Earth:Erfurt Formation
| Erfurt Formation Stratigraphic range: Ladinian ~242–237 Ma | |
|---|---|
 Outcrop of the formation at the Schumann quarry near Vellberg | |
| Type | Geological formation |
| Unit of | Lower Keuper |
| Sub-units | Bairdienkalk, Grenzdolomit, Lettenkeuper, Sandige Pflanzenschiefer, Untere Graue Mergel & Werksandstein Members |
| Underlies | Grabfeld Formation |
| Overlies | Upper Muschelkalk |
| Thickness | 20–700 m (66–2,297 ft)[1] |
| Lithology | |
| Primary | Marl |
| Other | Claystone, dolomite, limestone, sandstone |
| Location | |
| Coordinates | [ ⚑ ] : 50°56′57″N 11°04′12″E / 50.949036°N 11.070136°E |
| Paleocoordinates | [ ⚑ ] 15°06′N 16°36′E / 15.1°N 16.6°E |
| Region | Baden-Württemberg, Thuringia |
| Country | Germany |
| Extent | Mittelgebirge, North German Plain |
| Type section | |
| Named for | Erfurt |
| Named by | Hoffmann |
| Year defined | 1830 |

The Erfurt Formation, also known as the Lower Keuper (German: Untere Keuper, Lettenkeuper, Lettenkohle or Lettenkohlenkeuper), is a stratigraphic formation of the Keuper group and the Germanic Trias supergroup. It was deposited during the Ladinian stage of the Triassic period.[2] It lies above the Upper Muschelkalk and below the Middle Keuper.[1]
Definition
The formation was defined in Erfurt-Melchendorf in 1830 by Franz Xaver Hofmann and named for the nearby town of Erfurt.[1]
The Erfurt Formation is underlain by the Upper Muschelkalk. The lower boundary to the Erfurt Formation is the "Lettenkohlensandstein" in northern Germany and the "Grenz-bone-beds" in southern Germany.
The formation is a sequence of dolomite, lacustrine limestones, claystone, evaporites, and fluviatile sandstones. The color is usually grey but can also be brown or reddish brown. The average thickness is 60 to 80 meter, with a maximum thickness of 700 meter in the Glückstadt-Graben.[1]
The upper boundary is marked by dolomites, or claystones of the Grabfeld Formation.[1]
Fossil content
Template:Paleobiota-key-compact
The Erfurt Formation is known for its vertebrate fossils. Different kinds of fish, amphibians and archosauriforms have been found. Usually they are found as bone beds, but in 1977 the first complete skeletons were found near Kupferzell. They include Mastodonsaurus, Gerrothorax, Plagiosuchus, Callistomordax, Nanogomphodon, Batrachotomus, Kupferzellia and Palaeoxyris friessi.[3]
Reptiles
| Reptiles reported from the Erfurt Formation | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Genus | Species | Location | Stratigraphic position | Material | Notes | Images |
| Batrachotomus | B. kupferzellensis | Schwäbisch Hall.[4] | Albertischichten Member (Serrolepisbank).[4] | An archosaur. |  | |
| Wirtembergia | W. hauboldae | Vellberg.[5] | Untere Graue Mergel.[5] | 2 partial dentaries (SMNS 91060 & SMNS 91061),[5] and a partial skeleton (SMNS 91313).[6] | One of the oldest and the most primitive known rhynchocephalian. | 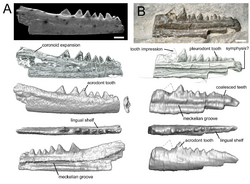 |
| Doswelliidae | Gen. et. sp. indet. | Schwäbisch Hall.[4] | Albertischichten Member (Serrolepisbank).[4] | An osteoderm (MHI 2078).[4] | An archosauriform. | |
| Fraxinisaura | F. rozynekae | Vellberg, Baden-Württemberg.[7] | Untere Graue Mergel Layer.[7] | A basal lepidosauromorph. |  | |
| Jaxtasuchus | J. salomoni | Baden-Württemberg.[8] | Estherienschichten to Anoplophora Dolomite.[8] | Multiple skeletal remains.[8] | A doswelliid. | |
| Nothosaurus | N. cristatus | Eschenau Quarry, Baden-Württemberg.[9] | Lettenkeuper.[9] | Almost complete skull lacking mandible (GPIT/RE/09800).[9] | A nothosaur | |
