups.[3][4][5]
Thianthrene can be prepared by treating benzene with disulfur dichloride in the presence of aluminium chloride.[6]
History
Thianthrene was first synthesized by John Stenhouse by dry distillation of sodium benzenesulfonate.[7] Thianthrene is oxidized by sulfuric acid forming a red radical cation.[8] Thianthrene•+ has been characterized by Electron paramagnetic resonance. Four different publications describe the crystal structure of salts of thianthrene•+.[9]
References
- ↑ International Union of Pure and Applied Chemistry (2014). Nomenclature of Organic Chemistry: IUPAC Recommendations and Preferred Names 2013. The Royal Society of Chemistry. pp. 216. doi:10.1039/9781849733069. ISBN 978-0-85404-182-4.
- ↑ Thianthrene at Sigma-Aldrich
- ↑ Hosoya, S. (1963). "Molecular shapes of thianthrene and related heterocyclic compounds". Acta Crystallographica 16 (4): 310–312. doi:10.1107/S0365110X63000797.
- ↑ Gallaher, K. L.; Bauer, S. H. (1975). "Structure and inversion potential of thianthren". Journal of the Chemical Society, Faraday Transactions 2 71: 1173–1182. doi:10.1039/F29757101173.
- ↑ Aroney, M. J.; Le Fèvre, R. J. W.; Saxby, J. D. (1965). "92. Molecular polarisability. The apparent conformations of thianthren and of three of its oxides as solutes in benzene". Journal of the Chemical Society (Resumed): 571–575. doi:10.1039/JR9650000571.
- ↑ "Process for the manufacture of thianthrene" US patent 3997560, issued 1976-12-14.
- ↑ Stenhouse, J. (1869). "Ueber die Producte der trockenen Destillation der sulfobenzolsauren Salze" (in German). Annalen der Chemie und Pharmacie 149 (2): 247–255. doi:10.1002/jlac.18691490216. https://zenodo.org/record/1427287.
- ↑ W. Dilthey: Versammlungsberichte Bonner Chemische Gesellschaft, Angewandte Chemie, Volume 42, Issue 24, pp. 668–670, 15. June 1929; doi:10.1002/ange.19290422405.
- ↑ Shine, Henry J. (July 1998). "EPR and the History of the Thianthrene Cation Radical". Foundations of modern EPR. ISBN 978-981-02-3295-5. https://books.google.com/books?id=1LdKSYIQtPYC&pg=PA202.
 |

