Engineering:Oklo Mine

Template:FB Oklo Mine (sometimes Oklo Reactor or Oklo Mines), located in Oklo, Gabon on the west coast of Central Africa, is believed to have been the only natural nuclear fission reactor. Oklo consists of 16 sites at which self-sustaining nuclear fission reactions are thought to have taken place approximately 1.7 billion years ago, and ran for hundreds of thousands of years. It is estimated to have averaged under 100 kW of thermal power during that time.[1][2][3]
History
In May 1972 at the Tricastin uranium enrichment site at Pierrelatte in France, routine mass spectrometry comparing UF6 samples from Oklo showed a discrepancy in the amount of the 235U isotope. Normally the concentration is 0.72% while these samples had only 0.60%, a significant difference (some 17% less U-235 was contained in the samples than expected).[4] This discrepancy required explanation, as all civilian uranium handling facilities must meticulously account for all fissionable isotopes to ensure that none are diverted to the construction of nuclear weapons. Furthermore, since fissile material is why uranium is mined, a significant amount "going missing" was also of direct economic concern.
Thus the French Commissariat à l'énergie atomique (CEA) began an investigation. A series of measurements of the relative abundances of the two most significant isotopes of the uranium mined at Oklo showed anomalous results compared to those obtained for uranium from other mines. Further investigations into this uranium deposit discovered uranium ore with a 235U concentration as low as 0.44% (almost 40% below the normal value). Subsequent examination of isotopes of fission products such as neodymium and ruthenium also showed anomalies, as described in more detail below. However, the trace radioisotope 234U did not deviate significantly in its concentration from other natural samples. Both depleted uranium and reprocessed uranium will usually have 234U concentrations significantly different from the secular equilibrium of 55 ppm 234U relative to 238U. This is due to 234U being enriched together with 235U and due to it being both consumed by neutron capture and produced from 235U by fast neutron induced (n,2n) reactions in nuclear reactors. In Oklo any possible deviation of 234U concentration present at the time the reactor was active would have long since decayed away. 236U must have also been present in higher than usual ratios during the time the reactor was operating, but due to its half life of 2.348×107 years being almost two orders of magnitude shorter than the time elapsed since the reactor operated, it has decayed to roughly 1.4×10−22 its original value and thus basically nothing and below any abilities of current equipment to detect.
This loss in 235U is exactly what happens in a nuclear reactor. A possible explanation was that the uranium ore had operated as a natural fission reactor in the distant geological past. Other observations led to the same conclusion, and on 25 September 1972 the CEA announced their finding that self-sustaining nuclear chain reactions had occurred on Earth about 2 billion years ago. Later, other natural nuclear fission reactors were discovered in the region.
Mechanism
The natural nuclear reactor formed when a uranium-rich mineral deposit became inundated with groundwater, which could act as a moderator for the neutrons produced by nuclear fission. A chain reaction took place, producing heat that caused the groundwater to boil away; without a moderator that could slow the neutrons, however, the reaction slowed or stopped. The reactor thus had a negative void coefficient of reactivity, something employed as a safety mechanism in human-made light water reactors. After cooling of the mineral deposit, the water returned, and the reaction restarted, completing a full cycle every 3 hours. The fission reaction cycles continued for hundreds of thousands of years and ended when the ever-decreasing fissile materials, coupled with the build-up of neutron poisons, no longer could sustain a chain reaction.
Fission of uranium normally produces five known isotopes of the fission-product gas xenon; all five have been found trapped in the remnants of the natural reactor, in varying concentrations. The concentrations of xenon isotopes, found trapped in mineral formations 2 billion years later, make it possible to calculate the specific time intervals of reactor operation: approximately 30 minutes of criticality followed by 2 hours and 30 minutes of cooling down (exponentially decreasing residual decay heat) to complete a 3-hour cycle.[5] Xenon-135 is the strongest known neutron poison. However, it is not produced directly in appreciable amounts but rather as a decay product of iodine-135 (or one of its parent nuclides). Xenon-135 itself is unstable and decays to caesium-135 if not allowed to absorb neutrons. While caesium-135 is relatively long lived, all caesium-135 produced by the Oklo reactor has since decayed further to stable barium-135. Meanwhile xenon-136, the product of neutron capture in xenon-135, only decays extremely slowly via double beta decay and thus scientists were able to determine the neutronics of this reactor by calculations based on those isotope ratios almost two billion years after it stopped fissioning uranium.
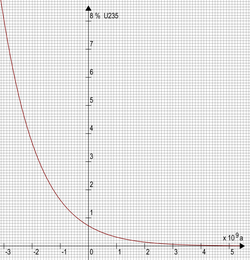
A key factor that made the reaction possible was that, at the time the reactor went critical 1.7 billion years ago, the fissile isotope 235U made up about 3.1% of the natural uranium, which is comparable to the amount used in some of today's reactors. (The remaining 96.9% was non-fissile 238U and roughly 55 ppm 234U.) Because 235U has a shorter half-life than 238U, and thus decays more rapidly, the current abundance of 235U in natural uranium is only 0.72%. A natural nuclear reactor is therefore no longer possible on Earth without heavy water or graphite.[6]
The Oklo uranium ore deposits are the only known sites in which natural nuclear reactors existed. Other rich uranium ore bodies would also have had sufficient uranium to support nuclear reactions at that time, but the combination of uranium, water and physical conditions needed to support the chain reaction was unique, as far as is currently known, to the Oklo ore bodies. It is also possible that other natural nuclear fission reactors were once operating but have since been geologically disturbed so much as to be unrecognizable, possibly even "diluting" the uranium so far that the isotope ratio would no longer serve as a "fingerprint". Only a small part of the continental crust and no part of the oceanic crust reaches the age of the deposits at Oklo or an age during which isotope ratios of natural uranium would have allowed a self sustaining chain reaction with water as a moderator.