| N. mirabilis | Hoheneck & Molsdorf.[10] | Upper Lettenkeuper.[10] | Multiple specimens.[10] | A nothosaur. |  | |
| N. sp. | Schwäbisch Hall.[4] | Albertischichten Member (Serrolepisbank).[4] | 2 dorsal vertebrae & a thoracic rib.[4] | A nothosaur. | ||
| Owenettidae, aff. Barasaurus | Kupferzell locality & Schumann quarry.[11] | Left humerus (SMNS 92101) & right humerus (SMNS 92100).[11] | An owenettid. | |||
| Pappochelys | P. rosinae | Schumann Quarry, Eschenau, Vellberg.[12] | Top of Untere Graue Mergel.[12] | 20 specimens.[12] | A stem-turtle. |  |
| Polymorphodon | P. adorfi | Schumann Quarry, Vellberg.[13] | Untere Graue Mergel.[13] | Disarticulated partial skeletons.[13] | An archosauriform. | 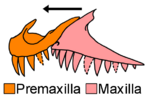 |
| Procolophonidae | Gen. indet. sp. indet. | Schumann Quarry.[11] | Left humerus (SMNS 91753).[11] | A procolophonid. | ||
| Psephosaurus | P. suevicus | Quarry "Hohenloher Steinwerk" & Hoheneck near Ludwigsburg.[14] | Isolated plates (MHI 1426/1-3 & SMNS 91007).[14] | A placodont. |  | |
| P. sp. | Hoheneck near Ludwigsburg.[14] | Isolated plates (SMNS 91008 & 91009).[14] | A placodont. |  | ||
| Rutiotomodon | R. tytthos | Schumann limestone quarry.[15] | Top of the Untere Graue Mergel.[15] | A nearly complete right maxilla with teeth (SMNS 97028) & a crushed dentary fragment (SMNS 97029).[15] | A trilophosaurid. | |
| Simosaurus | S. gaillardoti | Hoheneck near Ludwigsburg.[16] | Lettenkeuper.[16] | Skull.[16] | A nothosaur. |  |
| S. guilelmi | Hoheneck near Ludwigsburg.[16] | Lettenkeuper.[16] | Skull.[16] | Junior synonym of S. gaillardoti. |  | |
| Smilodon | S. laevis | Gaildorf Alumn Mine.[17] | Jaw fragment with teeth.[17] | Preoccupied generic name, renamed Zanclodon laevis. | ||
| ?Suchia | Indeterminate | Schwäbisch Hall.[4] | Albertischichten Member (Serrolepisbank).[4] | A tooth (MHI 2035).[4] | An archosaur. | |
| Tanystropheus | T. conspicuus | Vertebrae.[18] | Nomen dubium. |  | ||
| T. sp. | Steinbach near Crailsheim.[18] | Lower Lettenkeuper.[18] | Teeth & vertebrae.[18] | A tanystropheid. |  | |
| Vellbergia | V. bartholomaei | Schumann Quarry, Vellberg.[19] | Untere Graue Mergel.[19] | Partial skull (SMNS 91590).[19] | A stem-lepidosauromorph. | |
| Zanclodon | Z. laevis | Gaildorf Alumn Mine.[17] | Jaw fragment with teeth.[17] | An indeterminate archosaur. | ||
Synapsids
| Synapsids reported from the Erfurt Formation | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Genus | Species | Location | Stratigraphic position | Material | Notes | Images |
| Aff. Dinodontosaurus | Neidenfels, Baden-Württemberg.[20] | Isolated complete left humerus (SMNS 56891).[20] | Specimen now thought to represent a temnospondyl.[20] | |||
| Nanogomphodon | N. wildi | Michelbach an der Bilz.[21] | Sandige Pflanzenschiefer Member, lower Lettenkeuper.[21] | Teeth.[21] | A cynodont. | |
Amphibians
| Amphibians reported from the Erfurt Formation | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Genus | Species | Location | Stratigraphic position | Material | Notes | Images |
| Bystrowiella | B. schumanni | Kupferzell & Vellberg, Hohenlohe.[22] | Untere Graue Mergel.[22] | Osteoderms & vertebrae.[22] | A chroniosuchian. |  |
| Callistomordax | C. kugleri | Vellberg (Schumann quarry), Ummenhofen quarry & Kupferzell locality.[23] | Albertibank through Untere Graue Mergel.[23] | Numerous specimens.[23] | A metoposauroid. |  |
