Earth:Enhanced weathering
Enhanced weathering, also termed ocean alkalinity enhancement when proposed for carbon credit systems, is a process that aims to accelerate the natural weathering by spreading finely ground silicate rock, such as basalt, onto surfaces which speeds up chemical reactions between rocks, water, and air. It also removes carbon dioxide (CO
2) from the atmosphere, permanently storing it in solid carbonate minerals or ocean alkalinity.[1] The latter also slows ocean acidification.
Enhanced weathering is a chemical approach to remove carbon dioxide involving land- or ocean-based techniques. One example of a land-based enhanced weathering technique is in-situ carbonation of silicates. Ultramafic rock, for example, has the potential to store from hundreds to thousands of years' worth of CO2 emissions, according to estimates.[2][3] Ocean-based techniques involve alkalinity enhancement, such as grinding, dispersing, and dissolving olivine, limestone, silicates, or calcium hydroxide to address ocean acidification and CO2 sequestration.[4]
Although existing mine tailings[5] or alkaline industrial silicate minerals (such as steel slags, construction & demolition waste, or ash from biomass incineration) may be used at first,[6] mining more basalt might eventually be required to limit climate change.[7]
History
Enhanced weathering has been proposed for both terrestrial and ocean-based carbon sequestration. Ocean methods are being tested by the non-profit organization Project Vesta to see if they are environmentally and economically viable.[8][9]
In July 2020, a group of scientists assessed that the geo-engineering technique of enhanced rock weathering, i.e., spreading finely crushed basalt on fields – has potential use for carbon dioxide removal by nations, identifying costs, opportunities, and engineering challenges.[10][11]
Natural mineral weathering and ocean acidification

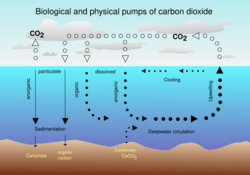
Weathering is the natural process of rocks and minerals dissolving to the action of water, ice, acids, salts, plants, animals, and temperature changes.[12] It is mechanical (breaking up rock—also called physical weathering or disaggregation) and chemical (changing the chemical compounds in the rocks).[12] Biological weathering is a form of weathering (mechanical or chemical) by plants, fungi, or other living organisms.[12]
Chemical weathering can happen by different mechanisms, depending mainly on the nature of the minerals involved. This includes solution, hydration, hydrolysis, and oxidation weathering.[13] Carbonation weathering is a particular type of solution weathering.[13]
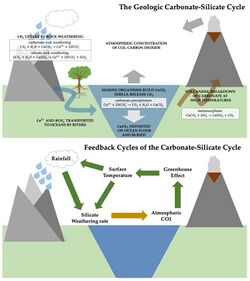
Carbonate and silicate minerals are examples of minerals affected by carbonation weathering. When silicate or carbonate minerals are exposed to rainwater or groundwater, they slowly dissolve due to carbonation weathering: that is the water (H2O) and carbon dioxide (CO
2) present in the atmosphere form carbonic acid (H2CO3) by the reaction:[12][14]
- H2O + CO
2 → H2CO3
This carbonic acid then attacks the mineral to form carbonate ions in solution with the unreacted water. As a result of these two chemical reactions (carbonation and dissolution), minerals, water, and carbon dioxide combine, which alters the chemical composition of minerals and removes CO
2 from the atmosphere. Of course, these are reversible reactions, so if the carbonate encounters H ions from acids, such as in soils, they will react to form water and release CO
2 back to the atmosphere. Applying limestone (a calcium carbonate) to acid soils neutralizes the H ions but releases CO
2 from the limestone[clarification needed].
In particular, forsterite (a silicate mineral) is dissolved through the reaction:
- Mg2SiO4(s) + 4H2CO3(aq) → 2Mg2+(aq) + 4HCO3−(aq) + H4SiO4(aq)
where "(s)" indicates a substance in a solid state and "(aq)" indicates a substance in an aqueous solution.
Calcite (a carbonate mineral) is instead dissolved through the reaction:
- CaCO3(s) + H2CO3(aq) → Ca2+(aq) + 2HCO3−(aq)
Although some of the dissolved bicarbonate may react with soil acids during the passage through the soil profile to groundwater, water with dissolved bicarbonate ions (HCO3−) eventually ends up in the ocean,[14] where the bicarbonate ions are biomineralized to carbonate minerals for shells and skeletons through the reaction:
- Ca2+ + 2HCO3− → CaCO3 + CO
2 + H2O
The carbonate minerals then eventually sink from the ocean surface to the ocean floor.[14] Most of the carbonate is redissolved in the deep ocean as it sinks.
