Chemistry:Transition metal oxalate complex
Transition metal oxalate complexes are coordination complexes with oxalate (C2O42−) ligands. Some are useful commercially, but the topic has attracted regular scholarly scrutiny. Oxalate (C2O42-) is a kind of dicarboxylate ligand.[1] As a small, symmetrical dinegative ion, oxalate commonly forms five-membered MO2C2 chelate rings. Mixed ligand complexes are known, e.g., [Co(C2O4)(NH3)4]κ+.[2]
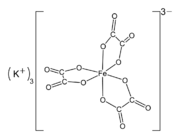
Potassium ferrioxalate (K
3[Fe(C
2O
4)
3] · 3H2O)Oxaliplatin, an anticancer drug
Homoleptic complexes
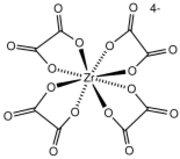
Homoleptic oxalato complexes are common, e.g., those with the formula [M(κ2-C2O4)3]n-: M = V(III), Mn(III),[3] Cr(III), Tc(IV), Fe(III), Ru(III), Co(III), Rh(III), Ir(III). These anions are chiral (D3 symmetry), and some have been resolved into their component enantiomers.[4] Some early metals form tetrakis complexes of the type [M(κ2-C2O4)4]n- M = Nb(V),[5] Zr(IV),[6] Hf(IV),[7] Ta(V),[8]
The Δ and Λ enantiomorphs of [Fe(C
2O
4)
3]3− have been separated.

Bi- and polymetallic complexes
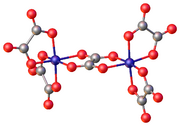
Oxalate is often a bridging ligand forming bi- and polynuclear complexes with (κ2,κ'2-C2O4)M2 cores. Illustrative binuclear complexes are [M2(C2O4)5]2- M = Fe(II)[10] and Cr(III)[11]
With only oxalate and water, many metals form polynuclear complexes.[12] In such materials, oxalate typically functions as a κ2-bidentate ligand, as illustrated by ferrioxalate, [Fe(C
2O
4)
3]3−. The Δ and Λ enantiomorphs of this trianion have been separated. In ferric oxalate, Fe
2(C
2O
4)
3 · 4H2O, one oxalate is bonded through all four oxygen atoms and another oxalate binds through only two oxygen atoms, in both cases bridging.
In ferric oxalate, Fe
2(C
2O
4)
3 · 4H2O, one oxalate is bonded through all four oxygen atoms and another oxalate binds through only two oxygen atoms, in both cases bridging.
Reactions and applications
Metal oxalate complexes are photoactive, degrading with loss of carbon dioxide. This reaction is the basis of the technique called actinometry. Ferrioxalate undergoes photoreduction. The iron centre is reduced (gains an electron) from the +3 to the +2 oxidation state, while an oxalate ion is oxidised to carbon dioxide:
- 2 [Fe(C2O4)3]3− + hν → 2 [Fe(C2O4)2]2− + 2 CO2 + C2O2−4
The redox reaction has been used to access unusual complexes. UV-irradiation of Pt(C2O4)(PPh3)2 gives derivatives of Pt0(PPh3)2.
Metal oxalates with the stoichiometry 1:1 are often insoluble. This fact provides a way to separate metal ions from solutions, including extract of ores. Combustion of metal oxalates gives metal oxides.[13]
See also
References
- ↑ Krishnamurty, Kotra V.; Harris, Gordon M. (1961). "The Chemistry of the Metal Oxalato Complexes". Chemical Reviews 61 (3): 213–246. doi:10.1021/cr60211a001.
- ↑ Bernal, Ivan; Cetrullo, James (1990). "The phenomenon of conglomerate crystallization. XIX. Clavic dissymmetry in coordination compounds. XVII". Structural Chemistry 1 (2–3): 235–243. doi:10.1007/BF00674267.