Another factor which probably contributed to the start of the Oklo natural nuclear reactor at 2 billion years, rather than earlier, was the increasing oxygen content in the Earth's atmosphere.[3] Uranium is naturally present in the rocks of the earth, and the abundance of fissile 235U was at least 3% or higher at all times prior to reactor startup. Uranium is soluble in water only in the presence of oxygen.[citation needed] Therefore, increasing oxygen levels during the aging of the Earth may have allowed uranium to be dissolved and transported with groundwater to places where a high enough concentration could accumulate to form rich uranium ore bodies. Without the new aerobic environment available on Earth at the time, these concentrations probably could not have taken place.
It is estimated that nuclear reactions in the uranium in centimeter- to meter-sized veins consumed about five tons of 235U and elevated temperatures to a few hundred degrees Celsius.[3][7] Most of the non-volatile fission products and actinides have only moved centimeters in the veins during the last 2 billion years.[3] Studies have suggested this as a useful natural analogue for nuclear waste disposal.[8] The overall mass defect from the fission of five tons of 235U is about 4.6 kilograms (10 lb). Over its lifetime the reactor produced roughly 100 megatonnes of TNT (420 PJ) in thermal energy, including neutrinos. If one ignores fission of plutonium (which makes up roughly a third of fission events over the course of normal burnup in modern humanmade light water reactors), then fission product yields amount to roughly 129 kilograms (284 lb) of technetium-99 (since decayed to ruthenium-99), 108 kilograms (238 lb) of zirconium-93 (since decayed to niobium-93), 198 kilograms (437 lb) of caesium-135 (since decayed to barium-135, but the real value is probably lower as its parent nuclide, xenon-135, is a strong neutron poison and will have absorbed neutrons before decaying to Cs-135 in some cases), 28 kilograms (62 lb) of palladium-107 (since decayed to silver), 86 kilograms (190 lb) of strontium-90 (long since decayed to zirconium) and 185 kilograms (408 lb) of caesium-137 (long since decayed to barium).[citation needed]
See also
- Geology of Gabon
References
- ↑ Meshik, A. P. (November 2005). "The Workings of an Ancient Nuclear Reactor". Scientific American 293 (5): 82–6, 88, 90–1. doi:10.1038/scientificamerican1105-82. PMID 16318030. Bibcode: 2005SciAm.293e..82M. http://www.sciam.com/article.cfm?id=ancient-nuclear-reactor.
- ↑ Mervine, Evelyn (July 13, 2011). "Nature's Nuclear Reactors: The 2-Billion-Year-Old Natural Fission Reactors in Gabon, Western Africa". blogs.scientificamerican.com. https://blogs.scientificamerican.com/guest-blog/natures-nuclear-reactors-the-2-billion-year-old-natural-fission-reactors-in-gabon-western-africa/.
- ↑ 3.0 3.1 3.2 3.3 Gauthier-Lafaye, F.; Holliger, P.; Blanc, P.-L. (1996). "Natural fission reactors in the Franceville Basin, Gabon: a review of the conditions and results of a "critical event" in a geologic system". Geochimica et Cosmochimica Acta 60 (25): 4831–4852. doi:10.1016/S0016-7037(96)00245-1. Bibcode: 1996GeCoA..60.4831G.
- ↑ Davis, E. D.; Gould, C. R.; Sharapov, E. I. (2014). "Oklo reactors and implications for nuclear science". International Journal of Modern Physics E 23 (4): 1430007–236. doi:10.1142/S0218301314300070. ISSN 0218-3013. Bibcode: 2014IJMPE..2330007D.
- ↑ Meshik, A. P. (2004). "Record of Cycling Operation of the Natural Nuclear Reactor in the Oklo/Okelobondo Area in Gabon". Physical Review Letters 93 (18): 182302. doi:10.1103/PhysRevLett.93.182302. PMID 15525157. Bibcode: 2004PhRvL..93r2302M.
- ↑ Greenwood, Norman N.; Earnshaw, Alan (1997). Chemistry of the Elements (2nd ed.). Butterworth-Heinemann. p. 1257. ISBN 978-0-08-037941-8.
- ↑ De Laeter, J. R.; Rosman, K. J. R.; Smith, C. L. (1980). "The Oklo Natural Reactor: Cumulative Fission Yields and Retentivity of the Symmetric Mass Region Fission Products". Earth and Planetary Science Letters 50 (1): 238–246. doi:10.1016/0012-821X(80)90135-1. Bibcode: 1980E&PSL..50..238D.
- ↑ Gauthier-Lafaye, F. (2002). "2 billion year old natural analogs for nuclear waste disposal: the natural nuclear fission reactors in Gabon (Africa)". Comptes Rendus Physique 3 (7–8): 839–849. doi:10.1016/S1631-0705(02)01351-8. Bibcode: 2002CRPhy...3..839G. https://comptes-rendus.academie-sciences.fr/physique/articles/10.1016/S1631-0705(02)01351-8/.
External links
- "Meet Oklo, the Earth's Two-billion-year-old only Known Natural Nuclear Reactor", International Atomic Energy Agency
- This Two Billion Year-Old Natural Reactor May Hold The Key To Safe Nuclear Waste Disposal, Forbes 2018
- Gabon's Ancient Nuclear Reactor | Amusing Planet
[ ⚑ ] 1°24′03″S 13°09′24″E / 1.40083°S 13.15667°E
 |