| Gerrothorax | G. pulcherrimus | Schwäbisch Hall.[4] | Albertischichten Member (Serrolepisbank).[4] | Two skull fragments and some osteoderms.[4] | A plagiosaurid. |  |
| Mastodonsaurus | M. giganteus | Many localities in Baden-Württemberg, Bayern & in Thuringia.[4][24] | From the Grenzbonebed through the Hohenecker Kalk, covering nearly the whole Lettenkeuper sequence.[4][24] | Numerous specimens.[4][24] | A capitosaur. |  |
| Megalophthalma | M. ockerti | Schumann limestone quarry, Vellberg, Baden-Württemberg, southern Germany.[25] | Hauptsandstein (main sandstone unit).[25] | A partial skull with anterior portion of the left mandibular ramus (MHI 2047).[25] | A plagiosaurid. |  |
| Plagiosuchus | P. pustuliferus | Multiple localities in Baden-Württemberg & Thuringia.[26] | Vitriolschiefer, Sandige Pflanzenschiefer & Untere Graue Mergel.[26] | Multiple specimens.[26] | A plagiosaurid. |  |
| ?Temnospondyli | Gen. et. sp. indet. | Neidenfels & Schumann Quarry.[20] | Untere Graue Mergel.[20] | Isolated complete left humerus (SMNS 56891) & isolated almost complete right humerus (SMNS 90571).[20] | Originally thought to represent a dicynodont similar to Dinodontosaurus.[20] | |
| Trematolestes | T. hagdorni | Present in a range of localities in southern Germany.[27] | Estherienschichten through Untere Graue Mergel, upper Lettenkeuper.[27] | Numerous specimens including a nearly-complete skeleton.[27] | A trematosaurid. |  |
Bony fish
| Bony fish reported from the Erfurt Formation | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Genus | Species | Location | Stratigraphic position | Material | Notes | Images |
| "Ceratodus" | "C." concinnus | Schwäbisch Hall.[4] | Albertischichten Member (Serrolepisbank).[4] | Tooth plates, pterygoids & scales.[4] | A lungfish. | |
| ?Coelacanthidae | Gen. et. sp. indet. | Schwäbisch Hall.[4] | Albertischichten Member (Serrolepisbank).[4] | Numerous remains.[4] | A coelacanth. | |
| Parundichna | P. schoelli | Rot am See, Baden-Württemberg.[28] | Hauptsandstein.[28] | Clusters of sigmoidal scratches (MHI 1704).[28] | Swimming trace of a large coelacanth. | |
| Ptychoceratodus | P. serratus | Schwäbisch Hall.[4] | Albertischichten Member (Serrolepisbank).[4] | A mould of a juvenile left praearticular tooth (MHI 410) & a fragment of a juvenile tooth plate (MHI 1748/42).[4] | A lungfish. |  |
| ?Redfieldiiformes | Fam., gen. et. sp. indet. | Schwäbisch Hall.[4] | Albertischichten Member (Serrolepisbank).[4] | 2 fragmentary and dissociated skeletons.[4] | A redfieldiiform. | |
| Saurichthys | S. gypsophilus | Franconia.[29] | Skull fragment.[29] | A saurichthyiform. | ||
| S. sp. | Schwäbisch Hall.[4][29] | Albertischichten Member (Serreolepisbank).[4] | 1 fragmentary rostrum (MHI 1748/27).[4][29] | A saurichthyiform. |  | |
| Serrolepis | S. suevicus | Schwäbisch Hall.[4] | Albertischichten Member (Serrolepisbank).[4] | Numerous specimens.[4] | A perleidiform. | |
Cartilaginous fish
| Cartilaginous fish reported from the Erfurt Formation | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Genus | Species | Location | Stratigraphic position | Material | Notes | Images |
| Lonchidion | L. sp. | Schwäbisch Hall.[4] | Albertischichten Member (Serrolepisbank).[4] | Teeth.[4] | A hybodontiform. | |
| Palaeoxyris | P. friessi | Muschelkalk quarry, Baden-Württemberg.[3] | Top of Hauptsandstein.[3] | SMNS 95447 (egg capsule).[3] | Likely an egg capsule of Polyacrodus. | |
References
- ↑ 1.0 1.1 1.2 1.3 1.4 "Erfurt Formation". BGR. http://www.bgr.de/app/litholex/gesamt_ausgabe_neu.php?id=5000001.