Over geological time periods these processes are thought to stabilize the Earth's climate.[15] The ratio of carbon dioxide in the atmosphere as a gas (CO2) to the quantity of carbon dioxide converted into carbonate is regulated by a chemical equilibrium: in case of a change of this equilibrium state, it takes theoretically (if no other alteration is happening during this time) thousands of years to establish a new equilibrium state.[14]
For silicate weathering, the theoretical net effect of dissolution and precipitation is 1 mol of CO
2 sequestered for every mol of Ca2+ or Mg2+ weathered out of the mineral. Given that some of the dissolved cations react with existing alkalinity in the solution to form CO32− ions, the ratio is not exactly 1:1 in natural systems but is a function of temperature and CO
2 partial pressure. The net CO
2 sequestration of carbonate weathering reaction and carbonate precipitation reaction is zero.[clarification needed]
Weathering and biological carbonate precipitation are thought to be only loosely coupled on short time periods (<1000 years). Therefore, an increase in both carbonate and silicate weathering with respect to carbonate precipitation will result in a buildup of alkalinity in the ocean.[clarification needed]
Terrestrial enhanced weathering
Enhanced weathering was initially used to refer specifically to the spreading of crushed silicate minerals on the land surface.[16][17] Biological activity in soils has been shown to promote the dissolution of silicate minerals,[18] but there is still uncertainty surrounding how quickly this may happen. Because weathering rate is a function of saturation of the dissolving mineral in solution (decreasing to zero in fully saturated solutions), some have suggested that lack of rainfall may limit terrestrial enhanced weathering,[19] although others[20] suggest that secondary mineral formation or biological uptake may suppress saturation and promote weathering.
The amount of energy that is required for comminution depends on the rate at which the minerals dissolve (less comminution is required for rapid mineral dissolution). A 2012 study suggested a large range in potential cost of enhanced weathering largely due to the uncertainty surrounding mineral dissolution rates.[21]
Oceanic enhanced weathering
To overcome the limitations of solution saturation and to use natural comminution of sand particles from wave energy, silicate minerals may be applied to coastal environments,[22] although the higher pH of seawater may substantially decrease the rate of dissolution,[23] and it is unclear how much comminution is possible from wave action.
Alternatively, the direct application of carbonate minerals to the upwelling regions of the ocean has been investigated.[24] Carbonate minerals are supersaturated in the surface ocean but are undersaturated in the deep ocean. In areas of upwelling, this undersaturated water is brought to the surface. While this technology will likely be cheap, the maximum annual CO2 sequestration potential is limited.
Transforming the carbonate minerals into oxides and spreading this material in the open ocean ('Ocean Liming') has been proposed as an alternative technology.[25] Here the carbonate mineral (CaCO3) is transformed into lime (CaO) through calcination. The energy requirements for this technology are substantial.
Mineral carbonation
The enhanced dissolution and carbonation of silicates ('mineral carbonation') was first proposed by Seifritz in 1990,[26] and developed initially by Lackner et al.[27] and further by the Albany Research Center.[28] This early research investigated the carbonation of extracted and crushed silicates at elevated temperatures (~180 °C) and partial pressures of CO2 (~15 MPa) inside controlled reactors ("ex-situ mineral carbonation"). Some research explores the potential of "in-situ mineral carbonation" in which the CO2 is injected into silicate rock formations to promote carbonate formation underground (see: CarbFix).
Mineral carbonation research has largely focused on the sequestration of CO
2 from flue gas. It could be used for geoengineering if the source of CO
2 was derived from the atmosphere, e.g. through direct air capture or biomass-CCS.
Soil Remineralization contributes to the enhanced weathering process. Mixing the soil with crushed rock such as silicate benefits not only plants' health, but also carbon sequestration when calcium or magnesium are present.[29] Remineralize The Earth is a non-profit organization that promotes rock dust applications as natural fertilizers in agriculture fields to restore soils with minerals, improve the quality of vegetation and increase carbon sequestration.
