Chemistry:Tributylamine
From HandWiki
| |
| |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| Preferred IUPAC name
N,N-Dibutylbutan-1-amine | |
| Other names
(Tributyl)amine
(The name tributylamine is deprecated.) | |
| Identifiers | |
3D model (JSmol)
|
|
| ChemSpider | |
PubChem CID
|
|
| UNII | |
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| C12H27N | |
| Molar mass | 185.355 g·mol−1 |
| Appearance | Colorless liquid |
| Density | 0.78 g/cm3[1] |
| Melting point | −70 °C (−94 °F; 203 K)[1] |
| Boiling point | 214 °C (417 °F; 487 K)[1] |
| 50 mg/L (20 °C)[1] | |
| Hazards | |
| Flash point | 86 °C (187 °F; 359 K)[1] |
| Related compounds | |
Related
|
Tributylphosphine |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa). | |
| Infobox references | |
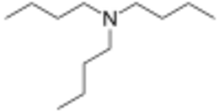
Tributylamine (TBA) is an organic compound with the molecular formula (C4H9)3N. It is a colorless liquid with an amine-like odor.
Uses
Tributylamine is used as a catalyst (proton acceptor) and as a solvent in organic syntheses and polymerization (including polyurethanes).[2]
References
- ↑ 1.0 1.1 1.2 1.3 1.4 Record in the GESTIS Substance Database of the Institute for Occupational Safety and Health
- ↑ Eller, Karsten; Henkes, Erhard; Rossbacher, Roland; Höke, Hartmut (2000). Amines, Aliphatic. doi:10.1002/14356007.a02_001. ISBN 3527306730.
 |