- ↑ Erfurt Formation at Fossilworks.org
- ↑ 3.0 3.1 3.2 3.3 Ronald Böttcher (2010). "Description of the shark egg capsule Palaeoxyris friessi n. sp. from the Ladinian (Middle Triassic) of SW Germany and discussion of all known egg capsules from the Triassic of the Germanic Basin". Palaeodiversity 3: 123–139. https://www.researchgate.net/publication/255485752. Retrieved 23 January 2012.
- ↑ 4.00 4.01 4.02 4.03 4.04 4.05 4.06 4.07 4.08 4.09 4.10 4.11 4.12 4.13 4.14 4.15 4.16 4.17 4.18 4.19 4.20 4.21 4.22 4.23 4.24 4.25 4.26 4.27 4.28 4.29 4.30 4.31 4.32 4.33 4.34 4.35 4.36 4.37 Hagdorn, Hans; Mutter, Raoul (January 2011). "The vertebrate fauna of the Lower Keuper Albertibank (Erfurt Formation, Middle Triassic) in the vicinity of Schwäbisch Hall (Baden-Württemberg, Germany)". Palaeodiversity 4: 223–243. https://www.researchgate.net/publication/309384510.
- ↑ 5.0 5.1 5.2 Jones, Marc EH; Anderson, Cajsa Lisa; Hipsley, Christy A; Müller, Johannes; Evans, Susan E; Schoch, Rainer R (2013-09-25). "Integration of molecules and new fossils supports a Triassic origin for Lepidosauria (lizards, snakes, and tuatara)". BMC Evolutionary Biology 13 (1): 208. doi:10.1186/1471-2148-13-208. ISSN 1471-2148. PMID 24063680. Bibcode: 2013BMCEE..13..208J.
- ↑ Sues, Hans-Dieter; Schoch, Rainer R. (2023-11-07). "The oldest known rhynchocephalian reptile from the Middle Triassic (Ladinian) of Germany and its phylogenetic position among Lepidosauromorpha" (in en). The Anatomical Record 307 (4): 776–790. doi:10.1002/ar.25339. ISSN 1932-8486. PMID 37937325. https://anatomypubs.onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/10.1002/ar.25339.
- ↑ 7.0 7.1 Rainer R. Schoch; Hans-Dieter Sues (18 April 2018). "A new lepidosauromorph reptile from the Middle Triassic (Ladinian) of Germany and its phylogenetic relationships". Journal of Vertebrate Paleontology 38 (2). doi:10.1080/02724634.2018.1444619. Bibcode: 2018JVPal..38E4619S. https://figshare.com/articles/dataset/A_new_lepidosauromorph_reptile_from_the_Middle_Triassic_Ladinian_of_Germany_and_its_phylogenetic_relationships/6154415.
- ↑ 8.0 8.1 8.2 Schoch, R. R.; Sues, H. D. (2013). "A new archosauriform reptile from the Middle Triassic (Ladinian) of Germany". Journal of Systematic Palaeontology 12 (1): 113–131. doi:10.1080/14772019.2013.781066. https://www.researchgate.net/publication/236172772.
- ↑ 9.0 9.1 9.2 Hinz, Juliane K.; Matzke, Andreas T.; Pfretzschner, Hans-Ulrich (2019-03-04). "A new nothosaur (Sauropterygia) from the Ladinian of Vellberg-Eschenau, southern Germany". Journal of Vertebrate Paleontology 39 (2). doi:10.1080/02724634.2019.1585364. ISSN 0272-4634. Bibcode: 2019JVPal..39E5364H. https://www.researchgate.net/publication/332796837.