Electrolytic dissolution of silicate minerals
Where abundant electric surplus electricity is available, the electrolytic dissolution of silicate minerals has been proposed[30] and experimentally shown. The process resembles the weathering of some minerals. In addition, hydrogen produced would be a carbon-negative.[31]
Cost
In a 2020 techno-economical analysis, the cost of utilizing this method on cropland was estimated at US$80–180 per tonne of CO2. This is comparable with other methods of removing carbon dioxide from the atmosphere currently available (BECCS (US$100–200 per tonne of CO2)- Bio-Energy with Carbon Capture and Storage) and direct air capture and storage at large scale deployment and low-cost energy inputs (US$100–300 per tonne of CO2). In contrast, the cost of reforestation was estimated lower than US$100 per tonne of CO2.[32]
Example projects
One example of a research project on the feasibility of enhanced weathering is the CarbFix project in Iceland.[33][34][35]
An Irish company named Silicate has run trials in Ireland and in 2023 is running trials in the USA near Chicago. Using concrete crushed down to dust it is scattered on farmland on the ratio 500 tonnes to 50 hectares, aiming to capture 100 tonnes of CO2 per annum from that area. Claiming it improves soil quality and crop productivity, the company sells carbon removal credits to fund the costs. The initial pilot funding comes from prize money awarded to the startup by the THRIVE/Shell Climate-Smart Agriculture Challenge.[36][37]
See also
References
- ↑ "Guest post: How 'enhanced weathering' could slow climate change and boost crop yields" (in en). 2018-02-19. https://www.carbonbrief.org/guest-post-how-enhanced-weathering-could-slow-climate-change-and-boost-crop-yields.
- ↑ "Maps show rocks ideal for sequestering carbon". https://archive.nytimes.com/www.nytimes.com/gwire/2009/03/09/09greenwire-maps-show-rocks-ideal-for-sequestering-carbon-10041.html.
- ↑ U.S. Department of the Interior. "Mapping the Mineral Resource Base for Mineral Carbon-Dioxide Sequestration in the Conterminous United States". U.S. Geological Survey Data Series 414. https://pubs.usgs.gov/ds/414/downloads/DS414_text_508.pdf. Retrieved May 15, 2018.
- ↑ "Cloud spraying and hurricane slaying: how ocean geoengineering became the frontier of the climate crisis" (in en). 2021-06-23. http://www.theguardian.com/environment/2021/jun/23/cloud-spraying-and-hurricane-slaying-could-geoengineering-fix-the-climate-crisis.
- ↑ Power, Ian M.; Dipple, Gregory M.; Bradshaw, Peter M. D.; Harrison, Anna L. (2020-03-01). "Prospects for CO
2 mineralization and enhanced weathering of ultramafic mine tailings from the Baptiste nickel deposit in British Columbia, Canada" (in en). International Journal of Greenhouse Gas Control 94: 102895. doi:10.1016/j.ijggc.2019.102895. ISSN 1750-5836. Bibcode: 2020IJGGC..9402895P. https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S1750583619302531. - ↑ Renforth, Phil (2019-03-28). "The negative emission potential of alkaline materials" (in en). Nature Communications 10 (1): 1401. doi:10.1038/s41467-019-09475-5. PMID 30923316. Bibcode: 2019NatCo..10.1401R.
- ↑ Goll, Daniel S.; Ciais, Philippe; Amann, Thorben; Buermann, Wolfgang; Chang, Jinfeng; Eker, Sibel; Hartmann, Jens; Janssens, Ivan et al. (August 2021). "Potential CO
2 removal from enhanced weathering by ecosystem responses to powdered rock" (in en). Nature Geoscience 14 (8): 545–549. doi:10.1038/s41561-021-00798-x. ISSN 1752-0908. Bibcode: 2021NatGe..14..545G. https://www.nature.com/articles/s41561-021-00798-x. Retrieved 2021-11-03. - ↑ Peters, Adele (2020-05-29). "Ever been to a green sand beach? The newest geohack to fight climate change" (in en-US). https://www.fastcompany.com/90510254/ever-been-to-a-green-sand-beach-the-newest-geohack-to-fight-climate-change.
- ↑ Delbert, Caroline (2020-06-11). "How This Strange Green Sand Could Reverse Climate Change" (in en-US). https://www.popularmechanics.com/science/environment/a32799266/green-sand-carbon-dioxide-climate-change/.
- ↑ "Applying rock dust to croplands could absorb up to 2 billion tonnes of CO2 from the atmosphere" (in en). phys.org. https://phys.org/news/2020-07-croplands-absorb-billion-tonnes-co2.html.