- ↑ Lis, T.; Matuszewski, J. (1980). "Structure of potassium tris(oxalato)manganate(III) trihydrate". Acta Crystallographica Section B 36 (8): 1938–1940. doi:10.1107/S0567740880007558.
- ↑ Kauffman, George B.; Takahashi, Lloyd T.; Sugisaka, Nobuyuki (1966). Resolution of the Trioxalatocobaltate(III) Ion. Inorganic Syntheses. 8. pp. 207–211. doi:10.1002/9780470132395.ch55. ISBN 9780470132395.
- ↑ Cotton, F. A.; Diebold, Michael P.; Roth, W. J. (1987). "Variable Stereochemistry of the Eight-Coordinate Tetrakis(oxalato)niobate(IV), Nb(C2O4)44-". Inorganic Chemistry 26 (17): 2889–2893. doi:10.1021/ic00264a035.
- ↑ Fu, Yun-Long; Ren, Jia-Lin; Xu, Zhi-Wei; Ng, Seik Weng (2005). "Bis(4,4′-bipyridinium) Tetrakis(oxalato-κ2O,O′)zirconate(IV)". Acta Crystallographica Section E 61 (11): m2397–m2399. doi:10.1107/S1600536805033829.
- ↑ Tranqui, D.; Boyer, P.; Laugier, J.; Vulliet, P. (1977). "Structure cristalline du tétrakisoxalatohafniate de Potassium Pentahydraté [K4Hf(C2O4)4.5H2O]". Acta Crystallographica Section B 33 (10): 3126–3133. doi:10.1107/S0567740877010395.
- ↑ Perić, Berislav; Brničević, Nevenka; Jurić, Marijana; Planinić, Pavica; Matković-Čalogović, Dubravka (2009). "[NH4][(CH3)2NH2]2[Ta(C2O4)4]·2H2O: The First (Oxalato)tantalate(V) Complex Structurally Characterized". Structural Chemistry 20 (5): 933–941. doi:10.1007/s11224-009-9494-0.
- ↑ Ahouari, Hania; Rousse, Gwenaëlle; Rodríguez-Carvajal, Juan; Sougrati, Moulay-Tahar; Saubanère, Matthieu; Courty, Matthieu; Recham, Nadir; Tarascon, Jean-Marie (2015). "Unraveling the Structure of Iron(III) Oxalate Tetrahydrate and Its Reversible Li Insertion Capability". Chemistry of Materials 27 (5): 1631–1639. doi:10.1021/cm5043149.
- ↑ Armentano, Donatella; De Munno, Giovanni; Lloret, Francesc; Julve, Miguel (2005). "Bis and Tris(oxalato)ferrate(III) Complexes as Precursors of polynuclear compounds". CrystEngComm 7 (7): 57. doi:10.1039/b417251e.
- ↑ Masters, Vanessa M.; Sharrad, Clint A.; Bernhardt, Paul V.; Gahan, Lawrence R.; Moubaraki, Boujemaa; Murray, Keith S. (1998). "Synthesis, Structure and Magnetism of the Oxalato-Bridged Chromium(III) Complex [NBun4]4[Cr2(ox)5]·2CHCl3". Journal of the Chemical Society, Dalton Transactions (3): 413–416. doi:10.1039/a705265k.
- ↑ Clemente-León, Miguel; Coronado, Eugenio; Martí-Gastaldo, Carlos; Romero, Francisco M. (2011). "Multifunctionality in Hybrid Magnetic Materials Based on Bimetallic Oxalate Complexes". Chemical Society Reviews 40 (2): 473–497. doi:10.1039/c0cs00111b. PMID 21210054.
- ↑ Verma, Ankit; Kore, Rajkumar; Corbin, David R.; Shiflett, Mark B. (2019). "Metal Recovery Using Oxalate Chemistry: A Technical Review". Industrial & Engineering Chemistry Research 58 (34): 15381–15393. doi:10.1021/acs.iecr.9b02598.
 |