- ↑ 10.0 10.1 10.2 Rieppel, O.; Wild, R. (1996) (in en). A revision of the genus Nothosaurus (Reptilia: Sauropterygia) from the Germanic Triassic, with comments on the status of Conchiosaurus clavatus / Olivier Rieppel --, Rupert Wild --.. doi:10.5962/bhl.title.2691.
- ↑ 11.0 11.1 11.2 11.3 Martinelli, Agustín G.; Soares, Marina Bento; Schoch, Rainer R. (January 2016). "Owenettids and procolophonids from the lower Keuper shed new light on the diversity of parareptiles in the German Middle Triassic". Journal of Paleontology 90 (1): 92–101. doi:10.1017/jpa.2016.26. ISSN 0022-3360. Bibcode: 2016JPal...90...92M. https://www.researchgate.net/publication/304005214.
- ↑ 12.0 12.1 12.2 Schoch, Rainer R.; Sues, Hans-Dieter (24 June 2015). "A Middle Triassic stem-turtle and the evolution of the turtle body plan" (in en). Nature 523 (7562): 584–587. doi:10.1038/nature14472. ISSN 1476-4687. PMID 26106865. Bibcode: 2015Natur.523..584S. https://www.nature.com/articles/nature14472.
- ↑ 13.0 13.1 13.2 Sues, Hans-Dieter; Schoch, Rainer R.; Sobral, Gabriela; Irmis, Randall B. (2020). "A new archosauriform reptile with distinctive teeth from the Middle Triassic (Ladinian) of Germany". Journal of Vertebrate Paleontology 40 (1). doi:10.1080/02724634.2020.1764968. ISSN 0272-4634. Bibcode: 2020JVPal..40E4968S. http://repository.si.edu/xmlui/handle/10088/106576.
- ↑ 14.0 14.1 14.2 14.3 Scheyer, Torsten M. (December 2007). "Skeletal histology of the dermal armor of Placodontia: the occurrence of "postcranial fibro-cartilaginous bone" and its developmental implications" (in en). Journal of Anatomy 211 (6): 737–753. doi:10.1111/j.1469-7580.2007.00815.x. PMID 17944862.
- ↑ 15.0 15.1 15.2 Sues, Hans-Dieter; Schoch, Rainer R. (March 2023). "A new Middle Triassic (Ladinian) trilophosaurid stem-archosaur from Germany increases diversity and temporal range of this clade" (in en). Royal Society Open Science 10 (3). doi:10.1098/rsos.230083. ISSN 2054-5703. PMID 36968237. Bibcode: 2023RSOS...1030083S.
- ↑ 16.0 16.1 16.2 16.3 16.4 16.5 Rieppel, Olivier (1994). Osteology of Simosaurus gaillardoti and the relationships of stem-group Sauropterygia. [Chicago, Ill.]: Field Museum of Natural History. https://www.biodiversitylibrary.org/bibliography/3399.
- ↑ 17.0 17.1 17.2 17.3 Schoch, Rainer R. (2011-04-01). "New archosauriform remains from the German Lower Keuper". Neues Jahrbuch für Geologie und Paläontologie - Abhandlungen 260 (1): 87–100. doi:10.1127/0077-7749/2011/0133. ISSN 0077-7749. https://www.researchgate.net/publication/233595276.
- ↑ 18.0 18.1 18.2 18.3 Spiekman, Stephan N. F.; Scheyer, Torsten M. (2019-12-16). "A taxonomic revision of the genus Tanystropheus (Archosauromorpha, Tanystropheidae)" (in English). Palaeontologia Electronica 22 (3): 1–46. doi:10.26879/1038. ISSN 1094-8074. https://palaeo-electronica.org/content/2019/2870-revision-of-tanystro-pheus.
- ↑ 19.0 19.1 19.2 Sobral, Gabriela; Simões, Tiago R.; Schoch, Rainer R. (2020-02-20). "A tiny new Middle Triassic stem-lepidosauromorph from Germany: implications for the early evolution of lepidosauromorphs and the Vellberg fauna" (in en). Scientific Reports 10 (1): 2273. doi:10.1038/s41598-020-58883-x. ISSN 2045-2322. PMID 32080209. Bibcode: 2020NatSR..10.2273S.