- ↑ Beerling, David J.; Kantzas, Euripides P.; Lomas, Mark R.; Wade, Peter; Eufrasio, Rafael M.; Renforth, Phil; Sarkar, Binoy; Andrews, M. Grace et al. (July 2020). "Potential for large-scale CO2 removal via enhanced rock weathering with croplands" (in en). Nature 583 (7815): 242–248. doi:10.1038/s41586-020-2448-9. ISSN 1476-4687. PMID 32641817. Bibcode: 2020Natur.583..242B. https://www.nature.com/articles/s41586-020-2448-9. Retrieved 16 August 2020.
- ↑ 12.0 12.1 12.2 12.3 "National Geographic - Weathering". https://www.nationalgeographic.org/encyclopedia/weathering/.
- ↑ 13.0 13.1 "Brandon Vogt, "Rock Weathering"". 17 October 2012. https://redrockcanyonopenspace.org/education/geology/rock-weathering/.
- ↑ 14.0 14.1 14.2 14.3 "Encyclopædia Britannica - Biological carbon cycle". https://www.britannica.com/topic/evolution-of-the-atmosphere-1703862/Biological-carbon-cycle#ref390494.
- ↑ Berner, Robert A. Berner; Kothavala, Zavareth (2001). "GEOCARB III: A revised model of atmospheric CO2 over Phanerozoic time". American Journal of Science 301 (2): 182–204. doi:10.2475/ajs.301.2.182. Bibcode: 2001AmJS..301..182B.
- ↑ Schuiling, R. D.; Krijgsman, P. (2006). "Enhanced Weathering: An Effective and Cheap Tool to Sequester CO2". Climatic Change 74 (1–3): 349–54. doi:10.1007/s10584-005-3485-y. Bibcode: 2006ClCh...74..349S.
- ↑ Manning, D. A. C. (2008). "Biological enhancement of soil carbonate precipitation: Passive removal of atmospheric CO2". Mineralogical Magazine 72 (2): 639–49. doi:10.1180/minmag.2008.072.2.639. Bibcode: 2008MinM...72..639M.
- ↑ Manning, David A. C.; Renforth, Phil (2013). "Passive Sequestration of Atmospheric CO2 through Coupled Plant-Mineral Reactions in Urban soils". Environmental Science & Technology 47 (1): 135–41. doi:10.1021/es301250j. PMID 22616942. Bibcode: 2013EnST...47..135M.
- ↑ Köhler, Peter; Hartmann, Jens; Wolf-Gladrow, Dieter A.; Schellnhuber, Hans-Joachim (2010). "Geoengineering potential of artificially enhanced silicate weathering of olivine". Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences 107 (47): 20228–33. doi:10.1073/pnas.1000545107. PMID 21059941. Bibcode: 2010EGUGA..12.6986K.
- ↑ Schuiling, Roelof D.; Wilson, Siobhan A.; Power, lan M. (2011). "Enhanced silicate weathering is not limited by silicic acid saturation". Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences 108 (12): E41. doi:10.1073/pnas.1019024108. PMID 21368192. Bibcode: 2011PNAS..108E..41S.
- ↑ Renforth, P. (2012). "The potential of enhanced weathering in the UK". International Journal of Greenhouse Gas Control 10: 229–43. doi:10.1016/j.ijggc.2012.06.011. Bibcode: 2012IJGGC..10..229R. http://orca.cf.ac.uk/60892/1/Renforth%25202012%2520-%2520IJGGC.pdf. Retrieved 2019-12-10.
- ↑ Schuiling, R.D.; de Boer, P.L. (2010). "Coastal spreading of olivine to control atmospheric CO2 concentrations: A critical analysis of viability. Comment: Nature and laboratory models are different". International Journal of Greenhouse Gas Control 4 (5): 855–6. doi:10.1016/j.ijggc.2010.04.012. Bibcode: 2010IJGGC...4..855S.
- ↑ Hangx, Suzanne J.T.; Spiers, Christopher J. (2009). "Coastal spreading of olivine to control atmospheric CO2 concentrations: A critical analysis of viability". International Journal of Greenhouse Gas Control 3 (6): 757–67. doi:10.1016/j.ijggc.2009.07.001. Bibcode: 2009IJGGC...3..757H.
- ↑ Harvey, L. D. D. (2008). "Mitigating the atmospheric CO2 increase and ocean acidification by adding limestone powder to upwelling regions". Journal of Geophysical Research 113 (C4): C04028. doi:10.1029/2007JC004373. Bibcode: 2008JGRC..113.4028H.
- ↑ Kheshgi, Haroon S. (1995). "Sequestering atmospheric carbon dioxide by increasing ocean alkalinity". Energy 20 (9): 915–22. doi:10.1016/0360-5442(95)00035-F.
- ↑ Seifritz, W. (1990). "CO2 disposal by means of silicates". Nature 345 (6275): 486. doi:10.1038/345486b0. Bibcode: 1990Natur.345..486S.
- ↑ Lackner, Klaus S.; Wendt, Christopher H.; Butt, Darryl P.; Joyce, Edward L.; Sharp, David H. (1995). "Carbon dioxide disposal in carbonate minerals". Energy 20 (11): 1153. doi:10.1016/0360-5442(95)00071-N.
- ↑ O'Connor, W. K.; Dahlin, D. C.; Rush, G. E.; Gedermann, S. J.; Penner, L. R.; Nilsen, D. N. (March 15, 2005). Aqueous mineral carbonation, Final Report. National Energy Technology Laboratory. https://www.netl.doe.gov/File%20Library/Research/Coal/NETLAlbanyAqueousMineralCarbonation.pdf. Retrieved December 29, 2015.[page needed]
- ↑ Lefebvre, David; Goglio, Pietro; Williams, Adrian; Manning, David; Azevedo, Antonio; Bergmann, Magda; Meersmans, Jeroen; Smith, Pete (2019-10-01). "Assessing the potential of soil carbonation and enhanced weathering through Life Cycle Assessment: A case study for Sao Paulo State, Brazil" (in en). Journal of Cleaner Production 233: 468–481. doi:10.1016/j.jclepro.2019.06.099. https://research.wur.nl/en/publications/assessing-the-potential-of-soil-carbonation-and-enhanced-weatheri.
- ↑ Scott, Allan; Oze, Christopher; Shah, Vineet; Yang, Nan; Shanks, Barney; Cheeseman, Chris; Marshall, Aaron; Watson, Matthew (2021-02-04). "Transformation of abundant magnesium silicate minerals for enhanced CO
2 sequestration" (in en). Communications Earth & Environment 2 (1): 25. doi:10.1038/s43247-021-00099-6. ISSN 2662-4435. Bibcode: 2021ComEE...2...25S. - ↑ Rau, Greg H.; Carroll, Susan A.; Bourcier, William L.; Singleton, Michael J.; Smith, Megan M.; Aines, Roger D. (2013-06-18). "Direct electrolytic dissolution of silicate minerals for air CO
2 mitigation and carbon-negative H2 production". Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences 110 (25): 10095–10100. doi:10.1073/pnas.1222358110. PMID 23729814. Bibcode: 2013PNAS..11010095R. - ↑ Beerling, David (2020-07-08). "Potential for large-scale CO2 removal via enhanced rock weathering with croplands" (in en). Nature 583 (7815): 242–248. doi:10.1038/s41586-020-2448-9. PMID 32641817. Bibcode: 2020Natur.583..242B. https://www.nature.com/articles/s41586-020-2448-9. Retrieved 2021-02-09.
- ↑ "CarbFix Project | Global Carbon Capture and Storage Institute" (in en). https://www.globalccsinstitute.com/projects/carbfix-sulfix-project.
- ↑ "The CarbFix Project" (in is). www.or.is. 2017-08-22. https://www.or.is/english/carbfix/carbfix-project.
- ↑ "Turning Carbon Dioxide Into Rock, and Burying It" (in en-US). The New York Times. 2015-02-09. ISSN 0362-4331. https://www.nytimes.com/2015/02/10/science/burying-a-mountain-of-co2.html.
- ↑ "Can concrete dust help to fight climate change? This Irish startup is trying it out on US farmland". 27 October 2023. https://www.euronews.com/green/2023/10/27/can-concrete-dust-help-to-fight-climate-change-irish-startup-is-trying-it-out-in-us.
- ↑ "CONGRATULATIONS TO OUR THRIVE SHELL CLIMATE-SMART AGRICULTURE CHALLENGE WINNERS". https://thriveagrifood.com/shell-challenge/.
External links