- ↑ 20.0 20.1 20.2 20.3 20.4 20.5 20.6 Maisch, Michael W. (2009-01-01). "No dicynodont in the Keuper - a reconsideration of the occurrence of aff. Dinodontosaurus in the Middle Triassic of Southern Germany". Palaeodiversity 2: 271–278. https://www.academia.edu/64960761.
- ↑ 21.0 21.1 21.2 Hopson, James A.; Sues, Hans-Dieter (2006-06-01). "A traversodont cynodont from the Middle Triassic (Ladinian) of Baden-Württemberg (Germany)" (in en). Paläontologische Zeitschrift 80 (2): 124–129. doi:10.1007/BF02988972. ISSN 0031-0220. Bibcode: 2006PalZ...80..124H.
- ↑ 22.0 22.1 22.2 Witzmann, Florian; Schoch, Rainer R.; Maisch, Michael W. (2007). "A relict basal tetrapod from Germany: first evidence of a Triassic chroniosuchian outside Russia". Naturwissenschaften 95 (1): 67–72. doi:10.1007/s00114-007-0291-6. ISSN 0028-1042. PMID 17653527. https://www.academia.edu/26483894.
- ↑ 23.0 23.1 23.2 Schoch, R. R. (2008). "A new stereospondyl from the German Middle Triassic, and the origin of the Metoposauridae". Zoological Journal of the Linnean Society 152: 79–113. doi:10.1111/j.1096-3642.2007.00363.x.
- ↑ 24.0 24.1 24.2 R., Schoch, Rainer (1999). Comparative osteology of Mastodonsaurus giganteus (Jaeger, 1828) from the Middle Triassic (Lettenkeuper: Longobardian) of Germany (Baden-Württemberg, Bayern, Thüringen). Staatl. Museum für Naturkunde. OCLC 247114091. https://www.researchgate.net/publication/235732311.
- ↑ 25.0 25.1 25.2 Schoch, Rainer R.; Milner, Andrew R.; Witzmann, Florian (September 2014). Ruta, Marcello. ed. "Skull morphology and phylogenetic relationships of a new Middle Triassic plagiosaurid temnospondyl from Germany, and the evolution of plagiosaurid eyes" (in en). Palaeontology 57 (5): 1045–1058. doi:10.1111/pala.12101. Bibcode: 2014Palgy..57.1045S.
- ↑ 26.0 26.1 26.2 Damiani, Ross; Schoch, Rainer R.; Hellrung, Hanna; Werneburg, Ralf; Gastou, STÉPHANIE (January 2009). "The plagiosaurid temnospondyl Plagiosuchus pustuliferus (Amphibia: Temnospondyli) from the Middle Triassic of Germany: anatomy and functional morphology of the skull". Zoological Journal of the Linnean Society 155 (2): 348–373. doi:10.1111/j.1096-3642.2008.00444.x. ISSN 0024-4082.
- ↑ 27.0 27.1 27.2 Schoch, Rainer R. (2006). "A Complete Trematosaurid Amphibian from the Middle Triassic of Germany". Journal of Vertebrate Paleontology 26 (1): 29–43. doi:10.1671/0272-4634(2006)26[29:ACTAFT2.0.CO;2]. ISSN 0272-4634.
- ↑ 28.0 28.1 28.2 Simon, Theo; Hagdorn, Hans; Hagdorn, Magnus K.; Seilacher, Adolf (September 2003). "Swimming trace of a coelacanth fish from the Lower Keuper of south-west Germany" (in en). Palaeontology 46 (5): 911–926. doi:10.1111/1475-4983.00326. ISSN 0031-0239. Bibcode: 2003Palgy..46..911S.
- ↑ 29.0 29.1 29.2 29.3 Romano, C.; Kogan, I.; Jenks, J.; Jerjen, I.; Brinkmann, W. (2012-09-28). "Saurichthys and other fossil fishes from the late Smithian (Early Triassic) of Bear Lake County (Idaho, USA), with a discussion of saurichthyid palaeogeography and evolution" (in en). Bulletin of Geosciences: 543–570. doi:10.3140/bull.geosci.1337. ISSN 1802-8225. https://www.researchgate.net/publication/233782250.
 |